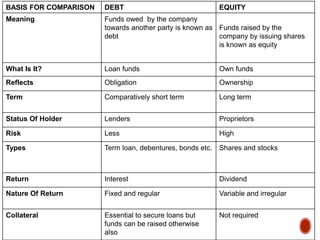
Debt refers to funds that a company owes to another entity that must be repaid within a specific term. Equity refers to funds raised by issuing shares to the public that can remain invested in the company long-term as ownership. Key differences are that debt is borrowed while equity is owned, debt carries obligation to repay while equity represents ownership, and debt has fixed regular interest payments while equity dividends are variable and irregular. Maintaining a balanced ratio between debt and equity, typically with equity twice that of debt, helps companies cover potential losses.