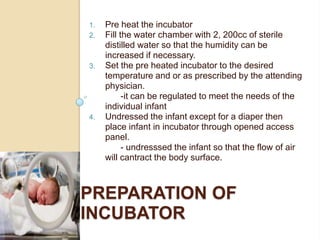
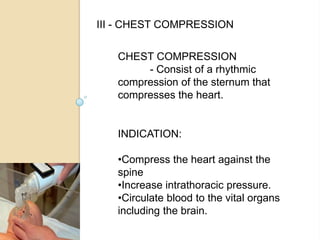
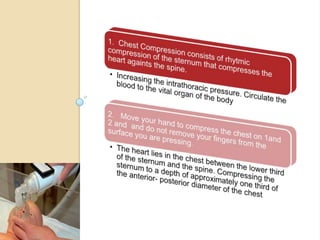
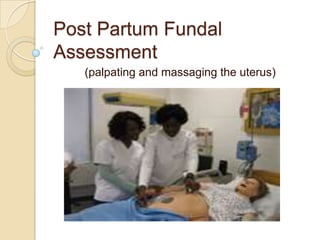
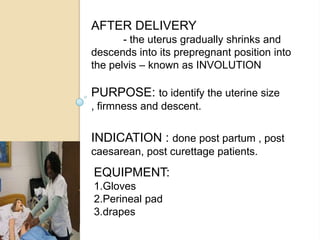
An incubator is a heated and humidified apparatus used to maintain an appropriate environmental temperature for newborn infants, especially those who are premature or sick. It allows close monitoring and helps regulate an infant's temperature. To use an incubator, it is first pre-heated to the desired temperature as prescribed by the physician. The undressed infant is then placed inside and the temperature is monitored hourly and compared to the infant's axillary or rectal temperature. Any abnormal temperatures should be reported.