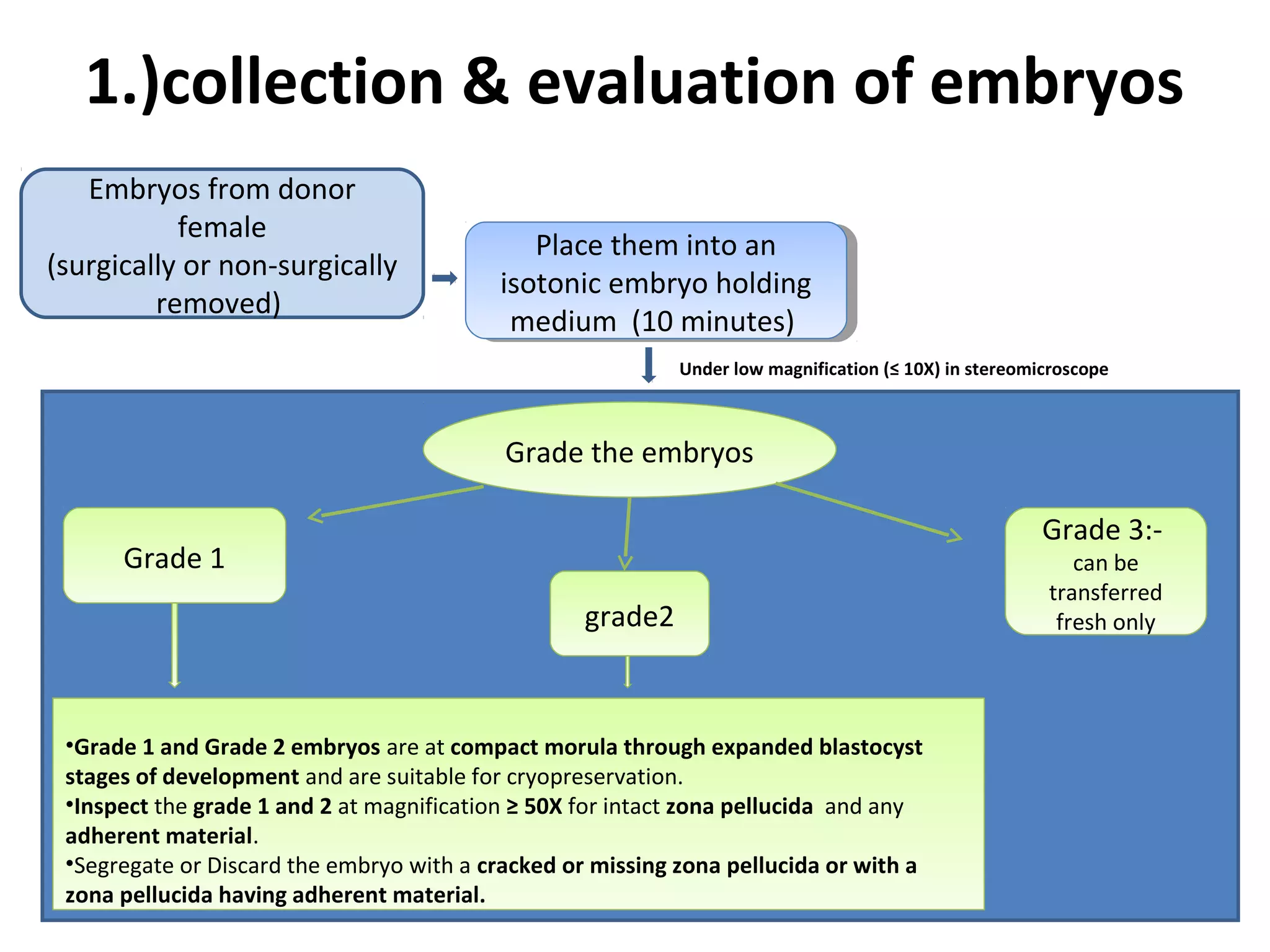
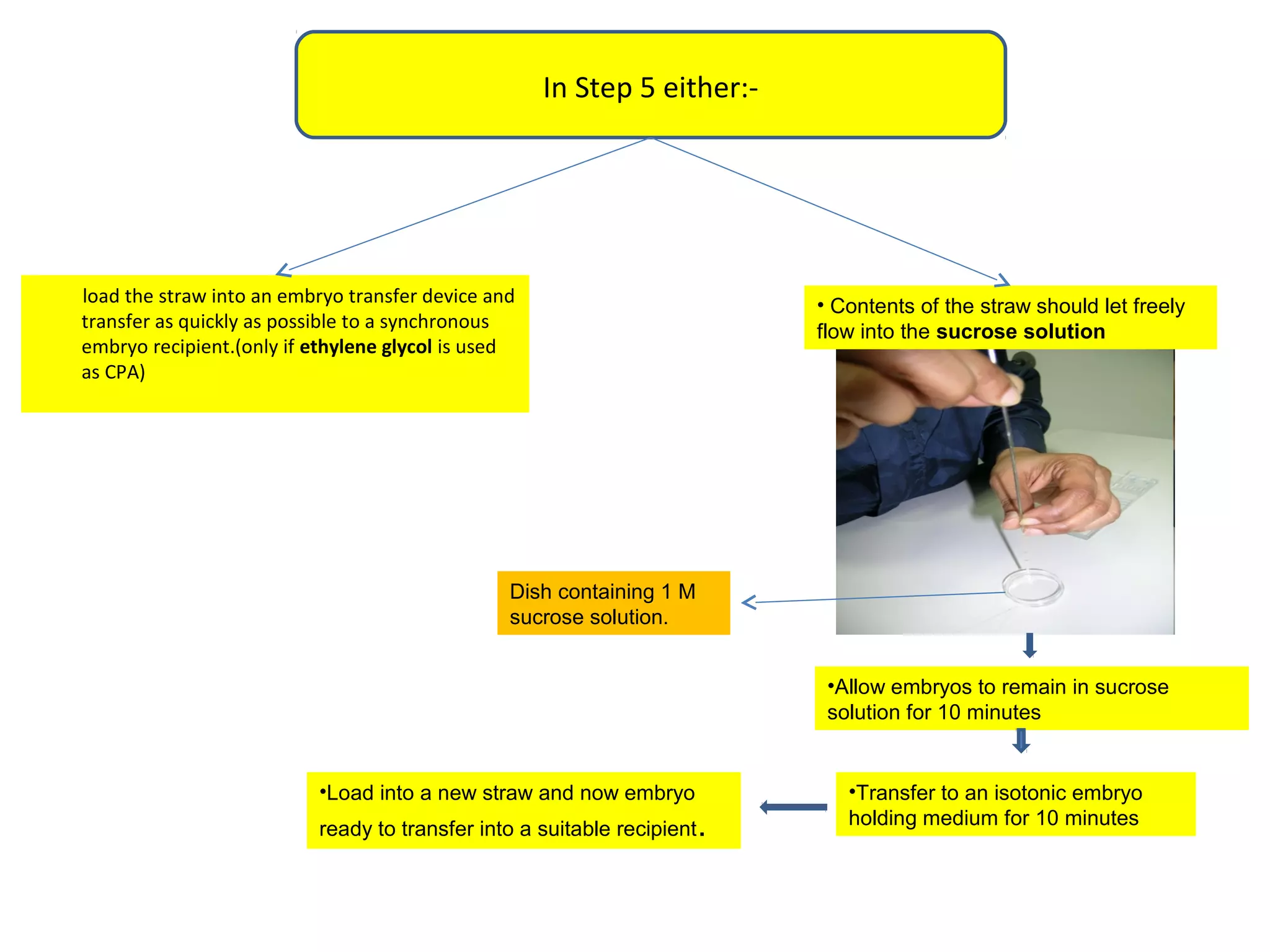
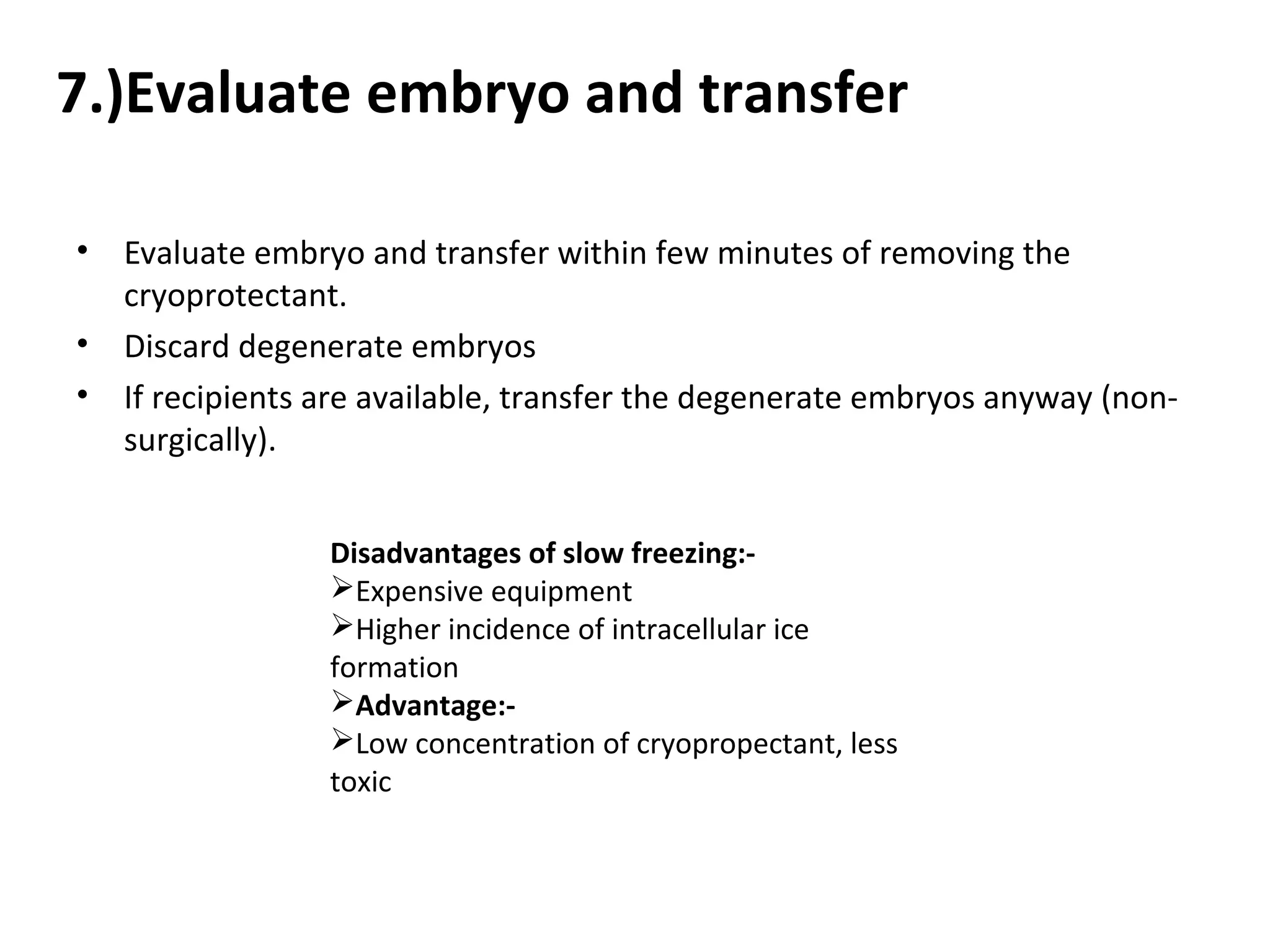
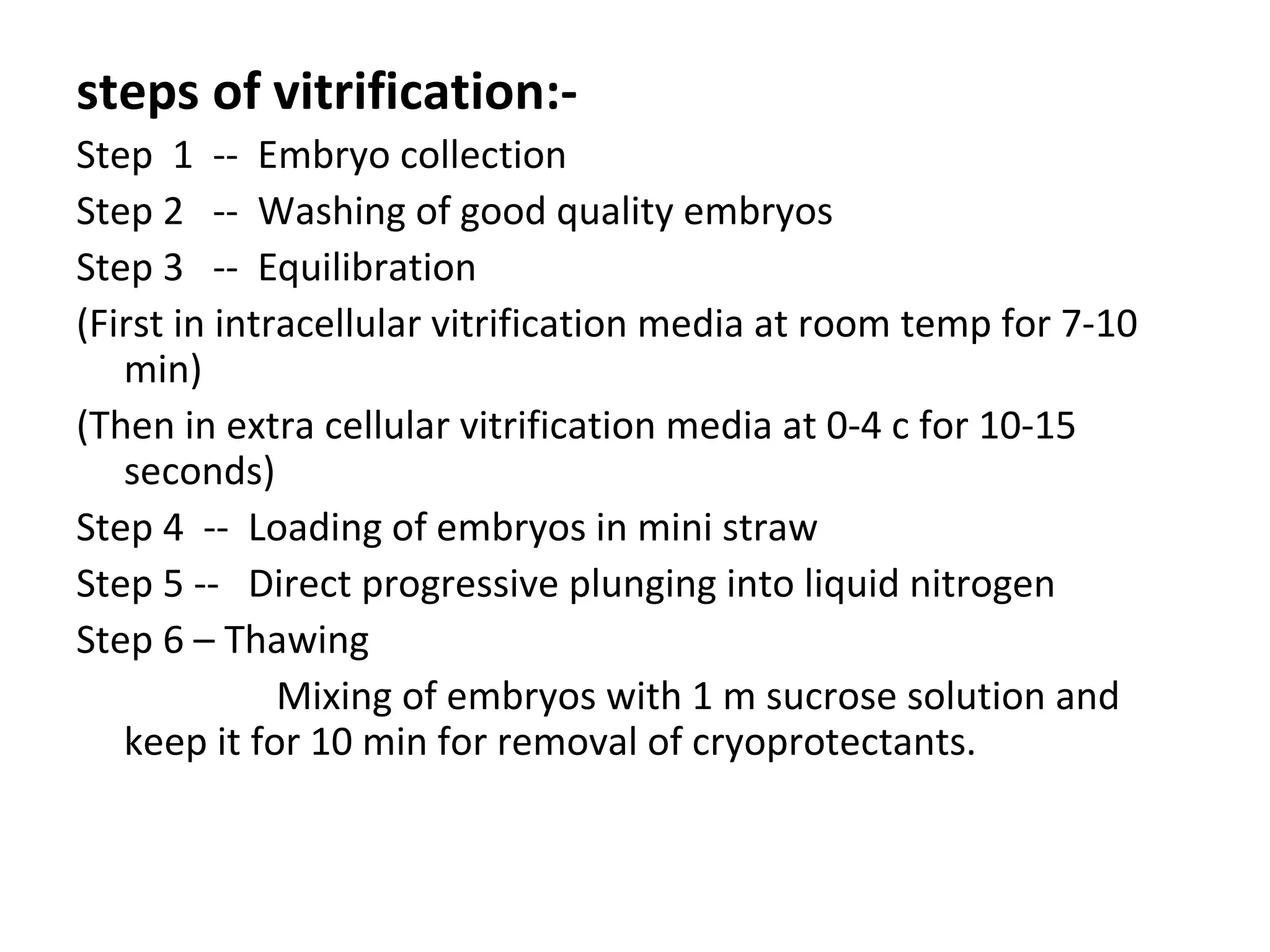
Embryo freezing involves preserving embryos at sub-zero temperatures, usually before implantation. There are two main methods - controlled rate freezing and vitrification. Controlled rate freezing involves slow cooling and seeding to prevent ice crystal formation, while vitrification solidifies the solution without any ice crystals using high concentrations of cryoprotectants. Both aim to minimize damage to embryos from freezing and thawing. Cryopreservation allows storage of surplus embryos and avoids multiple pregnancies from single retrievals. It also enables disease screening before transfer.