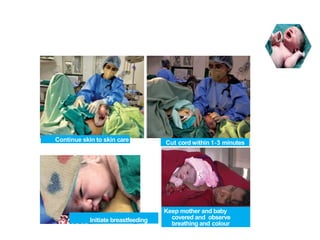
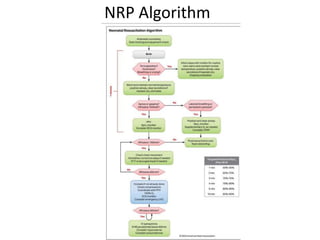
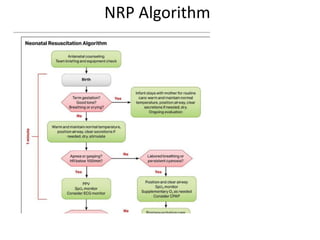
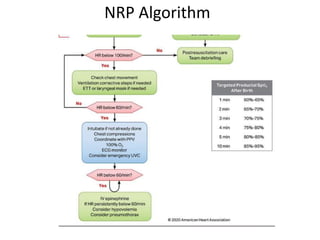
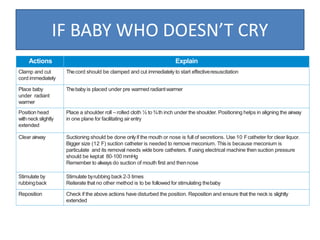
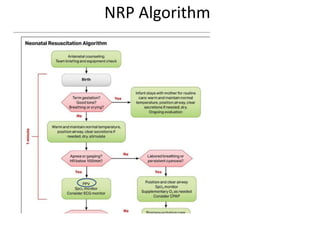
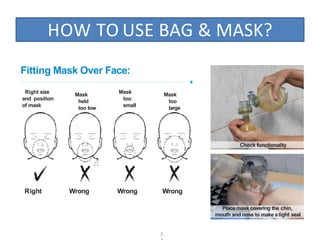
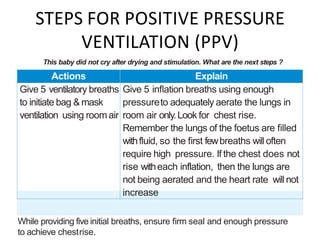
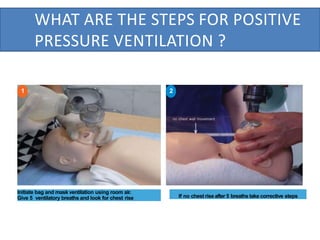
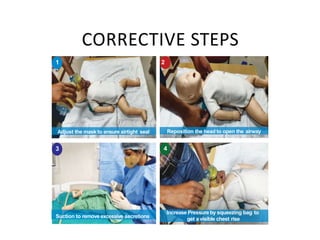
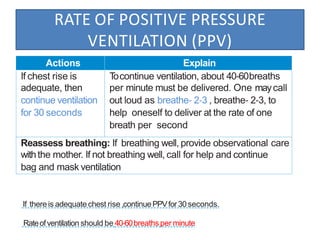
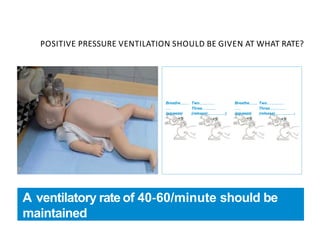
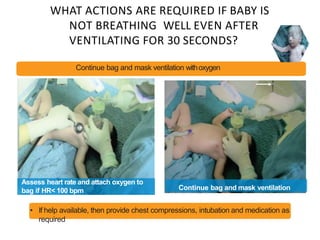
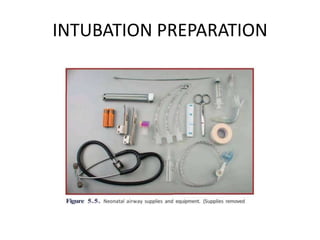
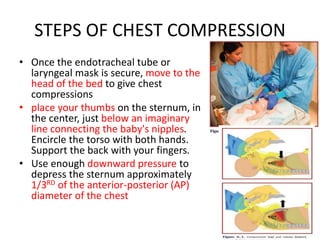
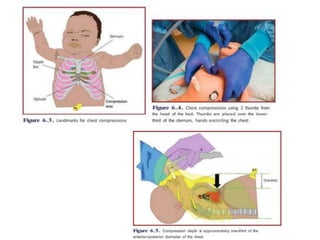
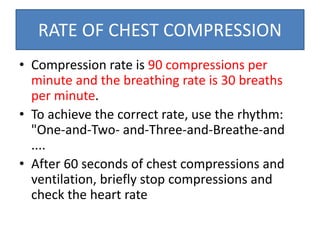
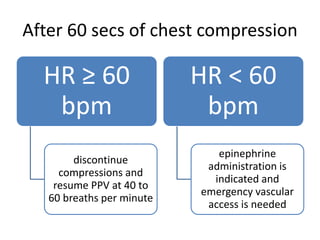
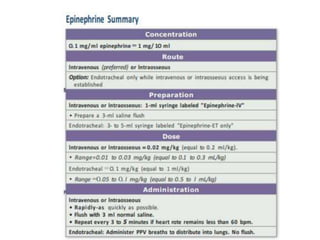
The document outlines key aspects of basic neonatal resuscitation including preparation for delivery, routine care, and emergency procedures. It emphasizes the importance of having a skilled attendant present, maintaining room temperature, and following strict infection prevention protocols to ensure the newborn's survival. The document also details specific actions to be taken during birth, resuscitation techniques, and the appropriate use of medications.