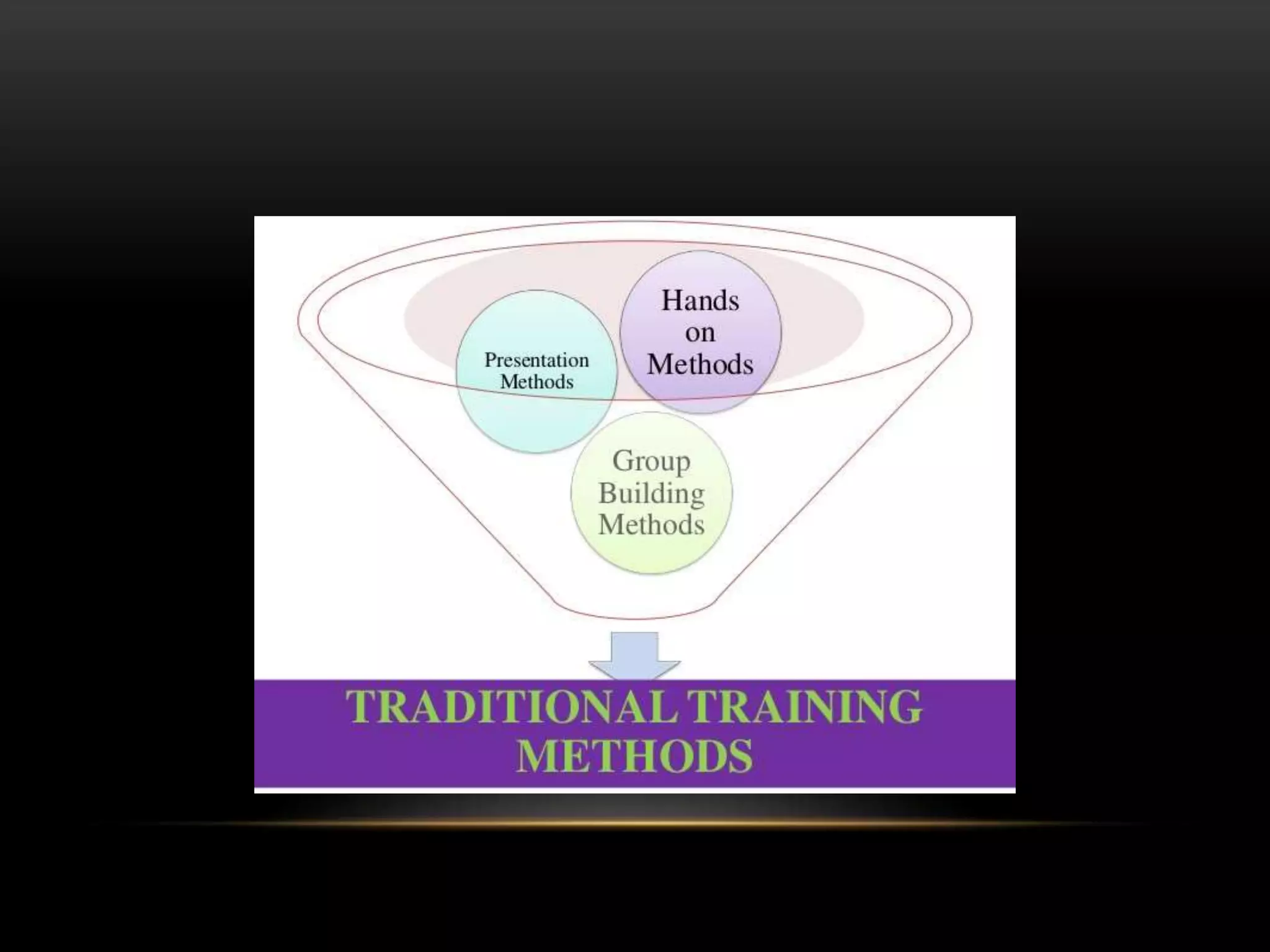
This document discusses traditional and computer-based training programs. It outlines several presentation methods for traditional training including lectures, audio-visual techniques, hands-on methods, and group building methods. Computer-based training involves the use of computers and can be delivered online, via web-based programs, or on mobile devices. Common types of computer-based training include demonstrations, tutorials, and simulations. While computer-based training has benefits like flexibility and feedback, it also has drawbacks such as high costs and limited interaction.