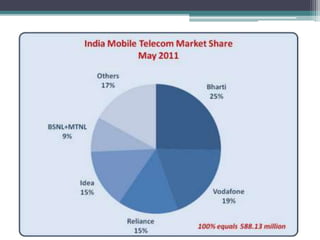
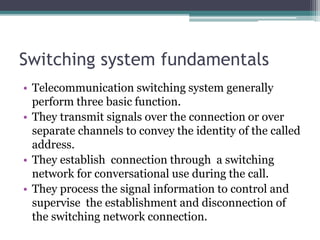
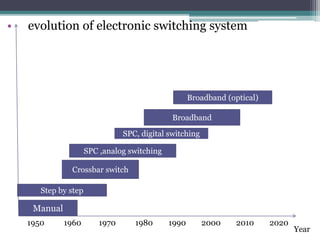
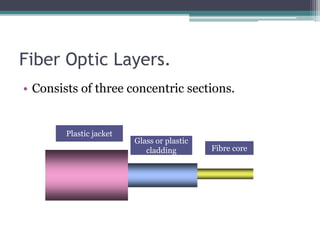
The document provides an overview of topics discussed in a seminar on summer training from BSNL, including:
1) An introduction to BSNL as India's largest telecommunications provider and its transition from DoT.
2) Overviews of telecommunication networks, broadband access technologies like DSL and cable, 3G communication, and optical fiber communication.
3) Details on broadband definitions and needs, technologies like DSL, cable, wireless, and applications.
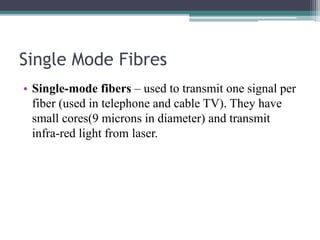
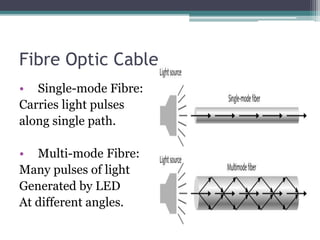
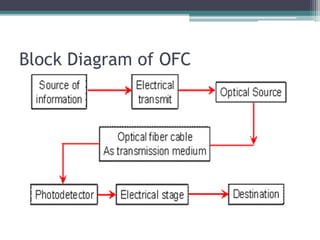
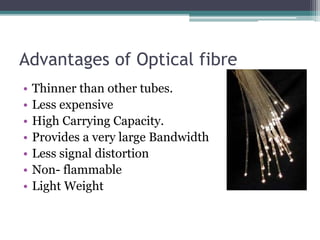
4) Explanations of 3G benefits like increased bandwidth and multimedia support, and optical fiber components, propagation modes, advantages, and applications in telecom, networks, and more.