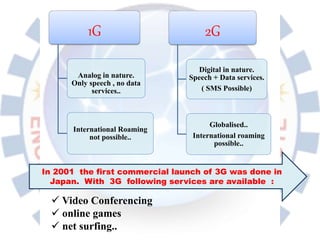
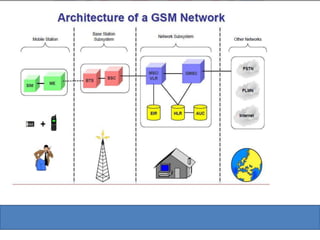
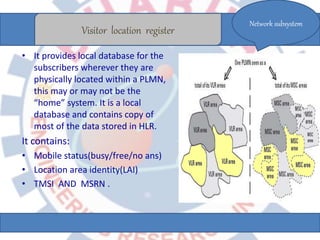
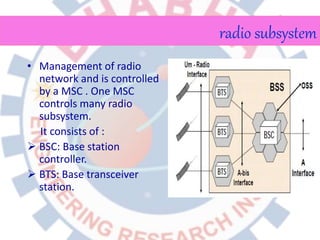
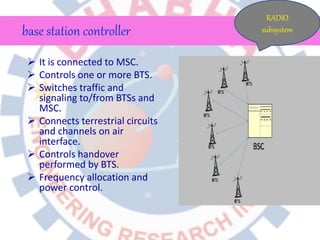
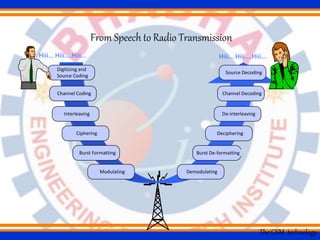
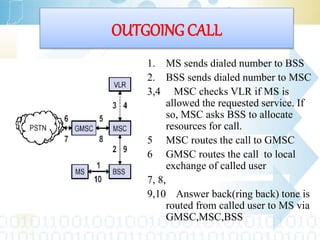
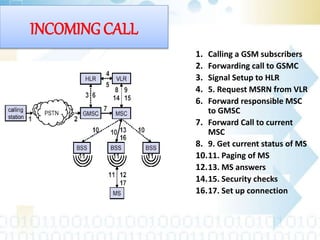
Global System for Mobile (GSM) is a second generation cellular standard developed to provide voice services and data delivery using digital modulation. It has a network subsystem, radio subsystem, and operation and maintenance subsystem. The network subsystem includes the MSC, HLR, VLR, AuC and EIR which perform call processing and subscriber functions. The radio subsystem consists of the BSC and BTS and manages the radio network. GSM supports teleservices, data services and supplementary services and its architecture allows for cellular communication and roaming between networks.