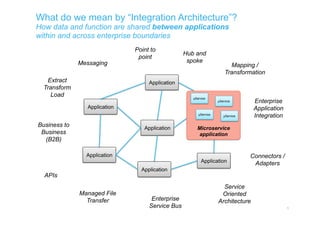
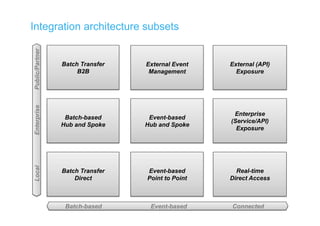
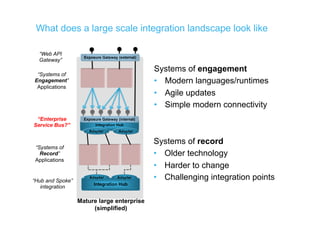
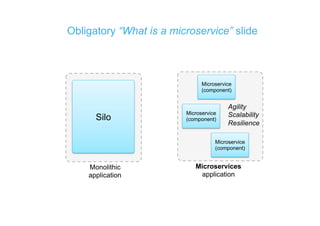
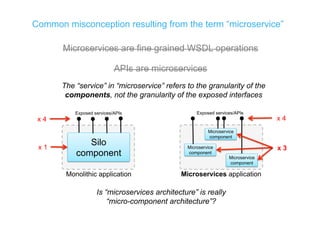
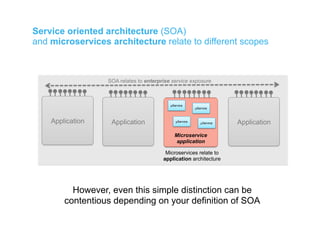
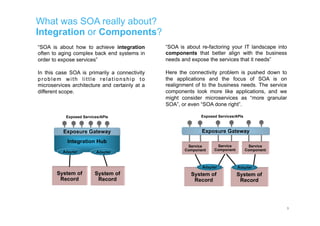
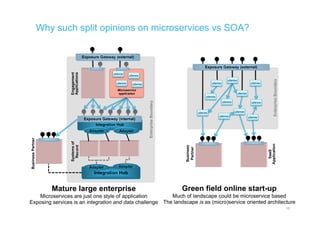
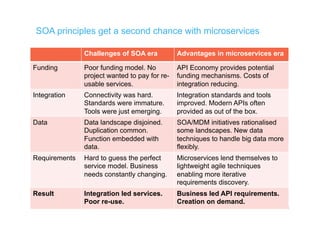
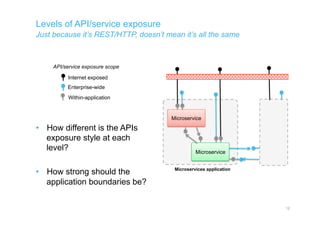
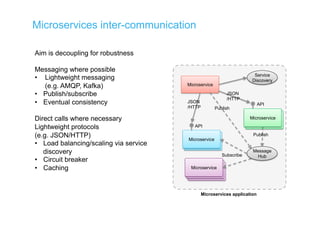
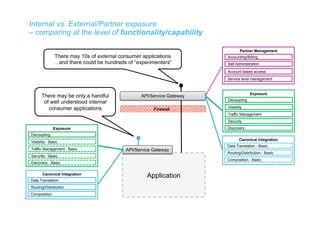
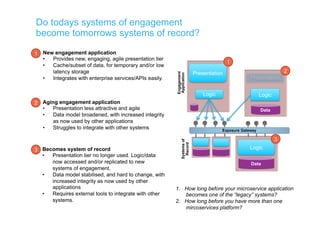
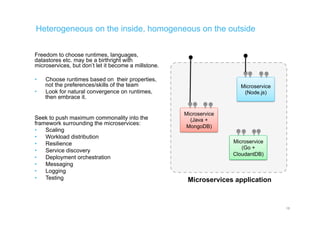
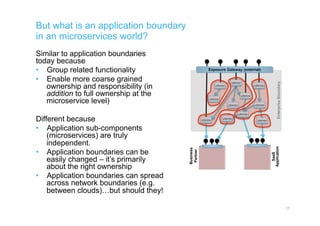
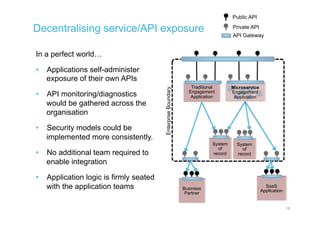
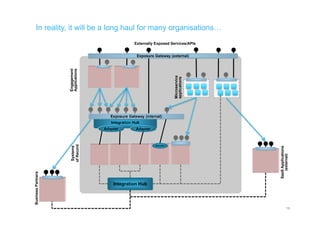
The document discusses integration architecture in a microservices world. It begins by defining integration architecture as how data and functions are shared between applications. It then discusses challenges with large enterprise landscapes that have undergone mergers and acquisitions. The document outlines different types of integration architectures like external, enterprise, batch-based, and event-based integration. It also discusses common misconceptions around microservices, such as thinking microservices refer to exposed APIs rather than application components. The summary concludes by noting debates around the differences between microservices and service-oriented architecture (SOA).