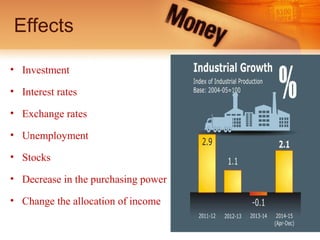
Inflation is defined as a general rise in prices over time that results in a loss of purchasing power of currency. It can be caused by an increase in the money supply or expenditures outpacing the supply of goods. In India, inflation impacts the wages of unorganized sector workers and is caused by factors like cost-push effects, demand-pull effects, and supply shocks. The types of inflation include open, suppressed, wartime, and sectoral inflation. The consequences of inflation are adverse effects on production, income distribution, development, and balance of payments. Measures to control inflation involve monetary policy, fiscal policy, increasing production, rational wage policies, and price controls.