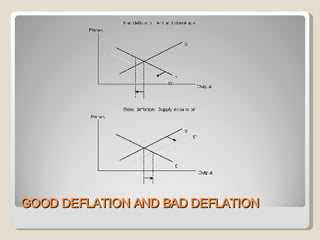
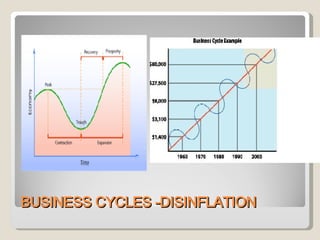
This document discusses whether inflation or deflation is better for a growing economy. It defines inflation, deflation, and disinflation, noting that deflation means falling prices while disinflation means slowing price increases. The document explores how deflation can occur and lists some potential causes like decreasing money supply, increasing goods supply, or falling demand. It argues that deflation from technological advances or globalization that increase efficiency can be "good" by enabling lower prices and greater consumption, while deflation in developed economies due to debt obligations can create a negative spiral.