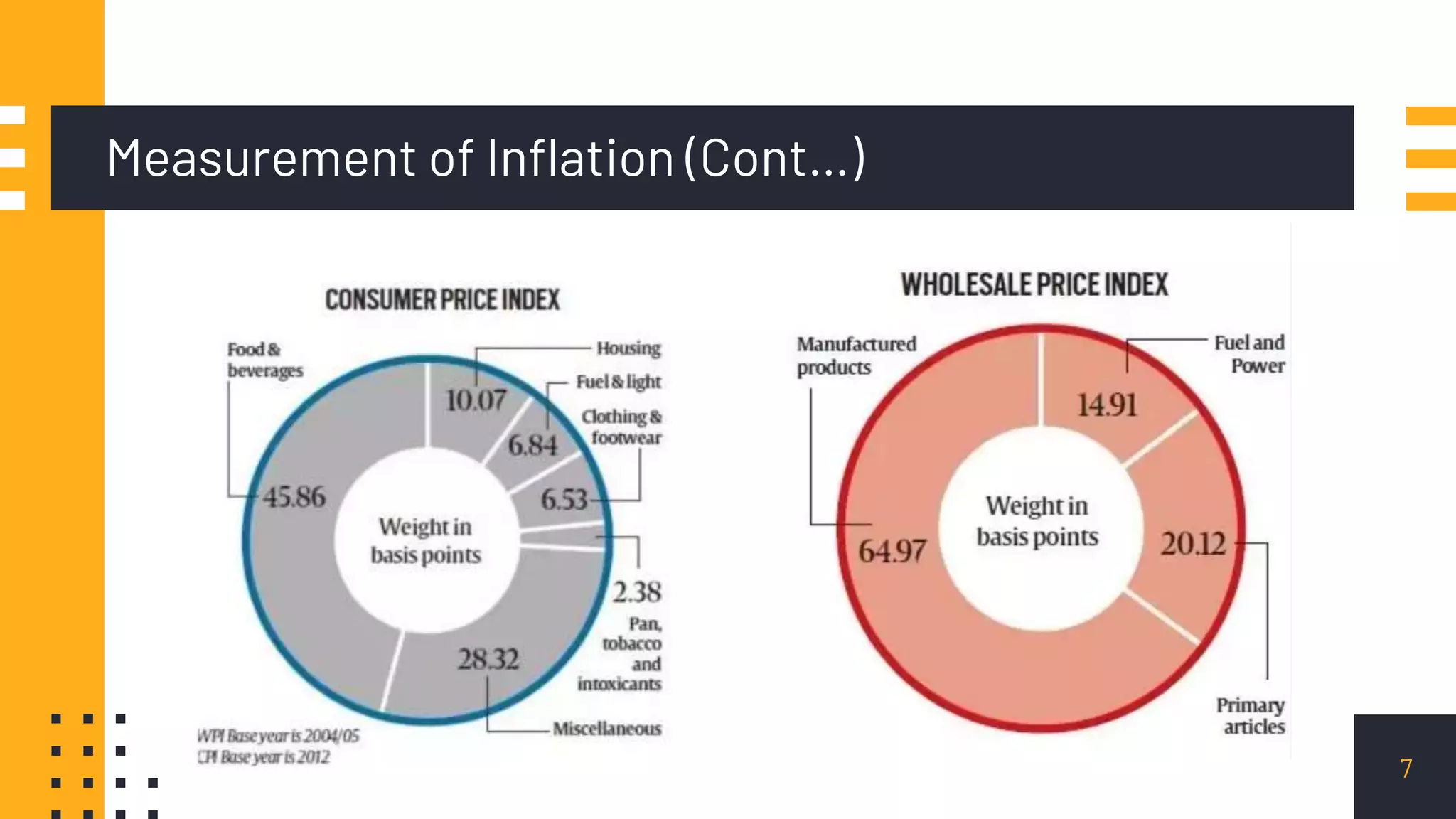
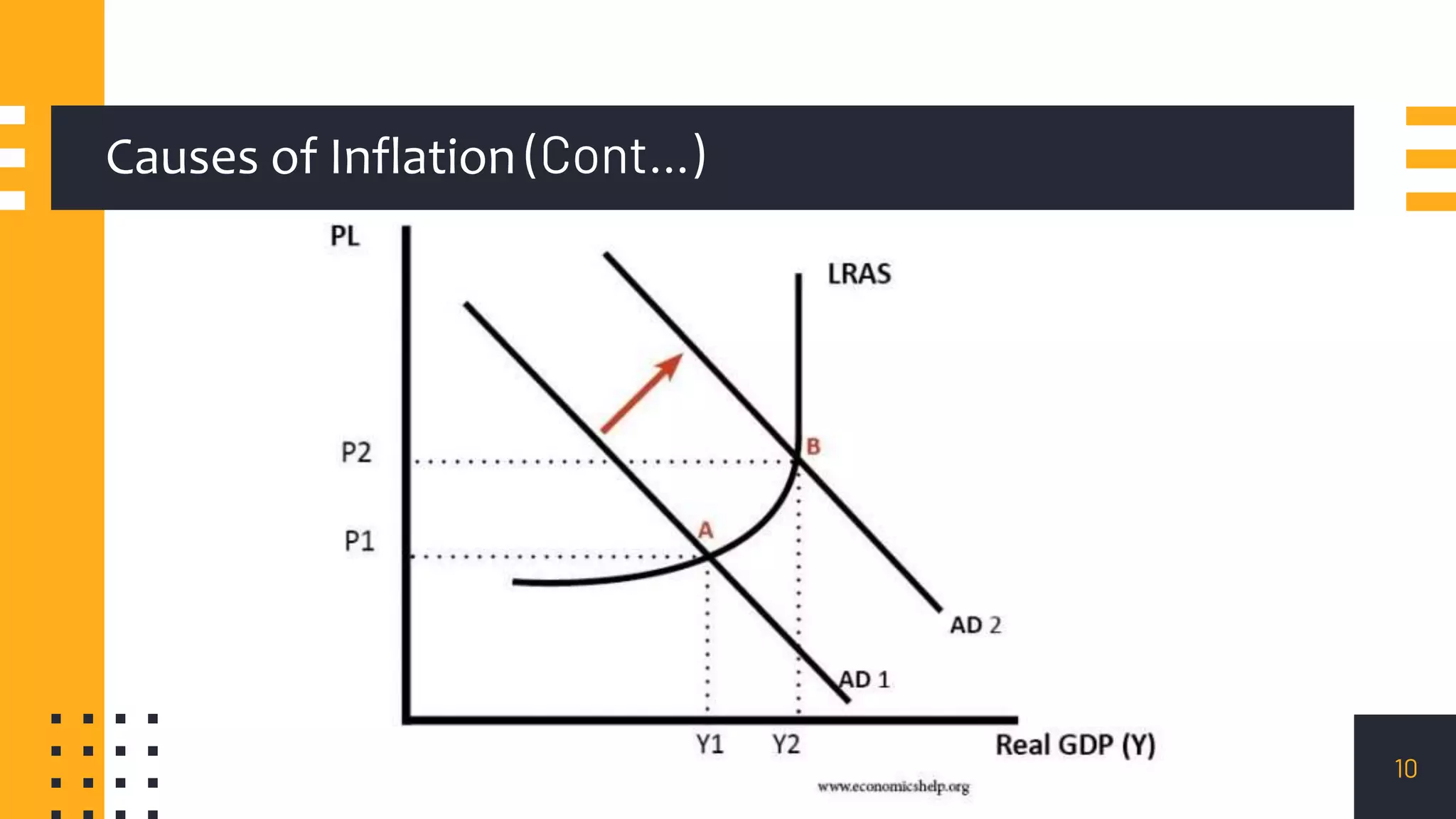
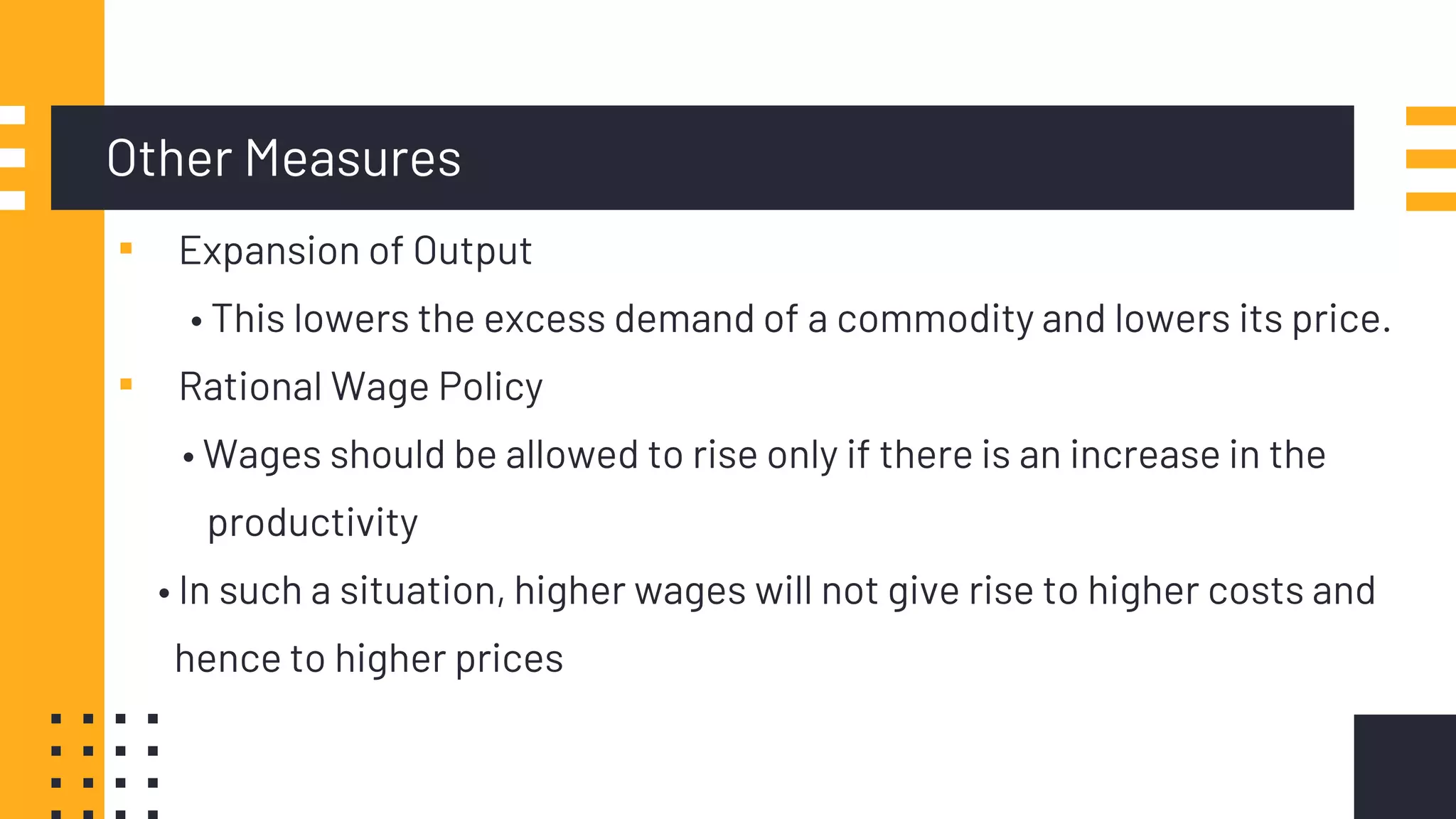
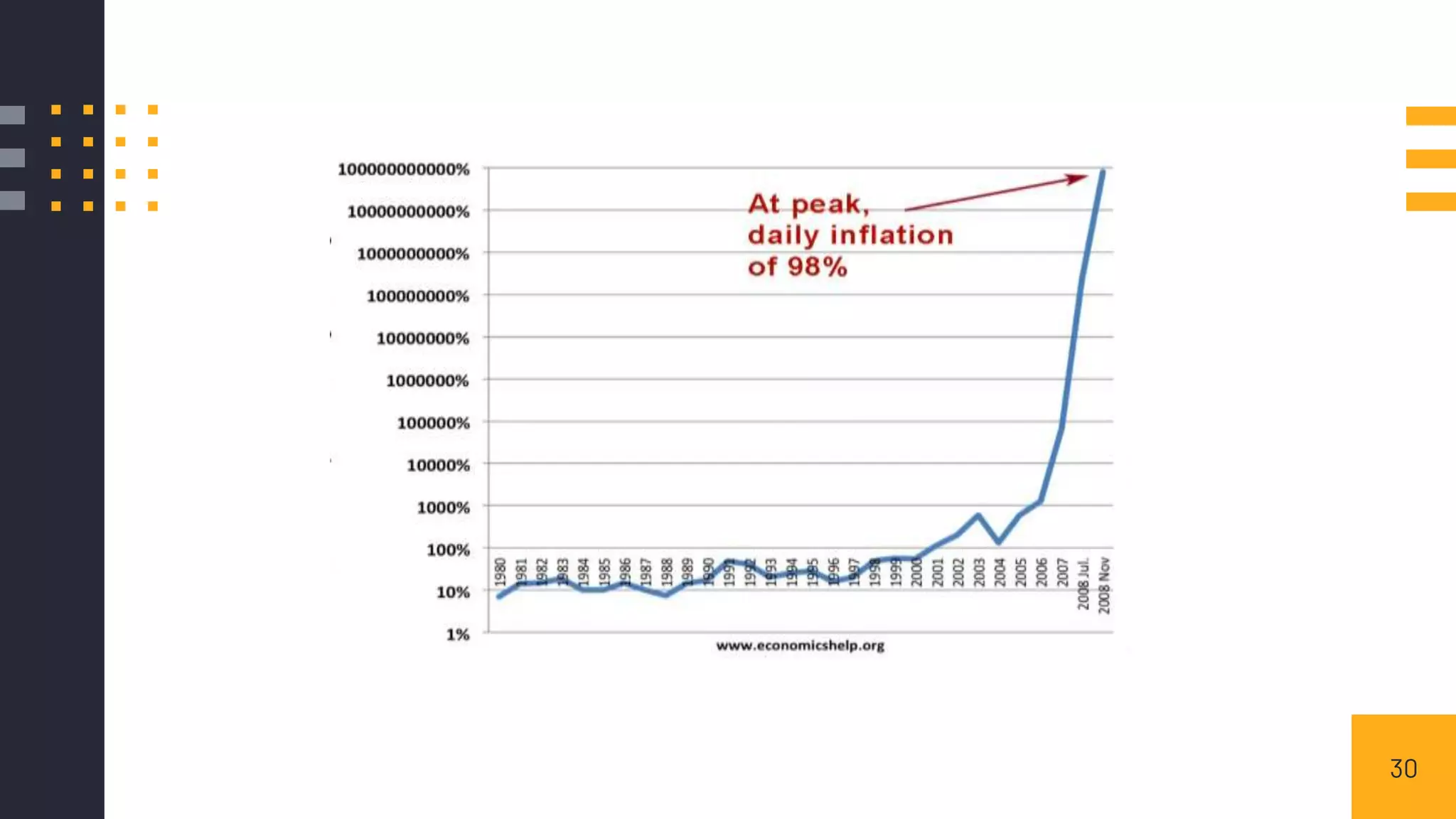
This document discusses inflation control. It begins by introducing inflation and how it is measured, primarily through the Consumer Price Index and Wholesale Price Index. It then covers the main causes of inflation, including demand-pull, cost-push, wage-push, and currency depreciation. The document outlines several measures to control inflation, such as monetary policies like adjusting bank rates, cash reserve ratios, and open market operations. Fiscal policies for controlling inflation include managing government spending, taxation, and public borrowing. The document also provides a case study on hyperinflation in Zimbabwe and policies pursued in India to maintain inflation between 2-6%. It concludes that reasonable inflation of 3-6% is ideal for economic growth while higher rates