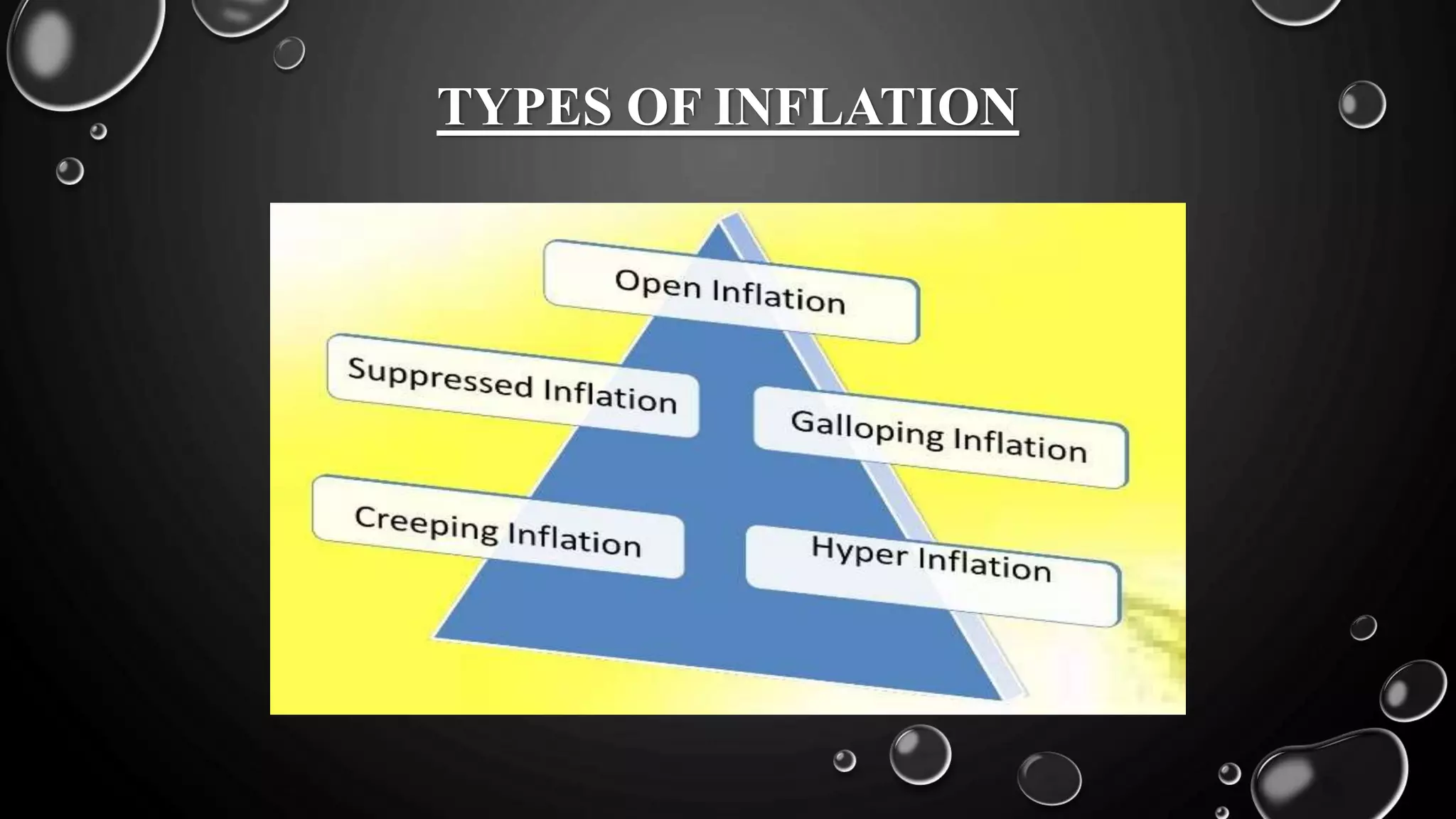
This document discusses inflation, including its definition, types, causes, effects, and measures to control it. Inflation is defined as a sustained increase in the general price level in an economy over time. The main causes of inflation include an increase in the money supply, rise in aggregate demand, and contraction of aggregate supply. Effects of uncontrolled inflation include inefficiencies in markets, uncertainty, and imbalance of trade. Measures to control inflation involve monetary policies like credit control, fiscal policies like increasing taxes, and other steps like price controls and increasing production.





![MEASURING INFLATION
• Inflation is rate of change in the price level.
• If the price level in the current year is p1 and in the previous year p0.
• The inflation for the current year is
[(p1 - p0) / p0] x 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflationandcontrolmeasures-160912062827/75/Inflation-and-control-measures-6-2048.jpg)