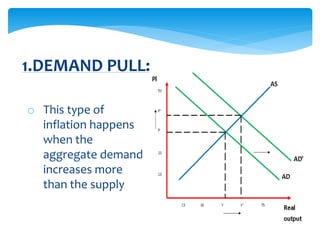
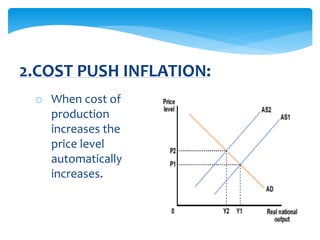
This document discusses inflation and was prepared by a group including Aqsa Bashir, Ayesha Khalid, Rizwana Ramzan, and Mehwish Amjad. It defines inflation as a sustained increase in prices or fall in a currency's value. Inflation can be caused by demand exceeding production or increased costs of goods. The document outlines types of inflation like open, creeping, hyper, and galloping inflation and discusses methods of measuring and addressing inflation through fiscal and monetary policy.




![o Inflation is rate of change in the price level.
[(P1 - P0) / P0] x 100
MEASURING INFLATION:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflation-161228162150/85/Inflation-5-320.jpg)