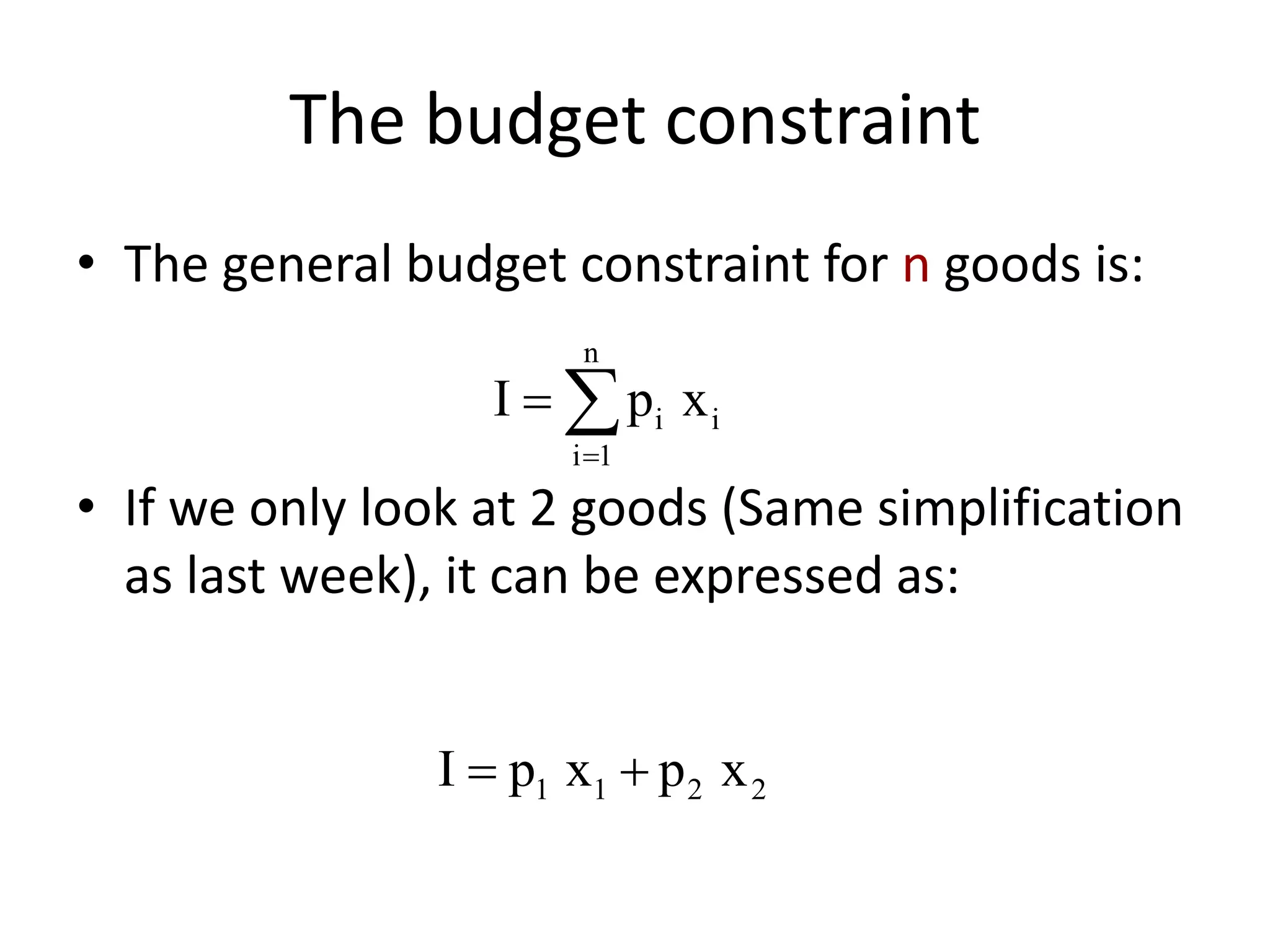
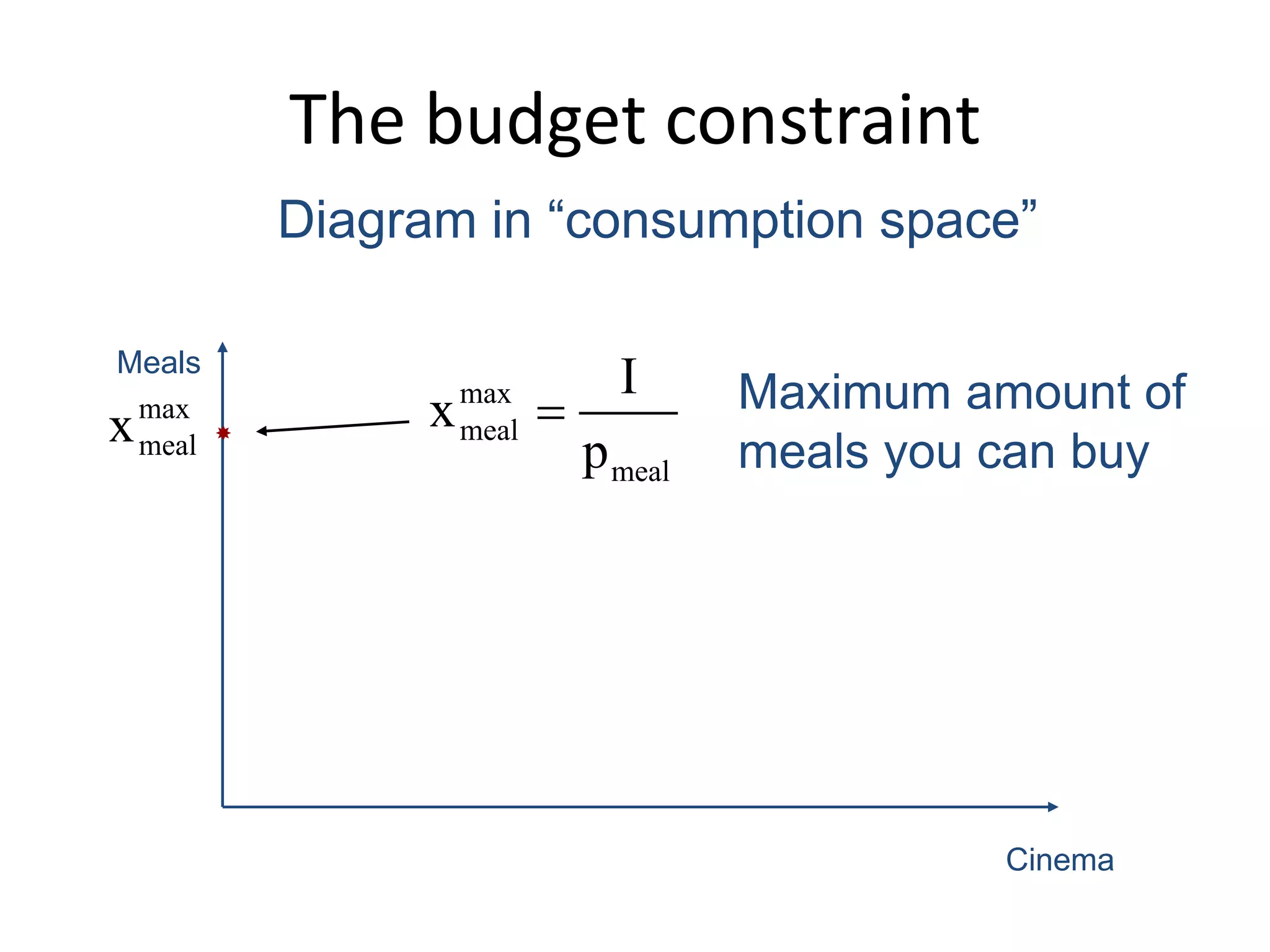
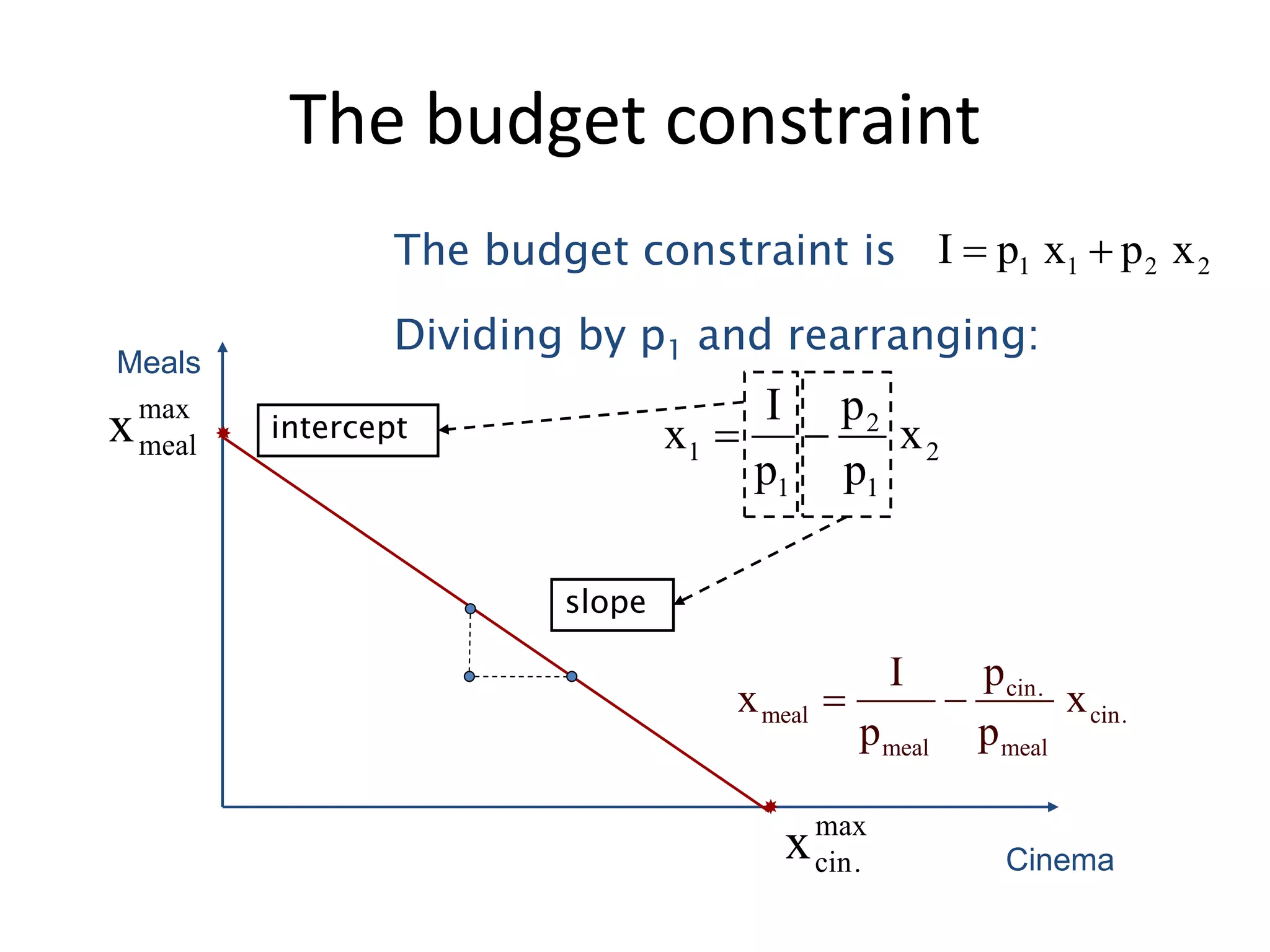
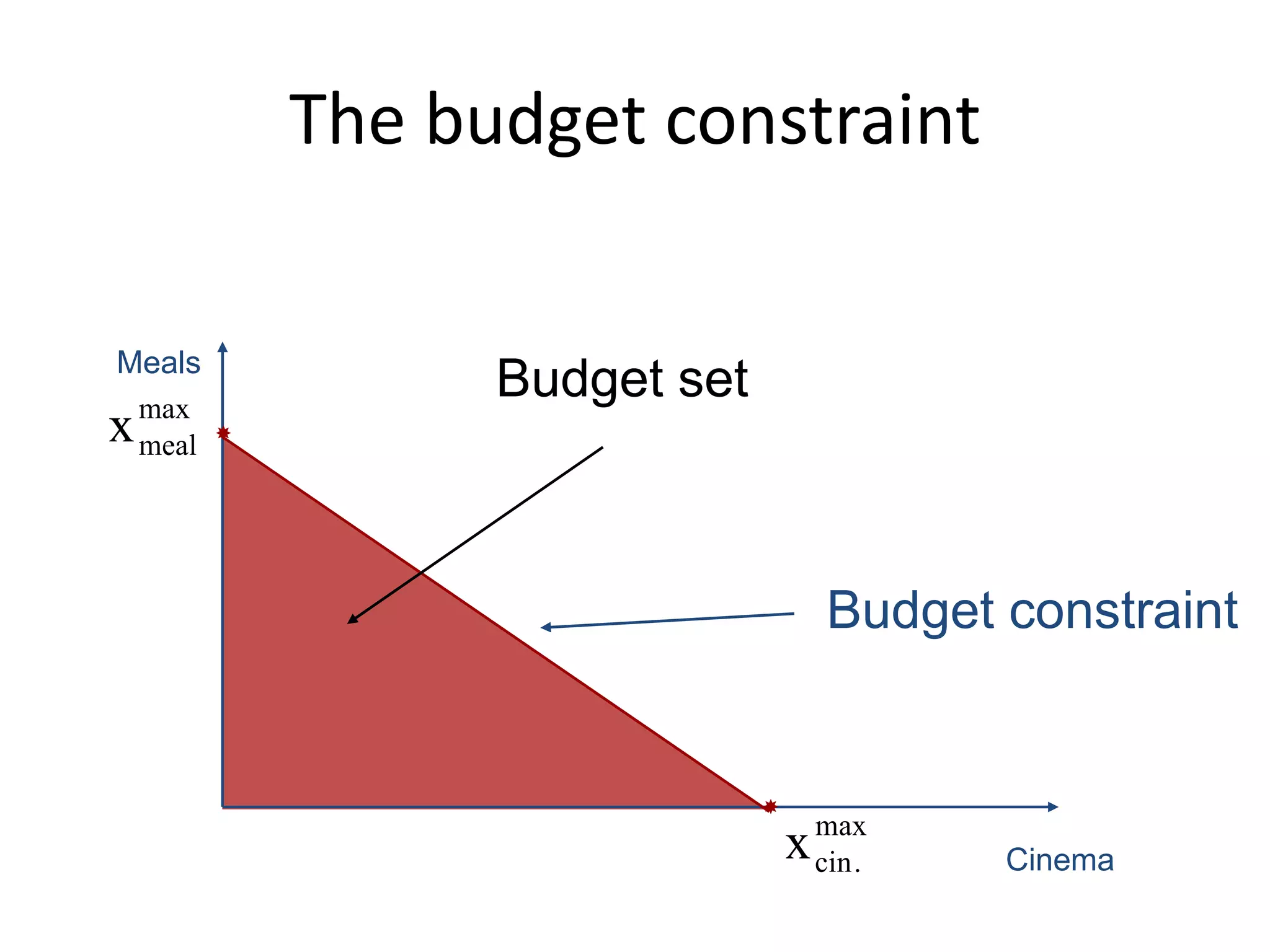
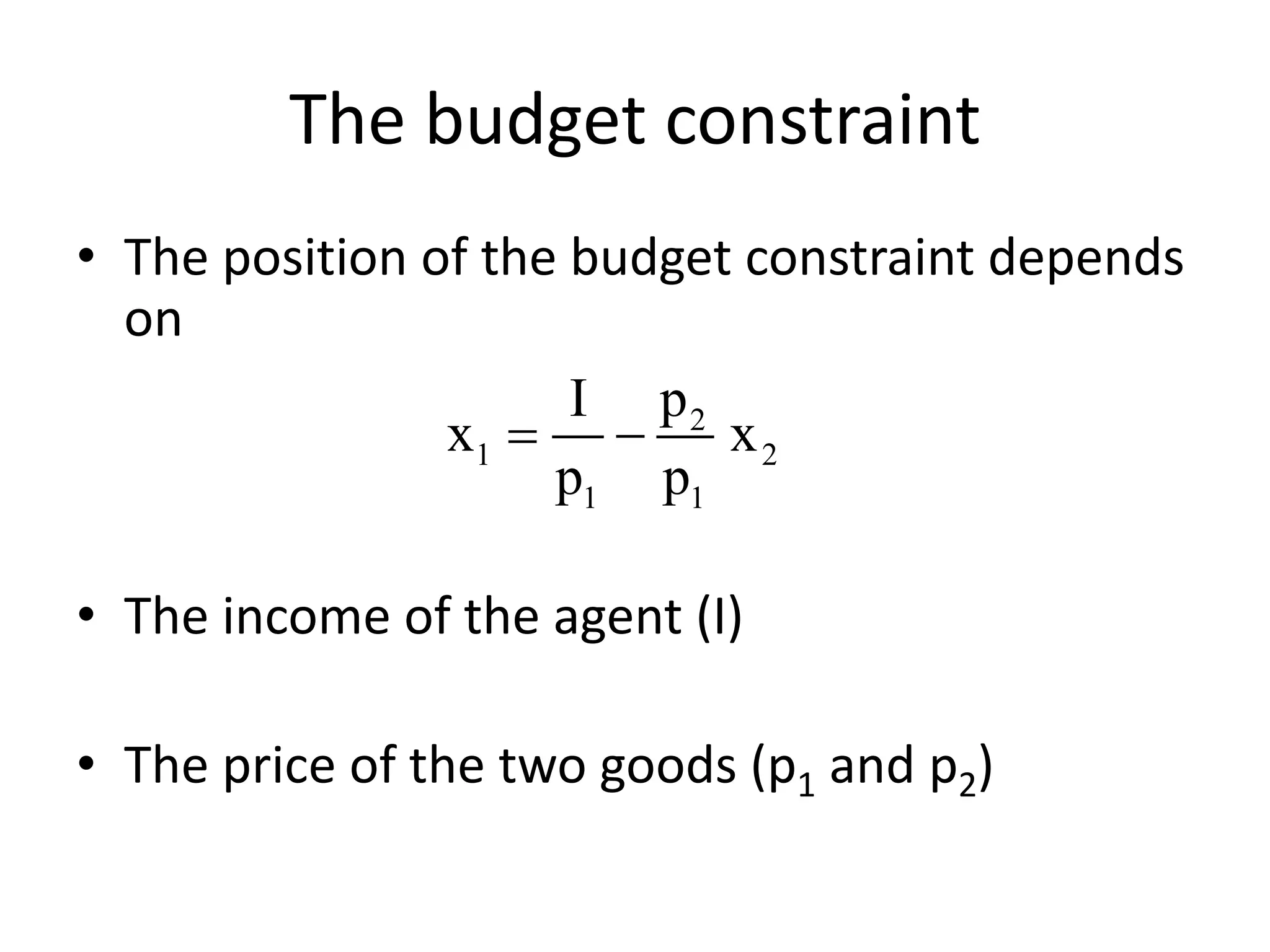
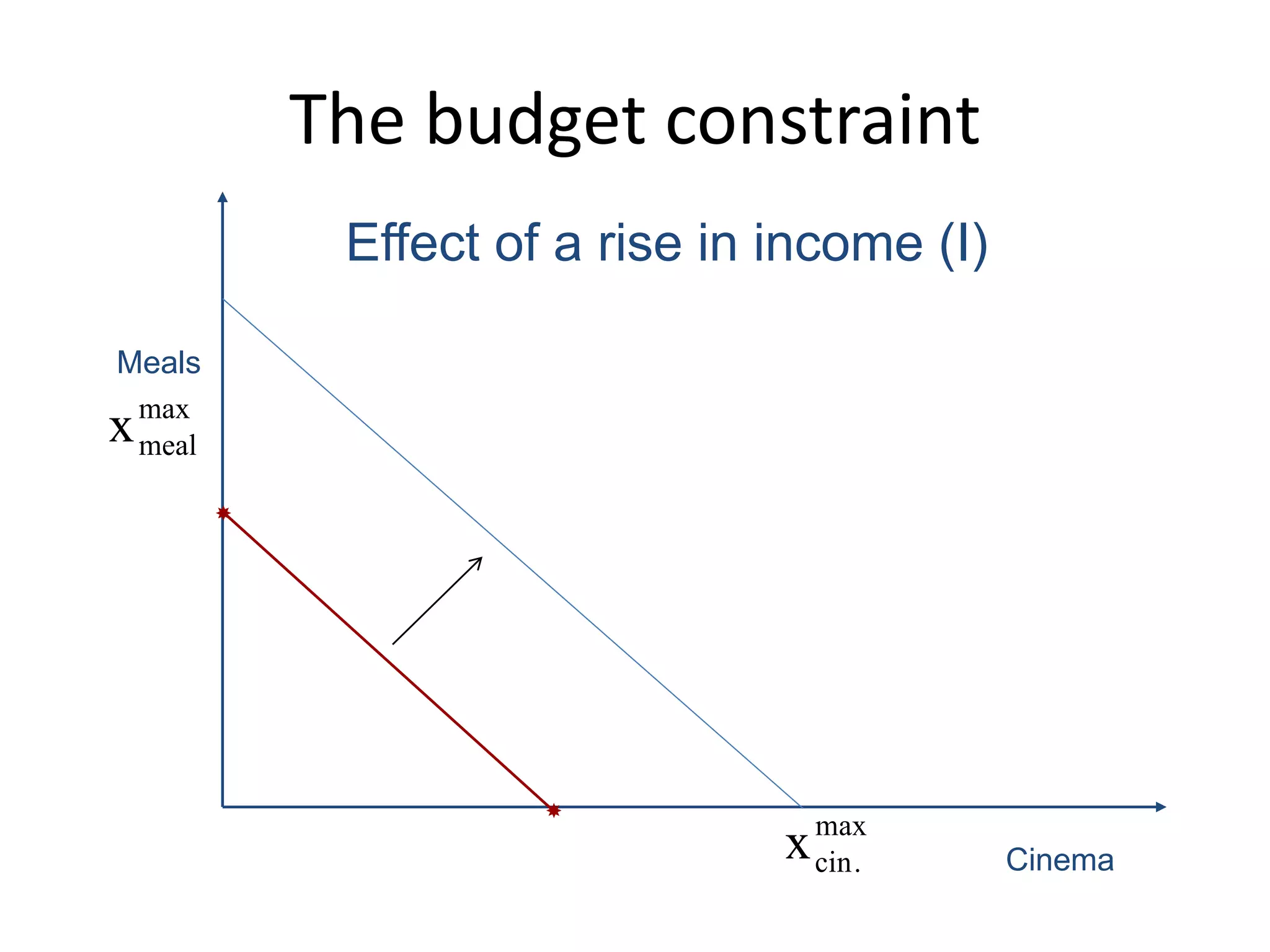
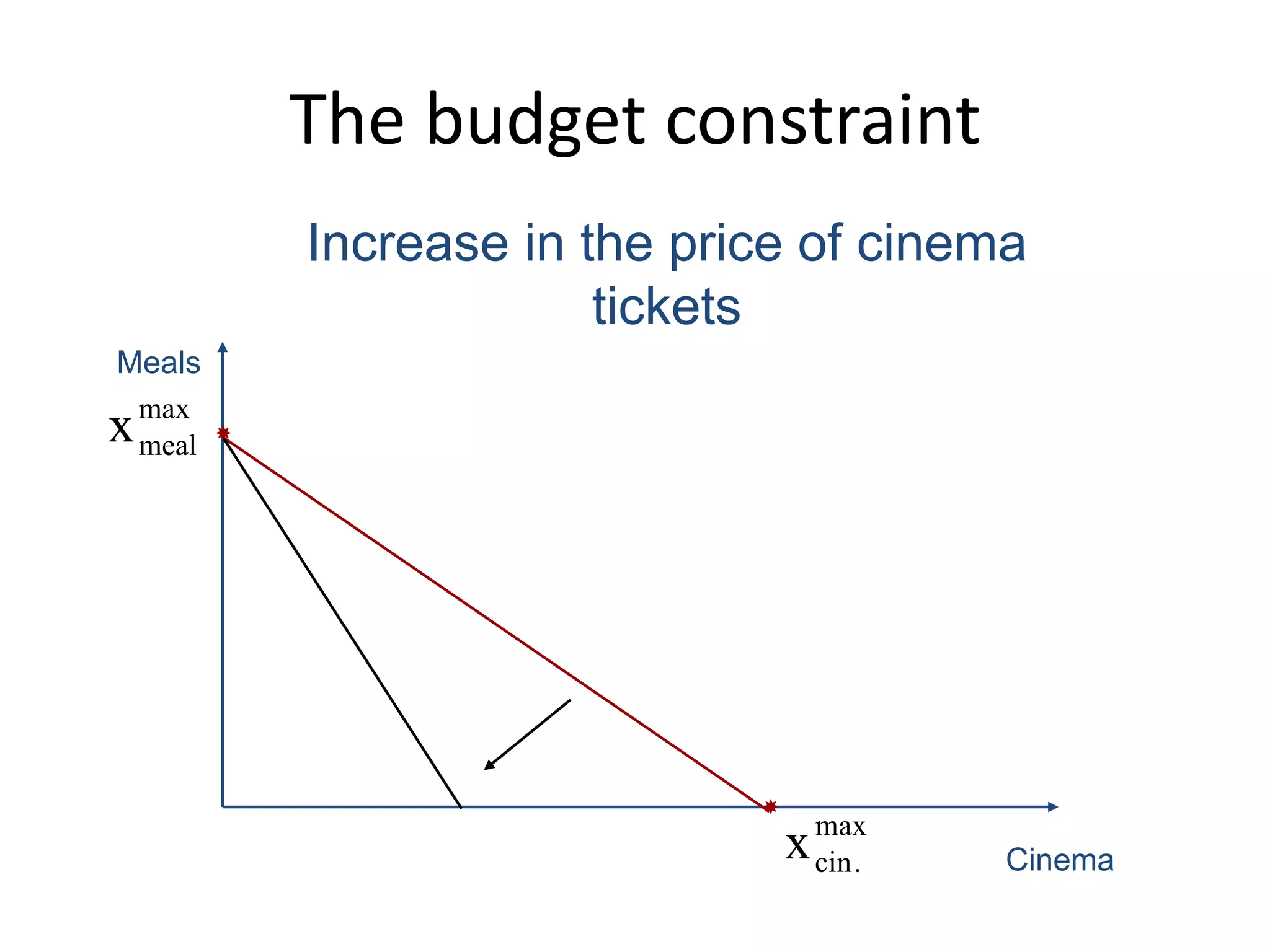
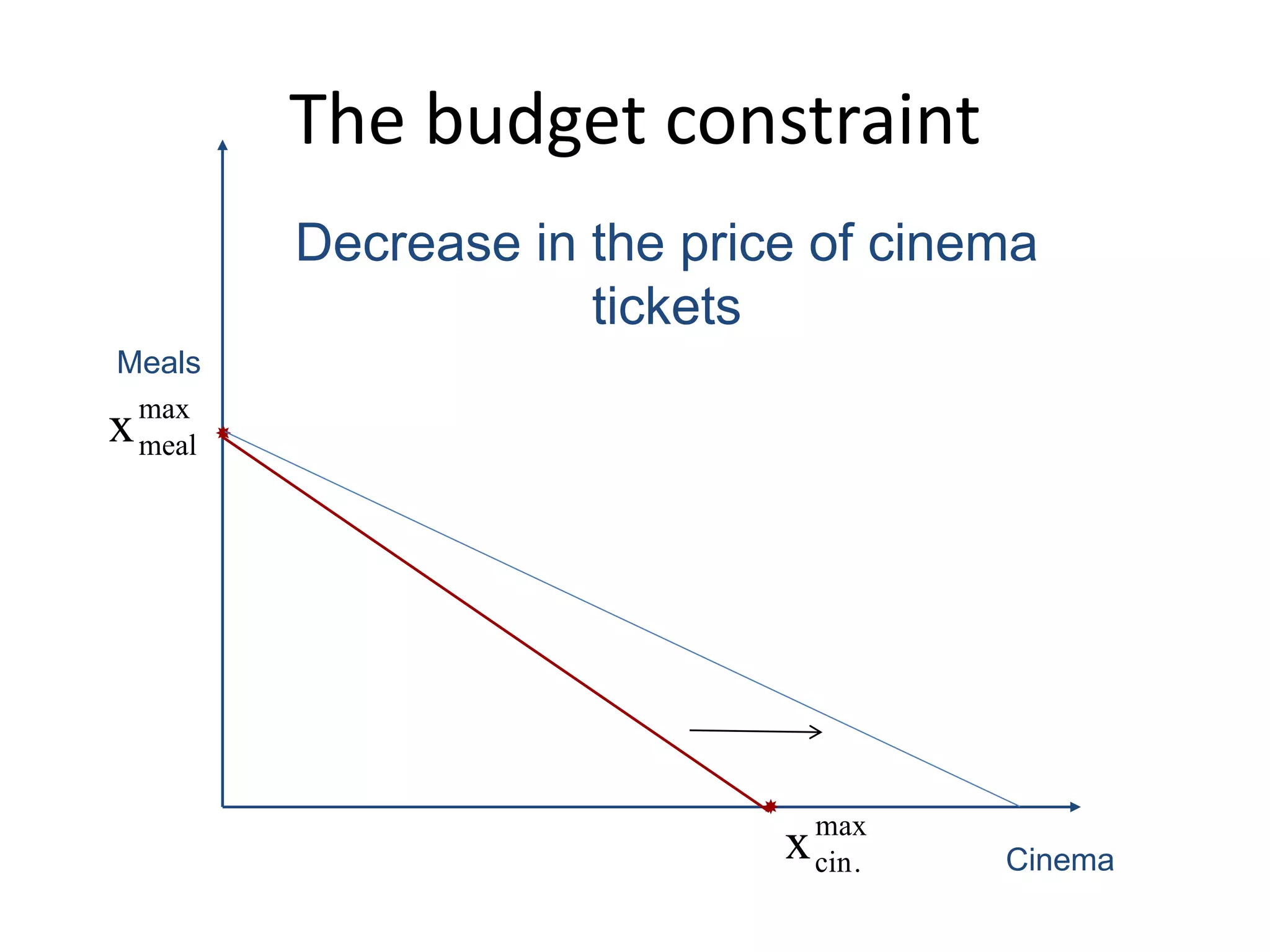
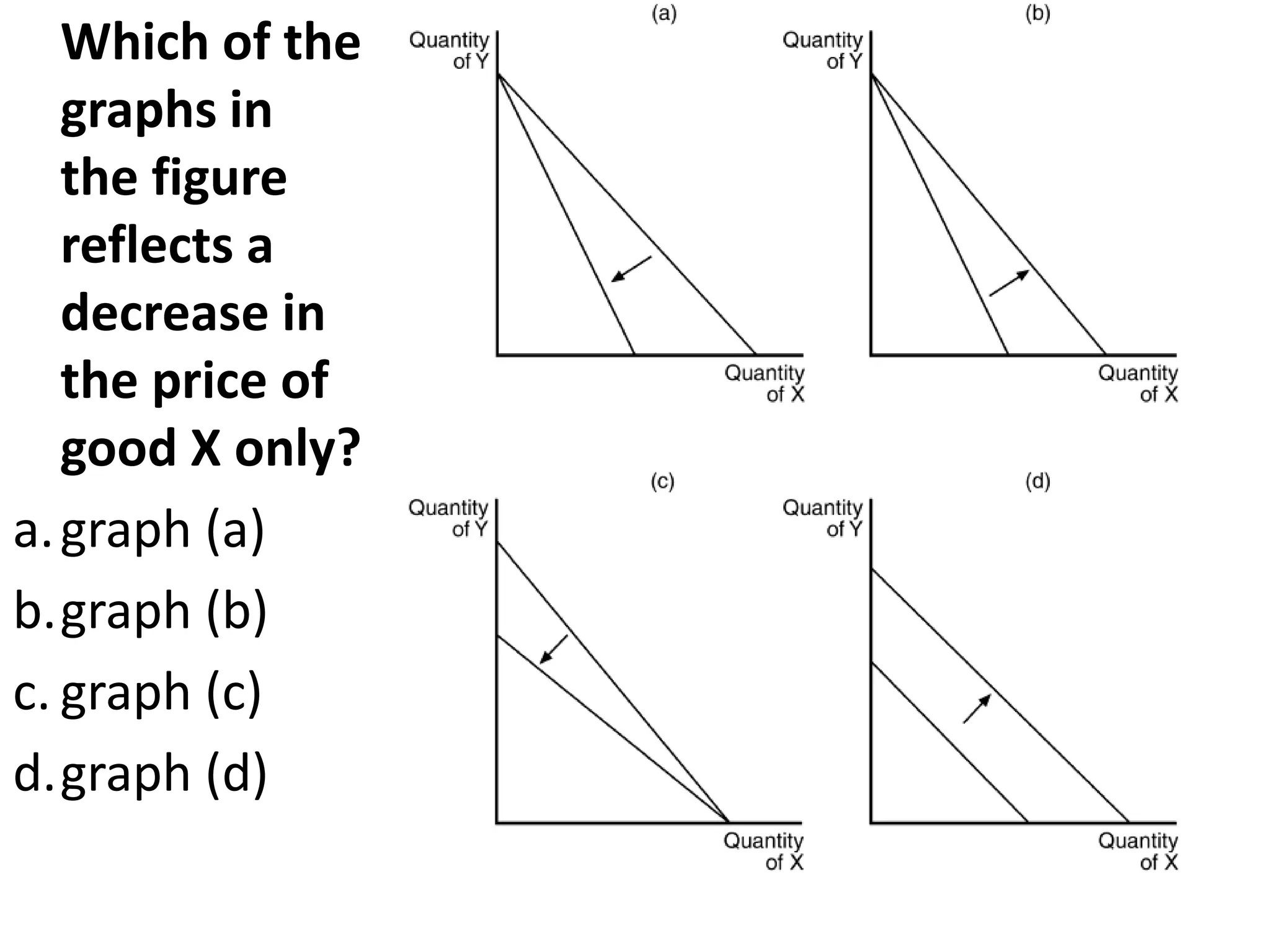
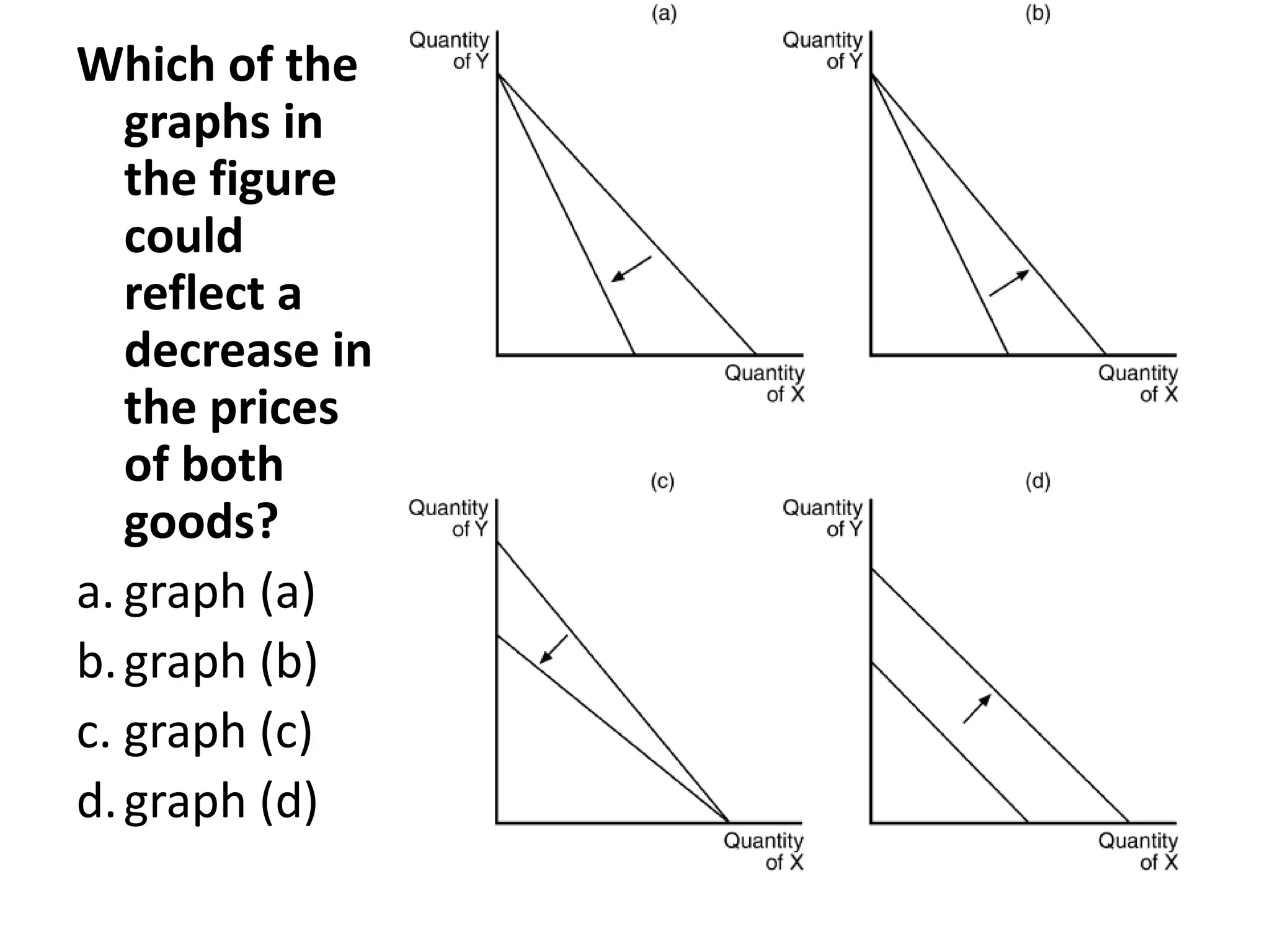
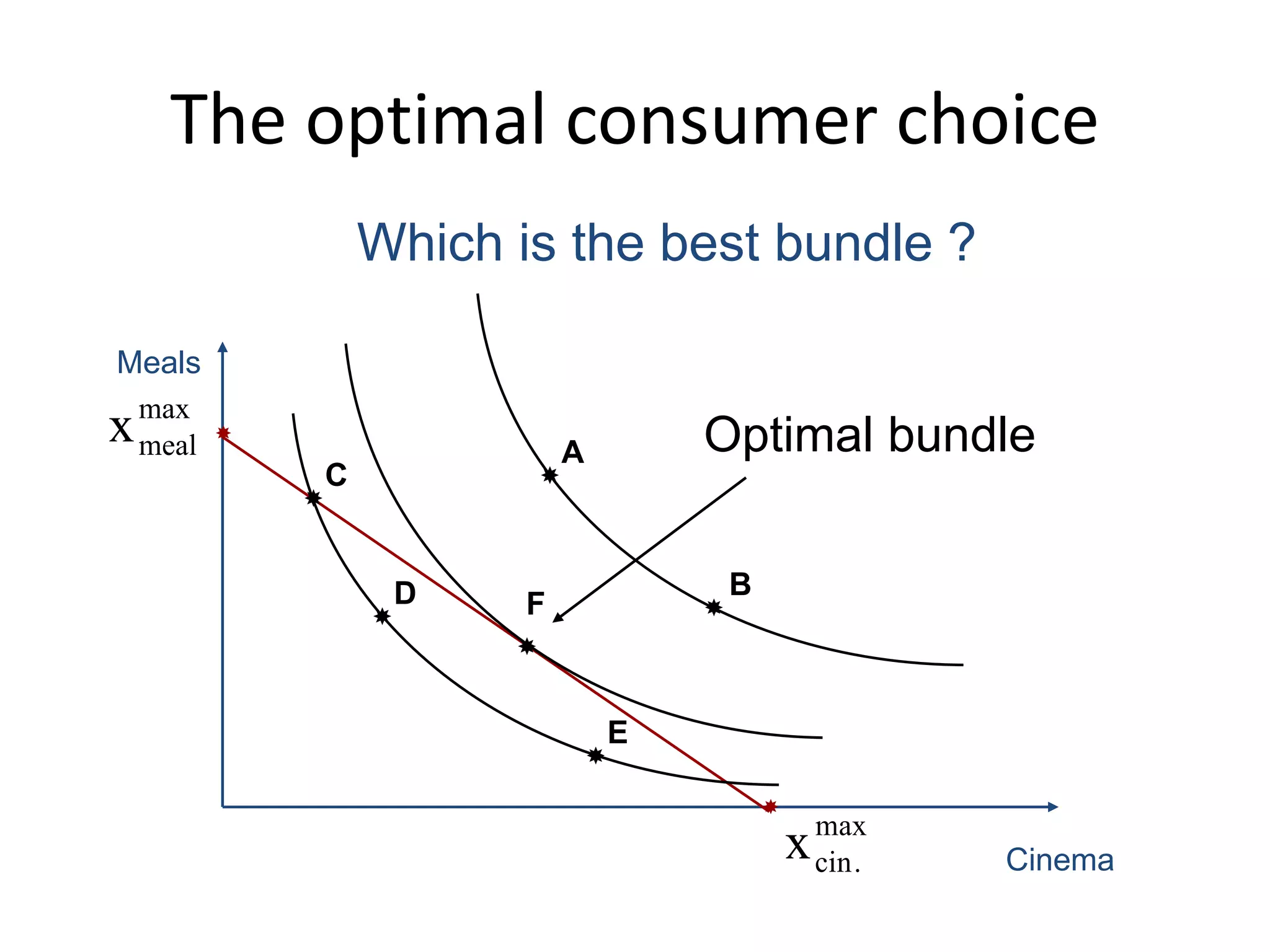
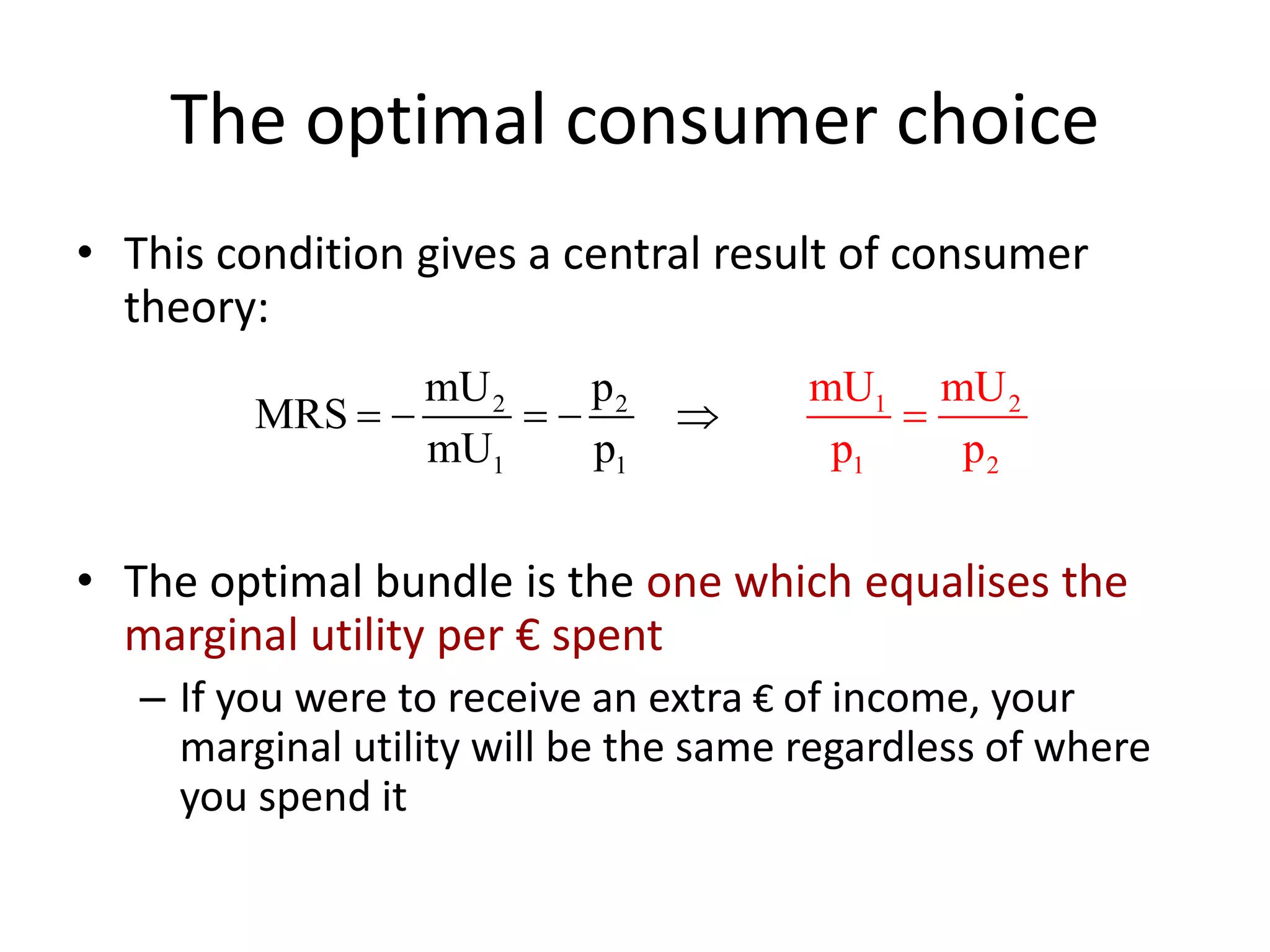
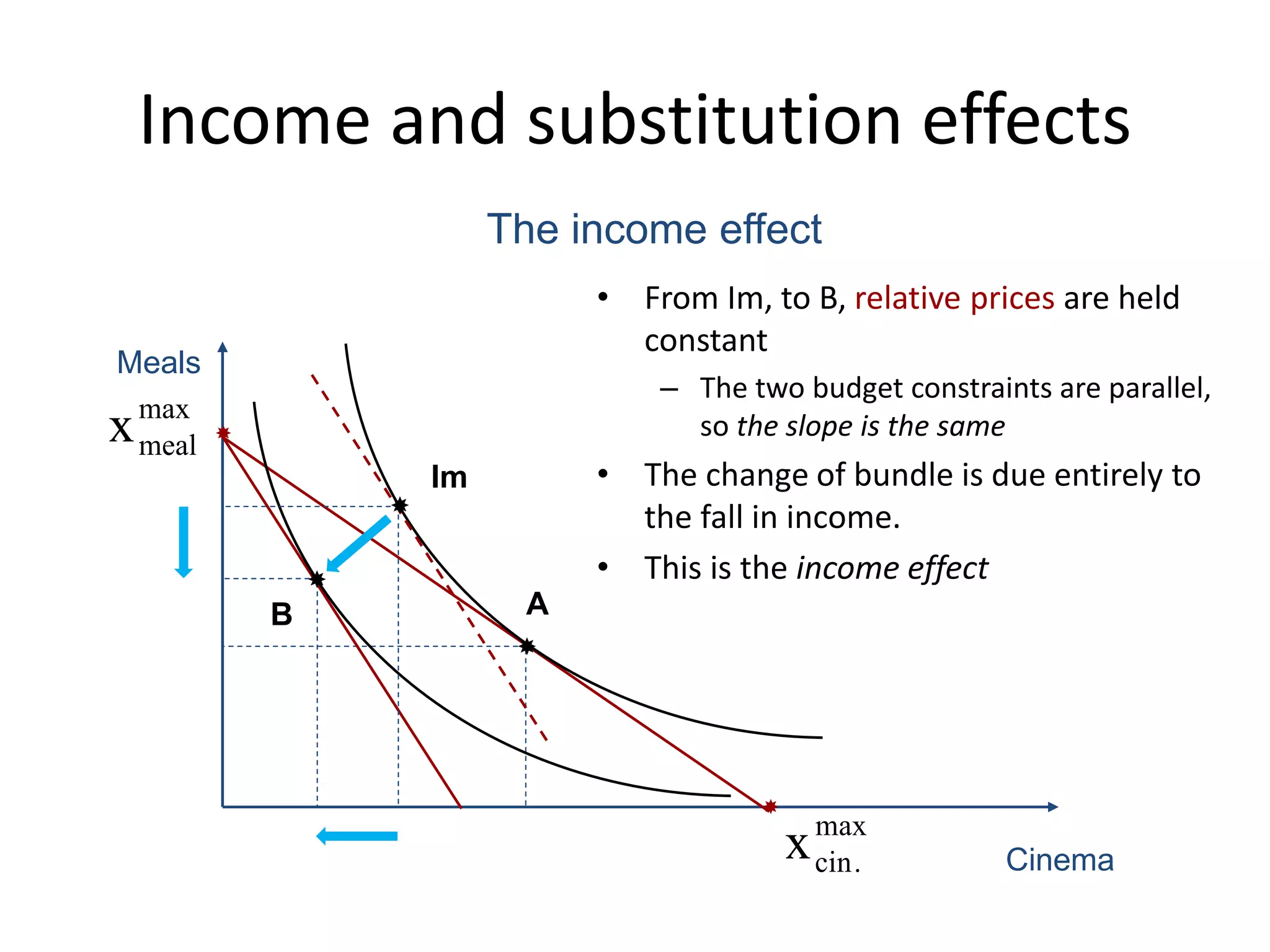
The document discusses the budget constraint and optimal consumer choice. It begins by explaining the budget constraint conceptually and mathematically, showing how a consumer's income and the prices of goods determine which bundles of goods are affordable. It then shows how consumers can determine their optimal bundle by finding the point where an indifference curve is tangent to the budget constraint. This ensures the marginal rate of substitution between goods equals the relative price ratio. Finally, it explains how changes in prices or income can be decomposed into substitution and income effects, with substitution effects occurring when relative prices change and income effects when real income changes.