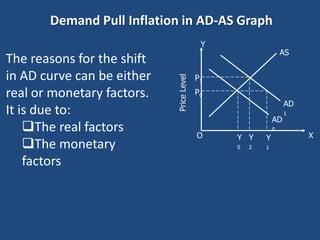
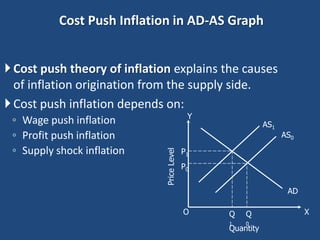
Inflation is defined as a sustained increase in the general price level in an economy over a period of time. It can be caused by demand-pull factors like excess money supply or cost-push factors like increases in production costs. There are three main types of inflation - creeping inflation (under 5%), running inflation (8-10%) and hyperinflation (double or triple digit price increases). Governments use monetary policy like increasing interest rates and fiscal policy like increasing taxes or reducing spending to control inflation. Both demand-pull and cost-push inflation impact the economy by hurting consumers and fixed income groups.


![Measuring Inflation
• Inflation is rate of change in the price level.
• If the price level in the current year is P1
and in the previous year P0.
• The inflation for the current year is
[(P1 - P0) / P0] x 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflation-121111201842-phpapp02/85/Inflation-3-320.jpg)