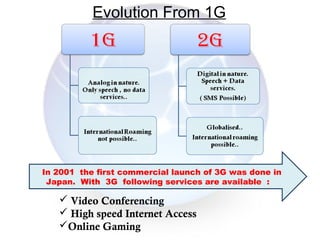
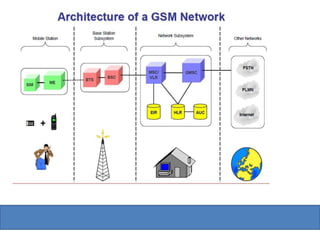
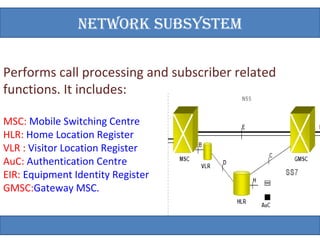
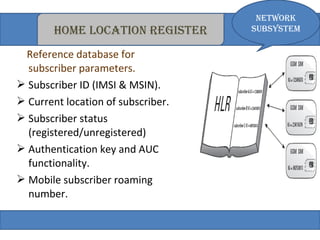
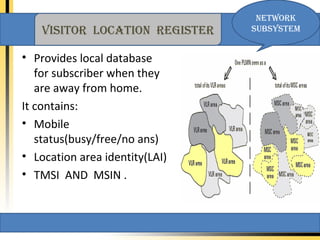
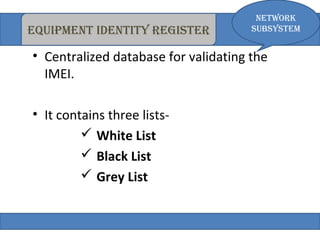
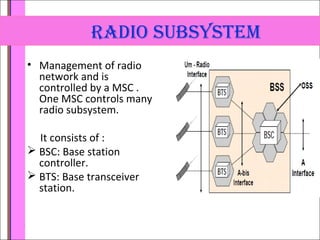
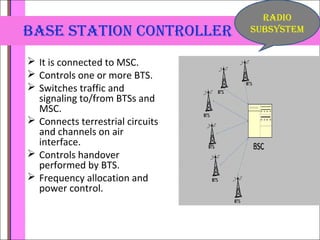
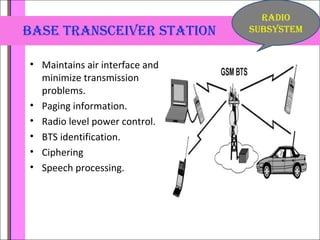
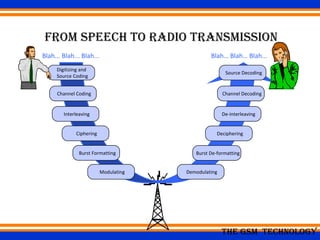
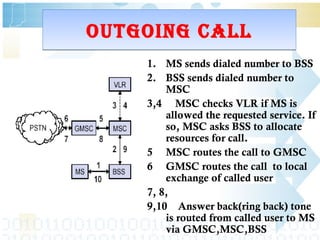
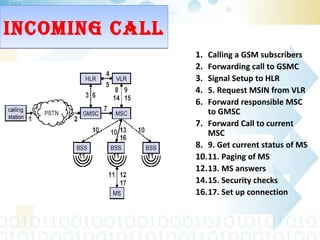
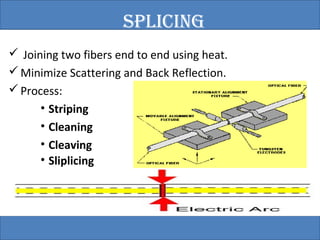
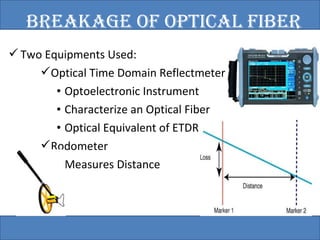
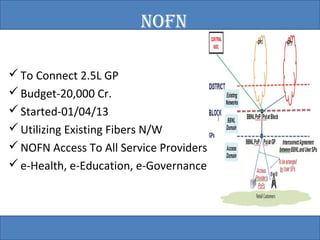
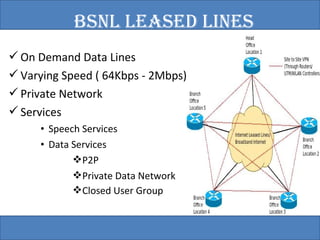
The document provides an overview of the GSM technology. It discusses the history and evolution of GSM, introduces GSM services, and describes the architecture and components of GSM networks including the network subsystem, radio subsystem, and operation and maintenance subsystem. It also covers the process of transmitting speech via radio signals in GSM networks and provides examples of call routing procedures. Finally, it lists some advantages of GSM and discusses practical knowledge about optical fiber networks.