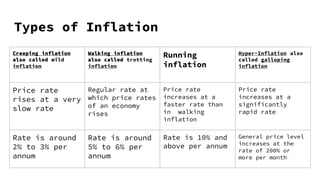
This document discusses inflation, defining it as a sustained rise in aggregate market prices. It identifies four types of inflation based on price increase rates: creeping, walking, running, and hyper. Demand-pull inflation occurs when demand exceeds supply, while cost-push inflation is due to increased production costs. Factors that can increase demand-pull inflation include population growth, money supply increases, and government spending, while cost-push factors include wage increases, taxes, and basic material prices. The effects of inflation vary among groups, with fixed-income earners hurt the most, farmers benefiting in the short-term, and producers seeing short-term gains but potential long-term losses.