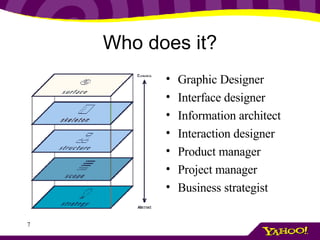
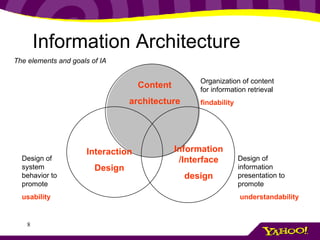
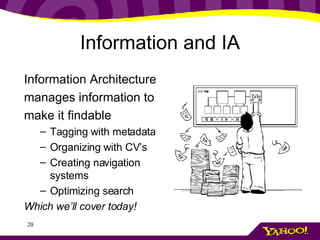
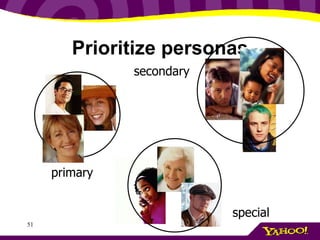
This document provides an overview of information architecture (IA) and its importance. It discusses the key elements and goals of IA, including organizing content, designing navigation, and classifying information. The document also stresses the importance of understanding user, business, technology, and content requirements through research and interviews. It presents an exercise for practicing requirements gathering and introduces the concept of personas as a way to represent different types of users.


































































































































































![Q&A Christina Wodtke www.yahoo.com [email_address] Tom Wailes [email_address] LEARN MORE! book : : www.blueprintsfortheweb.com zine : : www.boxesandarrows.com blog : : www.eleganthack.com peeps : : www.aifia.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blueprints-uie810120312620/85/Information-Architecture-101-205-320.jpg)

