This document discusses various accounting metrics used for managerial decision making, including:
1. Operating assets are assets necessary to run the business, divided into current and long-term assets. Non-operating assets are above operational needs.
2. Net operating working capital and operating long-term assets together make up total operating capital. Free cash flow is available for investors after investing in operating capital.
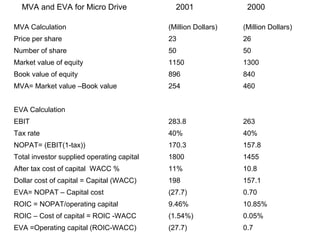
3. Metrics like net operating profit after tax, return on invested capital, market value added and economic value added are used to evaluate performance and value creation beyond traditional accounting measures.