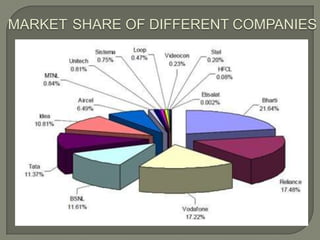
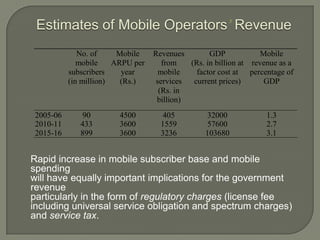
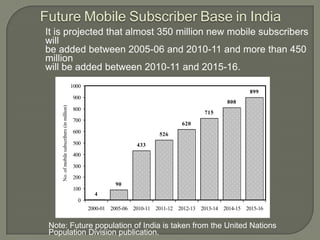
The Indian telecom industry has experienced significant growth, making it the fifth-largest telecom network globally. With an average addition of 6-7 million users per month, the market is the fastest-growing in wireless services, bolstered by government support in manufacturing and tax benefits. Future projections estimate an addition of approximately 350 million new mobile subscribers from 2005-06 to 2010-11 and over 450 million from 2010-11 to 2015-16.