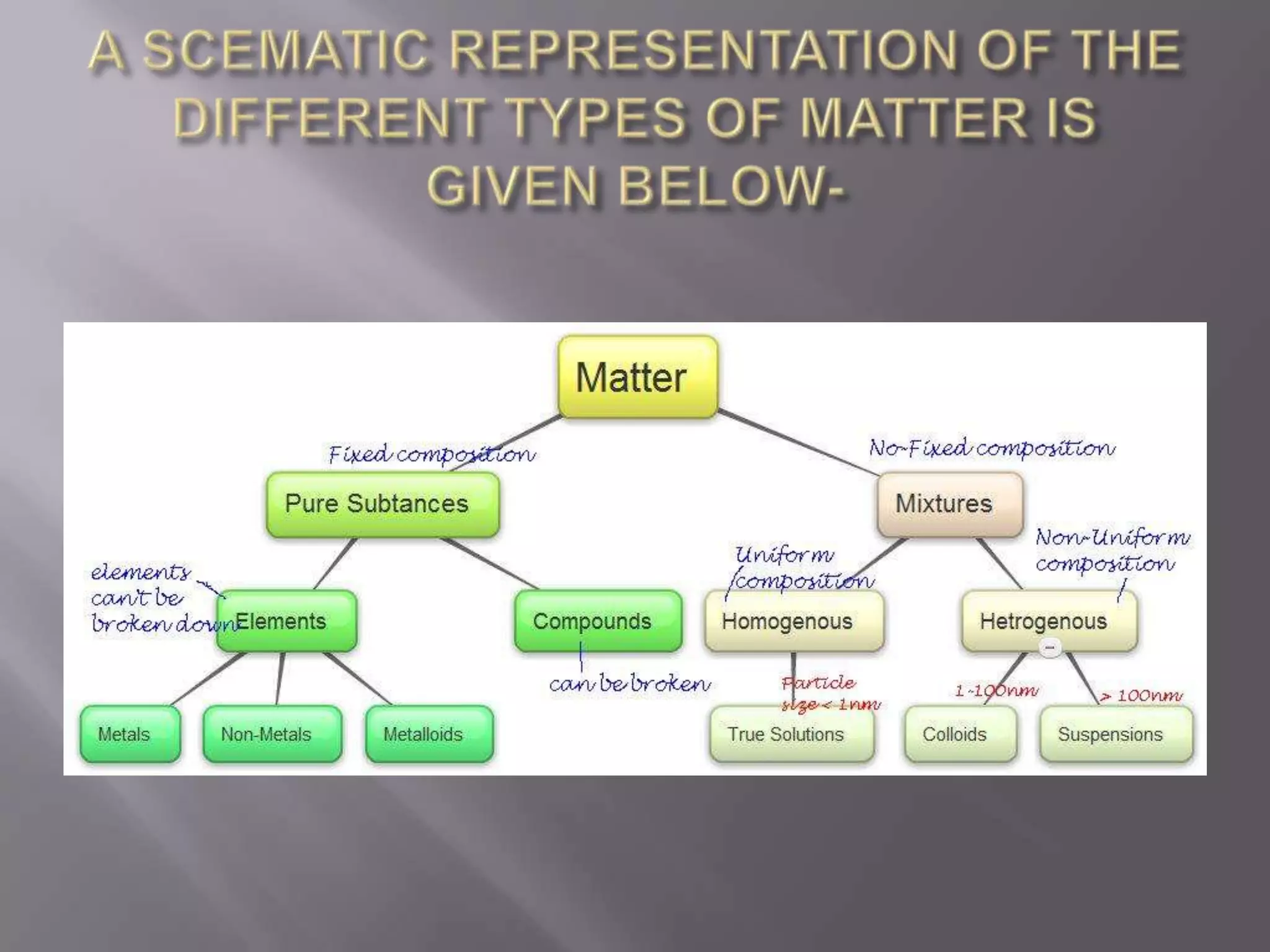
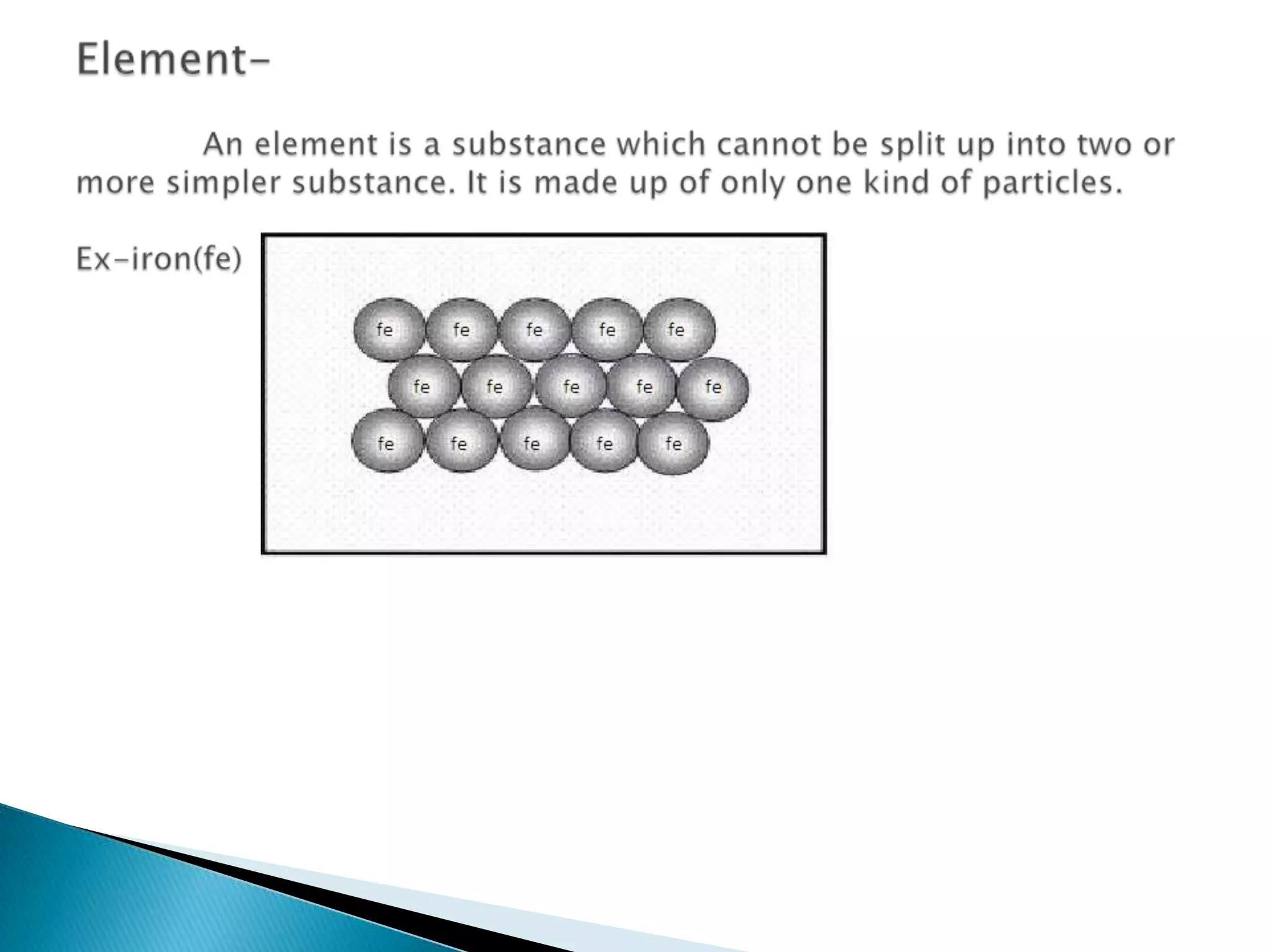
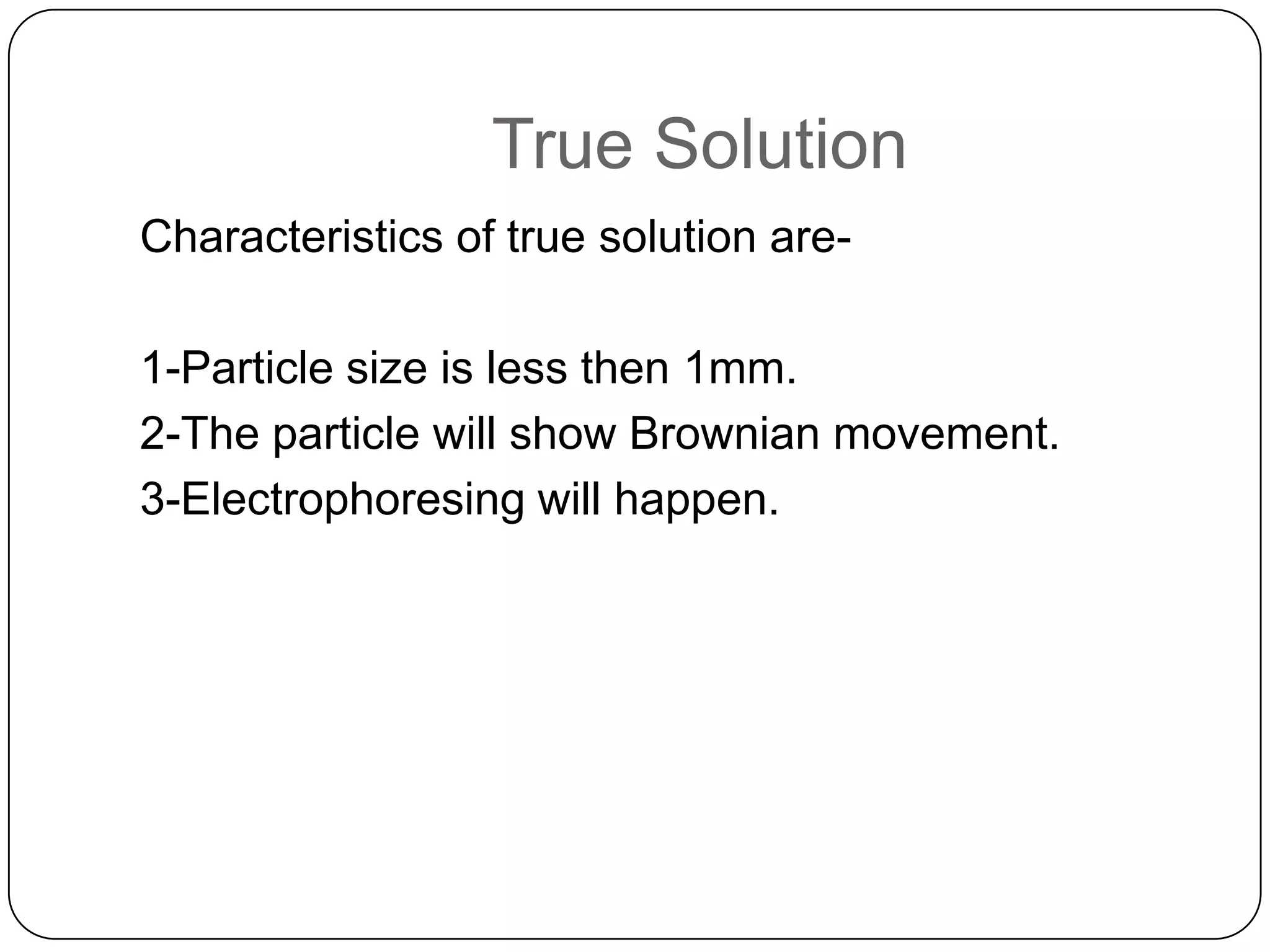
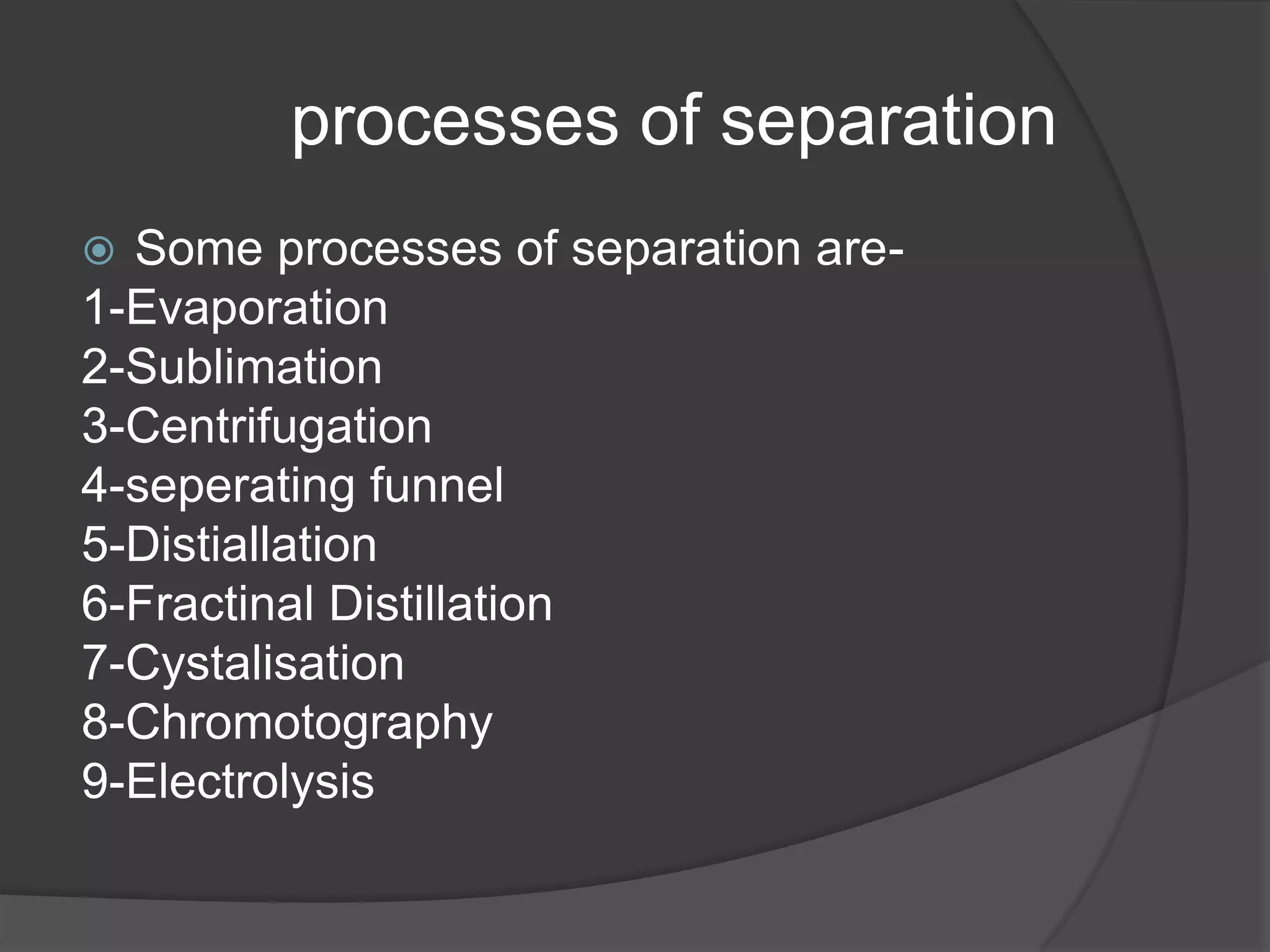
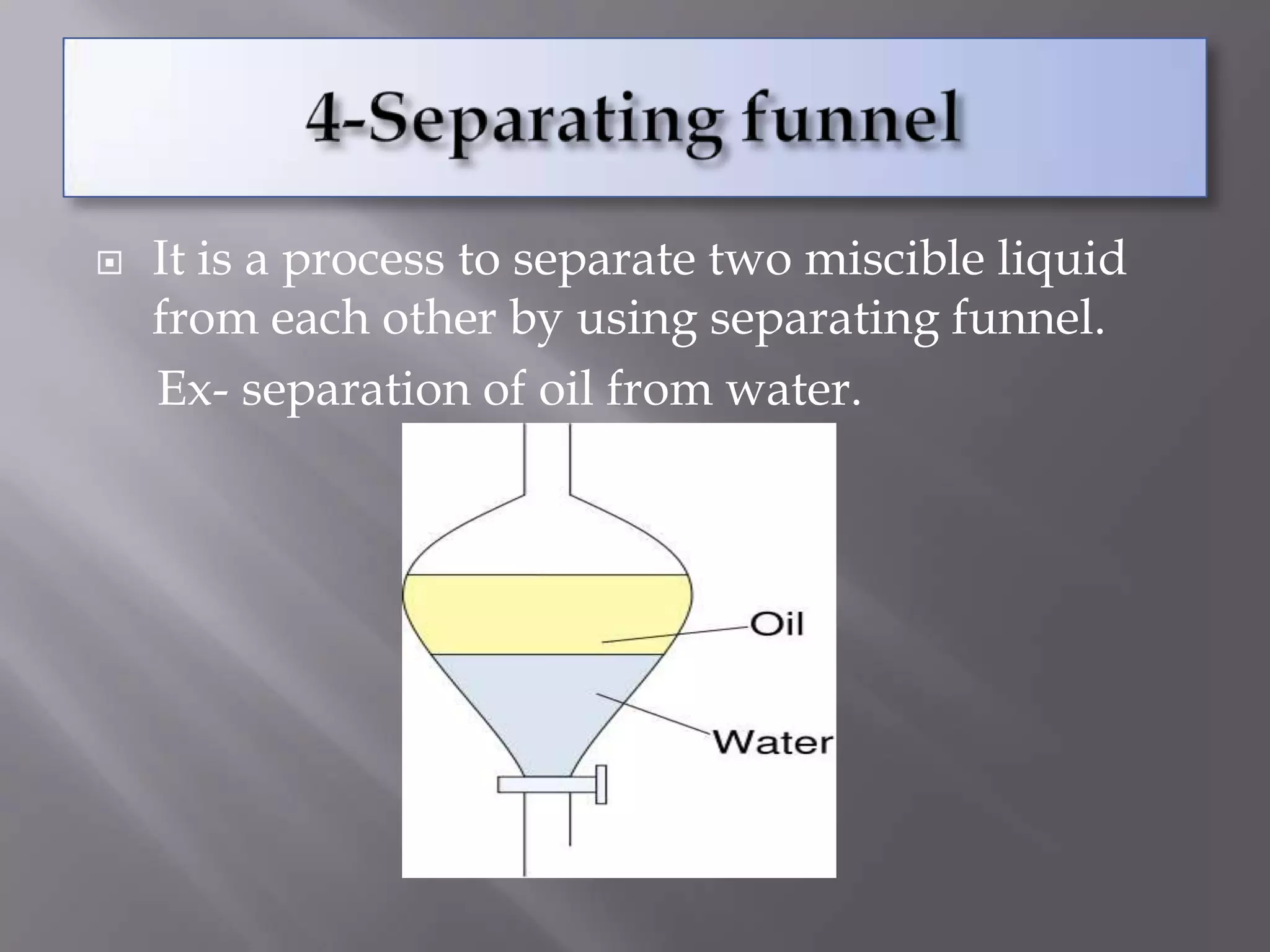
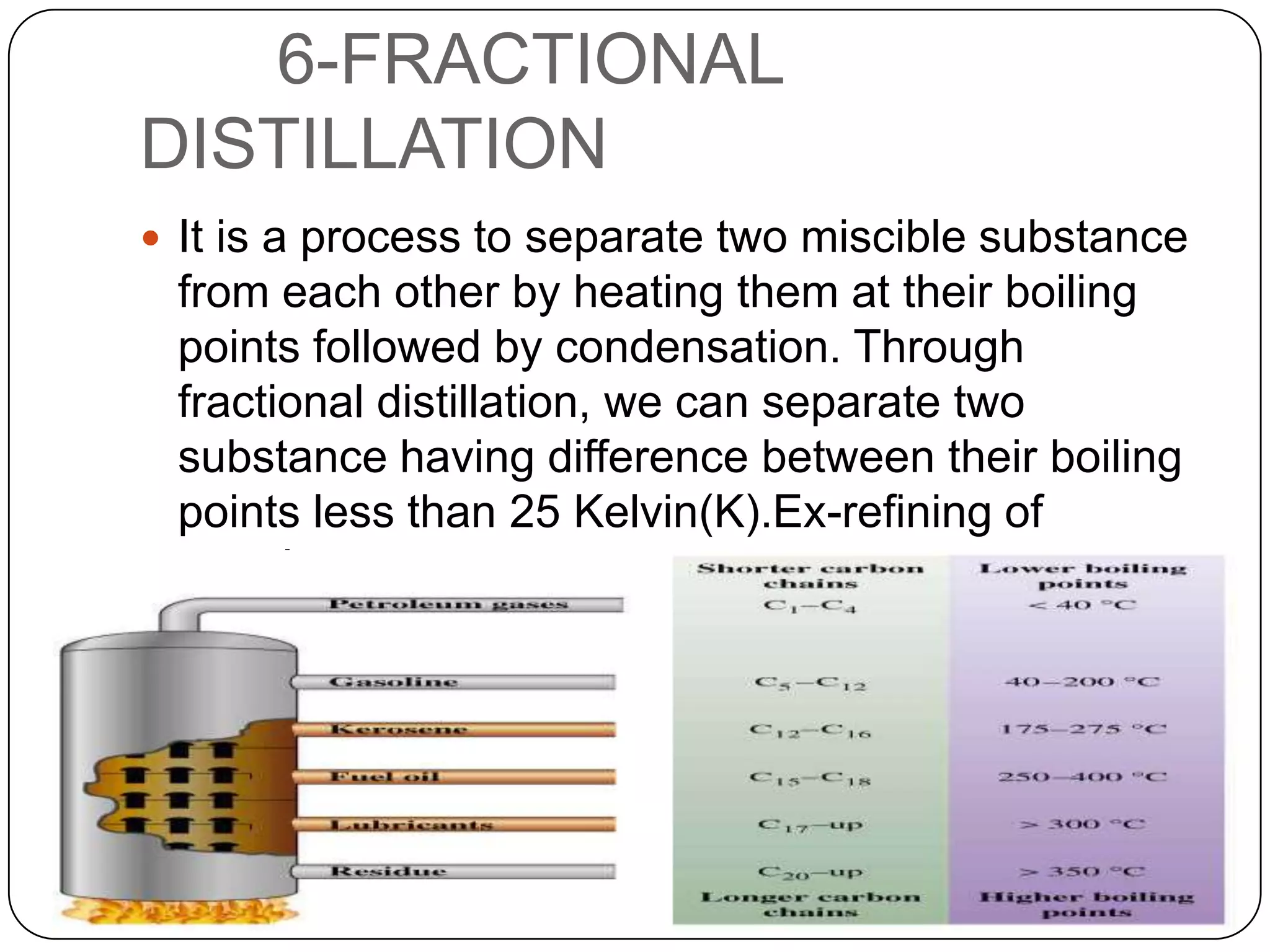
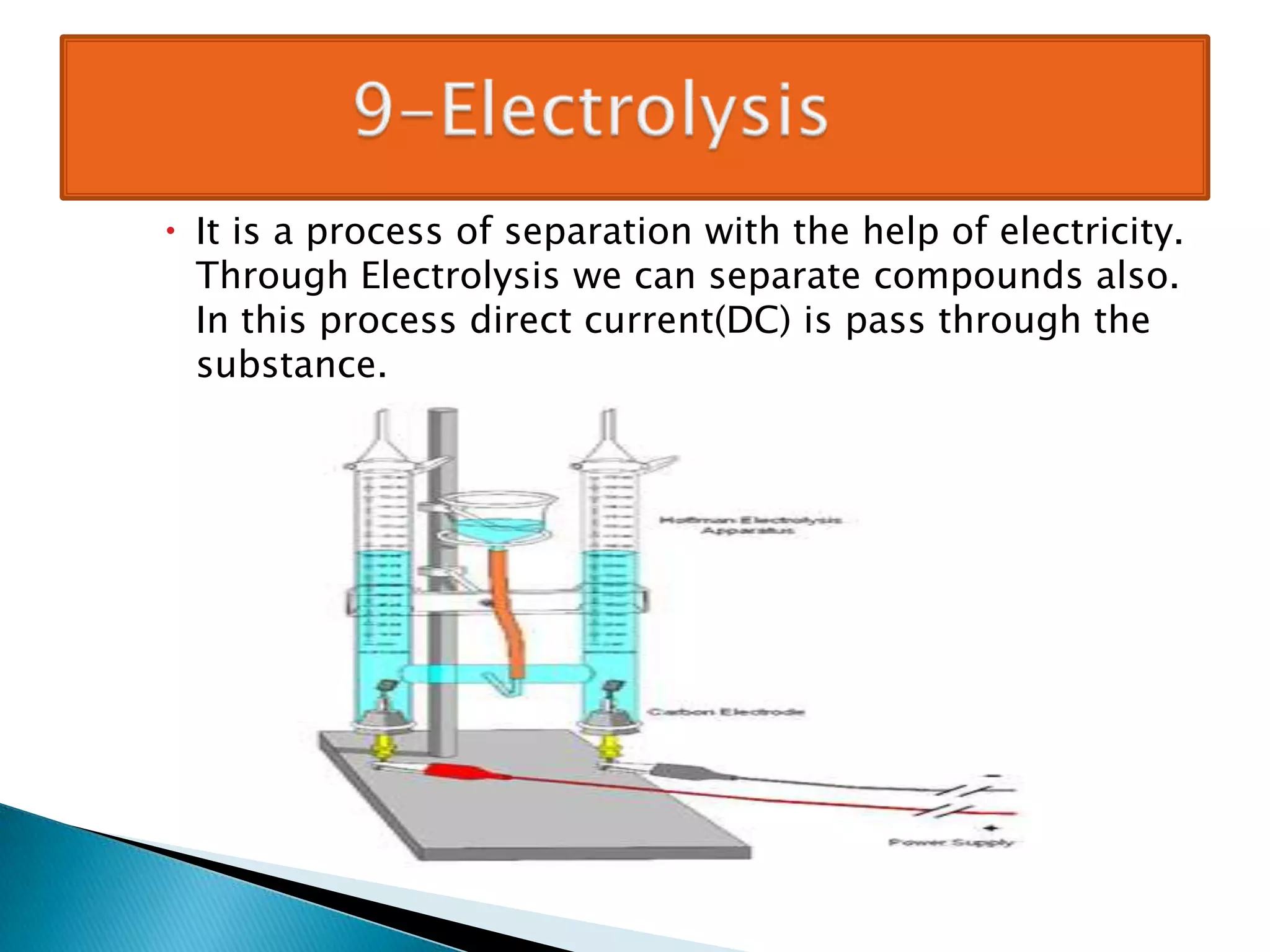
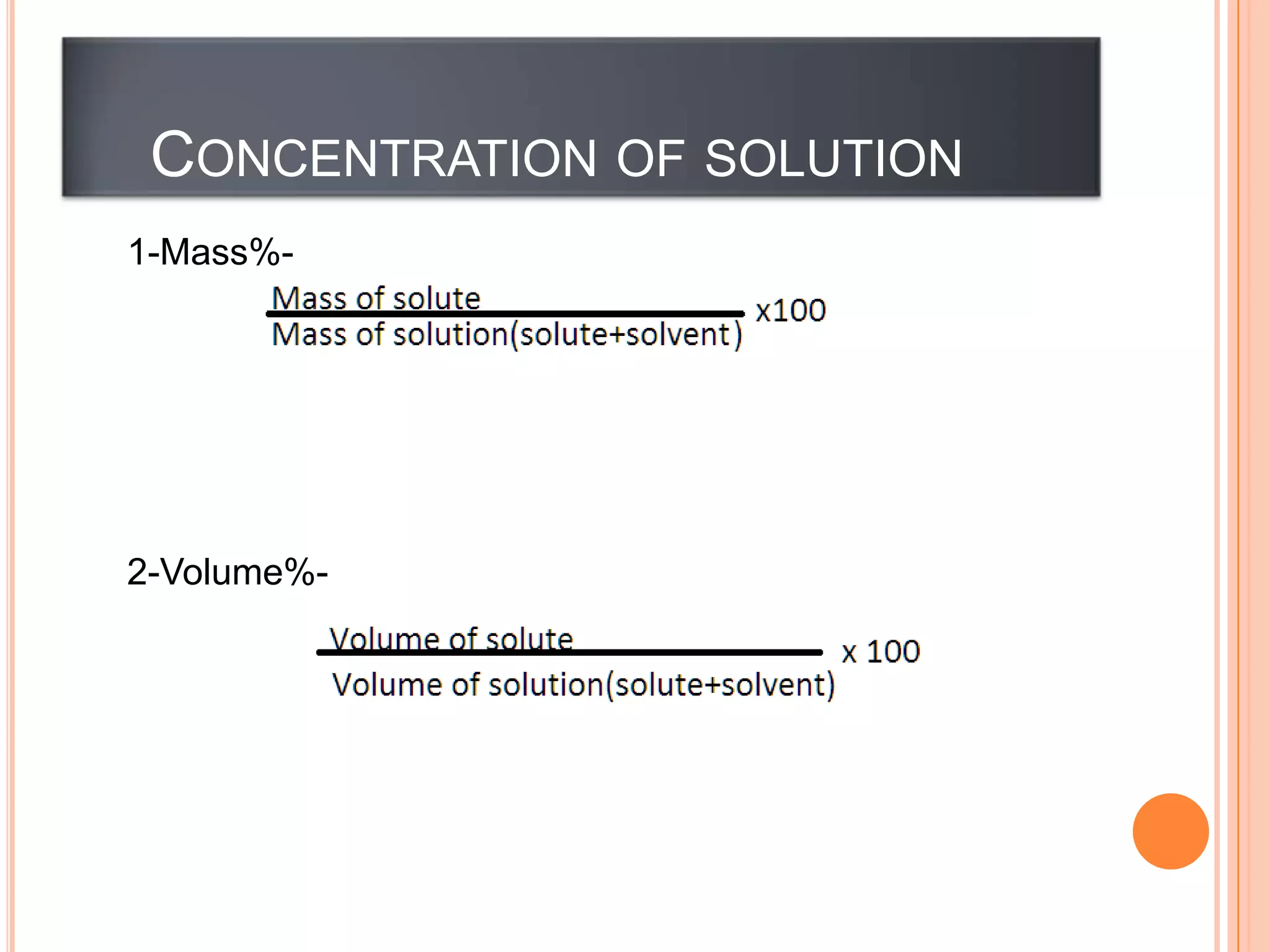
Matter can be classified as pure substances or mixtures. Pure substances are either elements or compounds, while mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures where one substance dissolves evenly throughout another. There are several processes that can separate mixtures into their component substances, such as evaporation, crystallization, centrifugation, chromatography, and distillation. Physical changes alter the state of matter but do not change its chemical makeup, while chemical changes form new substances through chemical reactions.