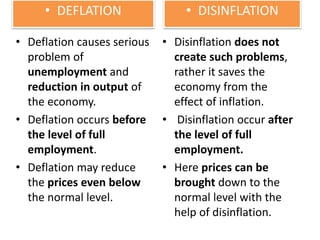
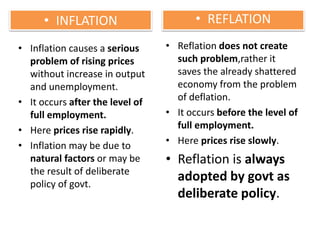
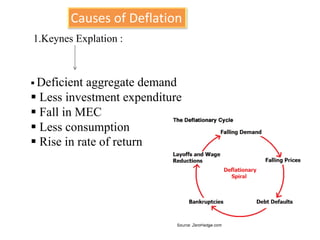
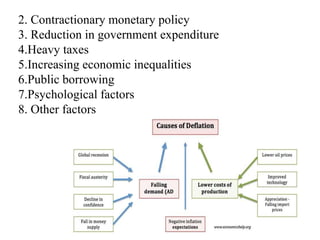
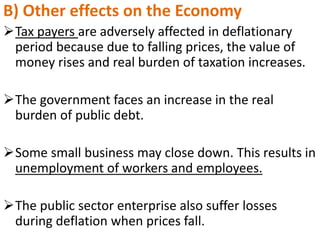
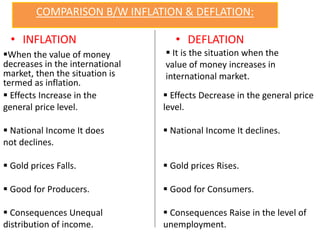
The document defines and discusses deflation. Deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services accompanied by falling levels of employment, output, and income. It is caused by factors like deficient demand, contractionary monetary policy, and taxes. Effects of deflation include problems for producers, traders, investors, laborers, and consumers as well as a decline in national income, rise in unemployment, and slower economic growth. While both inflation and deflation have costs, inflation is preferable to deflation as it does not reduce output and is easier for governments to counteract. The document concludes by explaining why Keynes and others view inflation as the lesser of the two evils compared to deflation.