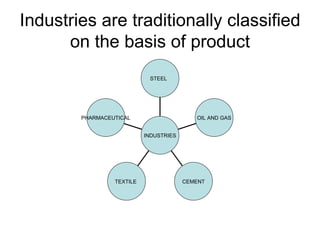
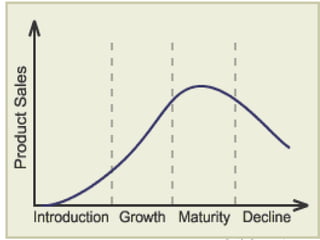
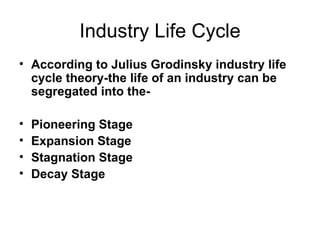
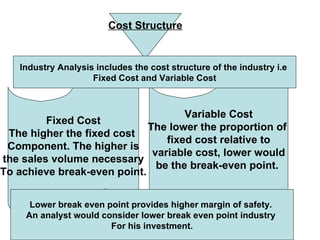
This document discusses fundamental analysis in portfolio management, focusing on industry and company analysis as crucial for assessing investment opportunities. It outlines the product life cycle, which comprises four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline, detailing the characteristics and implications of each stage. Additionally, it describes the industry life cycle concept, identifying stages from pioneering to decay, and highlights the importance of understanding cost structures in industry analysis.