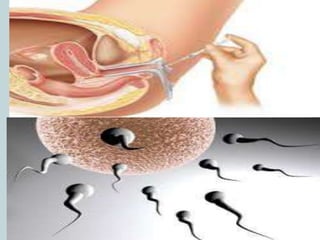
This document summarizes cryopreservation techniques for sperm banking and artificial insemination. It discusses how cryopreservation involves freezing biological material like sperm at ultra-low temperatures to preserve it using cryoprotectants like glycerol. Sperm banking involves collecting and storing frozen semen for future artificial insemination procedures to aid fertility. Artificial insemination is then described as the process of using a catheter to inject preserved sperm into the female's reproductive tract to facilitate conception.