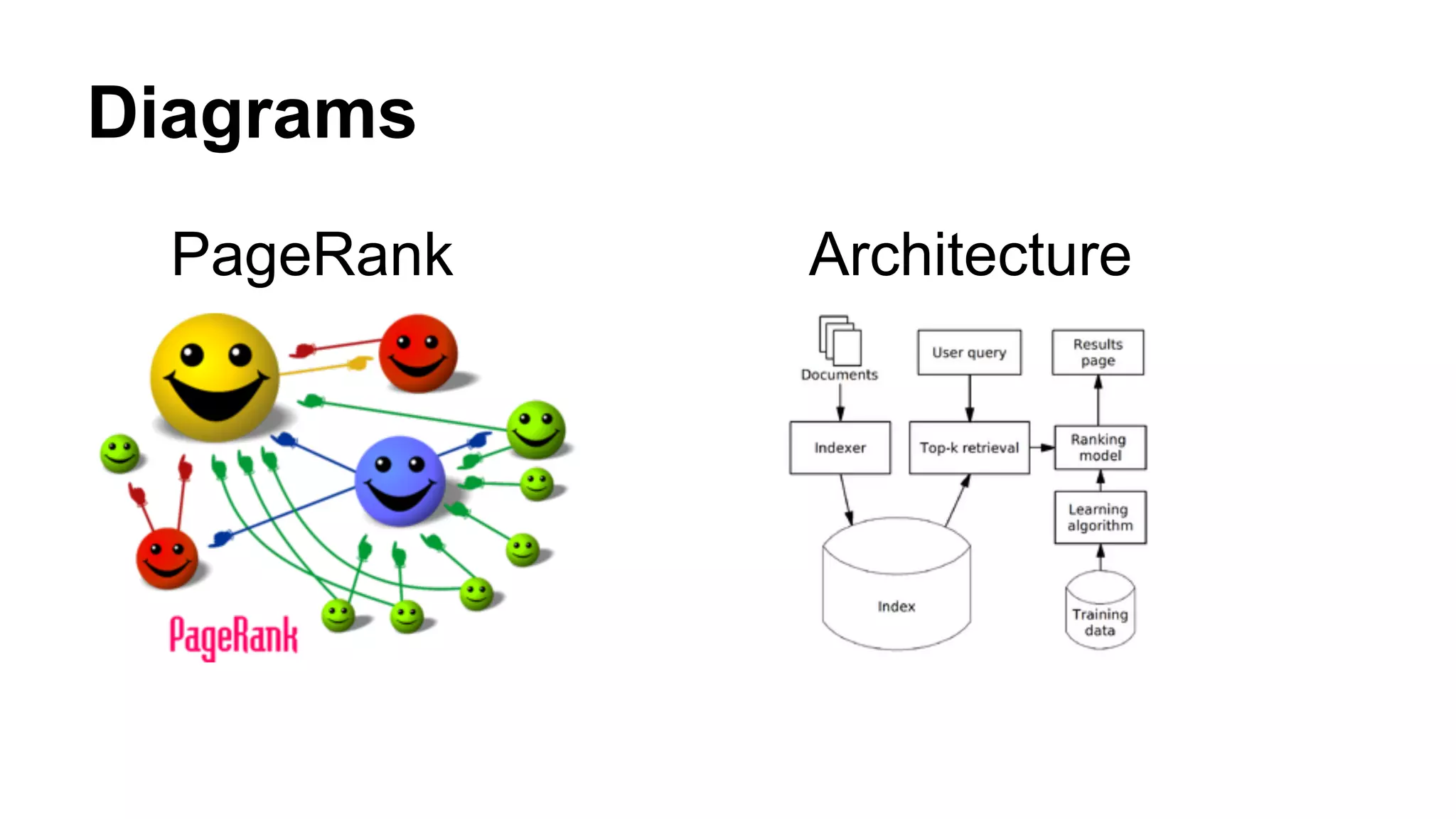
PageRank and Tf-Idf are two important algorithms used for ranking web pages. PageRank ranks pages based on the number and quality of links to a page, considering links as votes. The more votes (links from other pages), the higher the page ranks. Tf-Idf measures how important a word is to a document based on how often it appears in the document and across all documents. It is commonly used by search engines to score documents based on a user query. While both aim to determine the most relevant pages, PageRank provides an overall ranking, while Tf-Idf scores pages based on a specific search query.