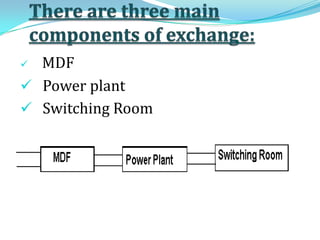
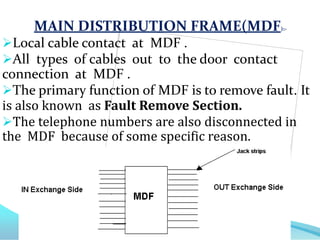
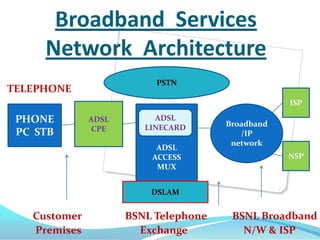
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) is India's largest telecommunications company that provides various telecom services across India. It operates through telephone exchanges that house switching equipment to facilitate call connections. The exchanges have different components like the main distribution frame for fault removal, power plants for electricity supply, and switch rooms containing cabinets for routing calls. BSNL also offers broadband internet through technologies like ADSL that provide high-speed connectivity to customers via the existing telephone network infrastructure.