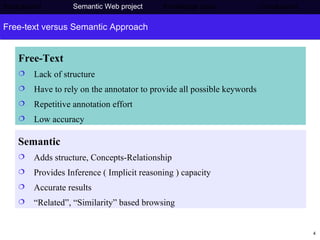
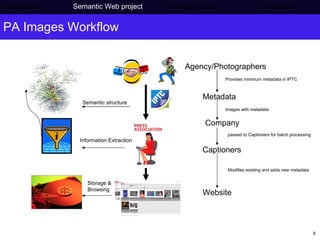
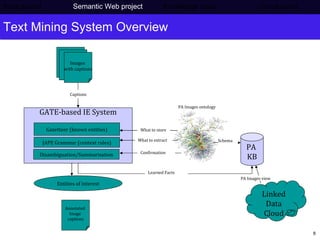
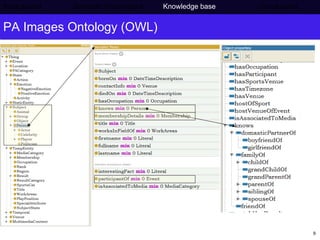
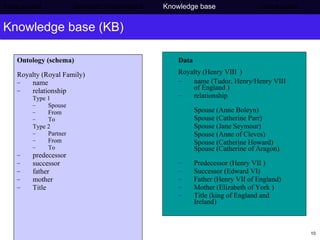
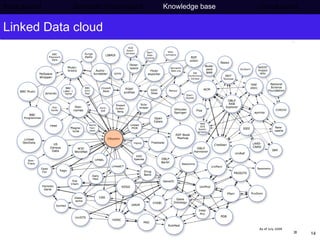
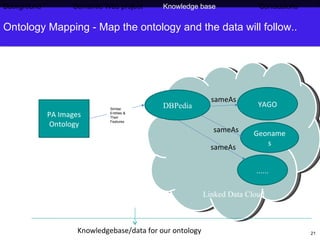
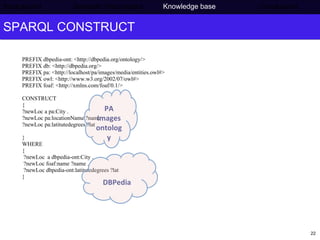
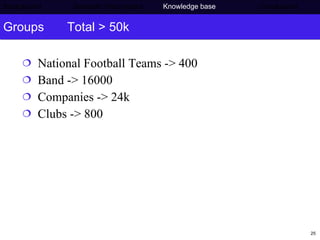
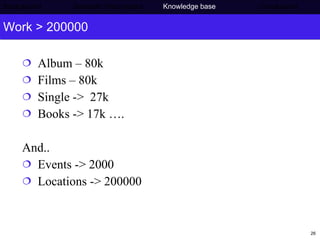
The document discusses Press Association's semantic technology project which aims to generate a knowledge base using information extraction and the Linked Data Cloud. It outlines Press Association's operations and workflow, and how semantic technologies can be used to develop taxonomies, annotate images, and extract entities from captions into an ontology-based knowledge base. The knowledge base can then be populated and interlinked with external datasets from the Linked Data Cloud like DBpedia to provide a comprehensive, semantically-structured source of information.