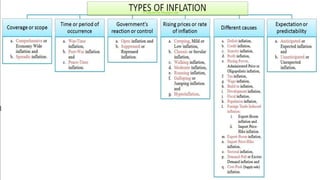
This document discusses inflation, including its definition, types, causes, effects, and consequences. Inflation is defined as a sustained increase in price levels or a fall in the value of money. It can be caused by factors that increase demand, like rising incomes or money supply, or factors that increase costs, like higher wages or material prices. Effects of inflation include inefficiencies in markets and uncertainty that discourage investment and saving. If left unchecked, inflation can lead to hyperinflation and damage an economy. The government uses various fiscal and monetary policies to control inflation.