This document outlines key concepts in systems analysis and design, including:
- The systems development life cycle (SDLC) which provides an overall framework using predictive or adaptive approaches.
- Phases of the SDLC include planning, analysis, design, implementation, and support. Current trends incorporate more iterative approaches.
- Methodologies provide guidelines combining models, tools, and techniques for traditional structured or object-oriented development approaches.
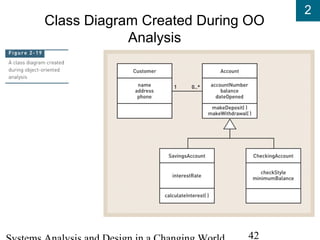
- Modeling techniques like data flow diagrams, entity-relationship diagrams, and use case diagrams are used in analysis and design.
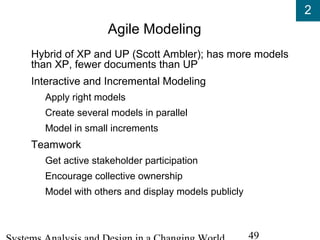
- Adaptive approaches like eXtreme Programming (XP), Unified Process (UP), Agile Modeling, and Scrum emphasize iterative development.
- Computer