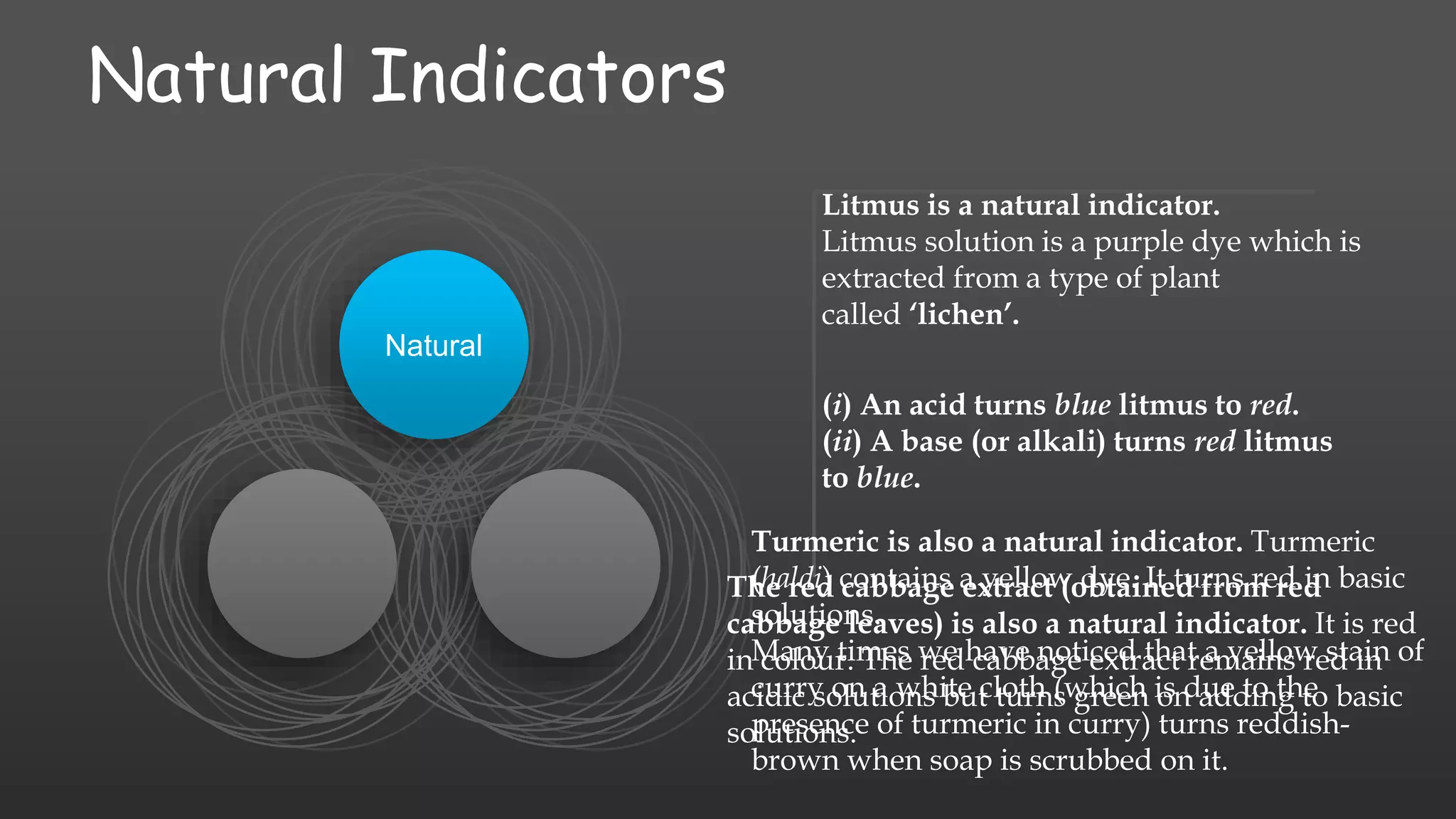
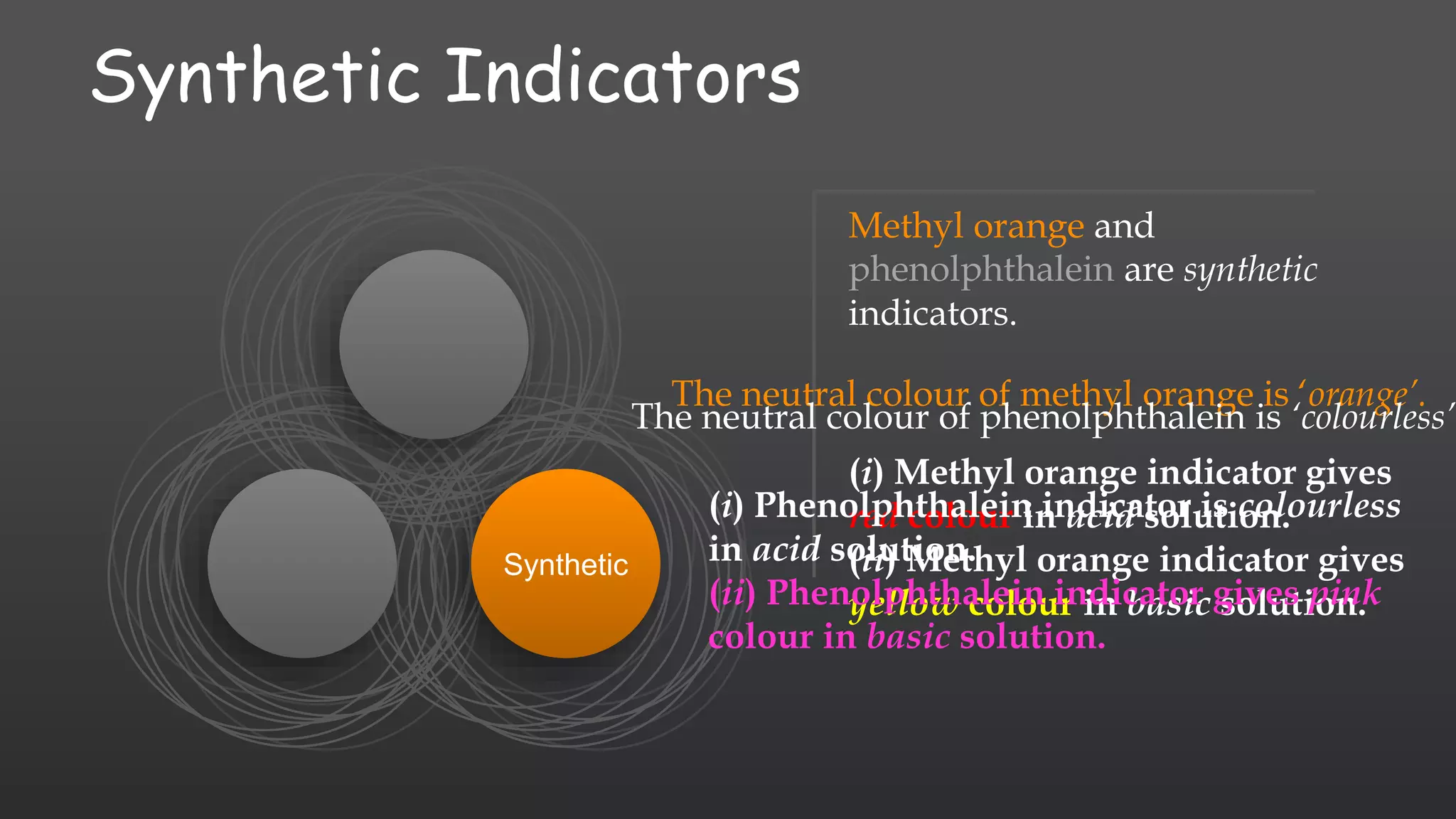
The document discusses the classification of chemical compounds into acids, bases, and salts, along with the concept of acid-base indicators, which are dyes that change color in response to acids and bases. It highlights natural indicators like litmus and turmeric, as well as synthetic indicators such as methyl orange and phenolphthalein, detailing their color changes in acidic and basic solutions. Additionally, it introduces olfactory indicators, like onion and vanilla extract, which change their smell in the presence of acids or bases.