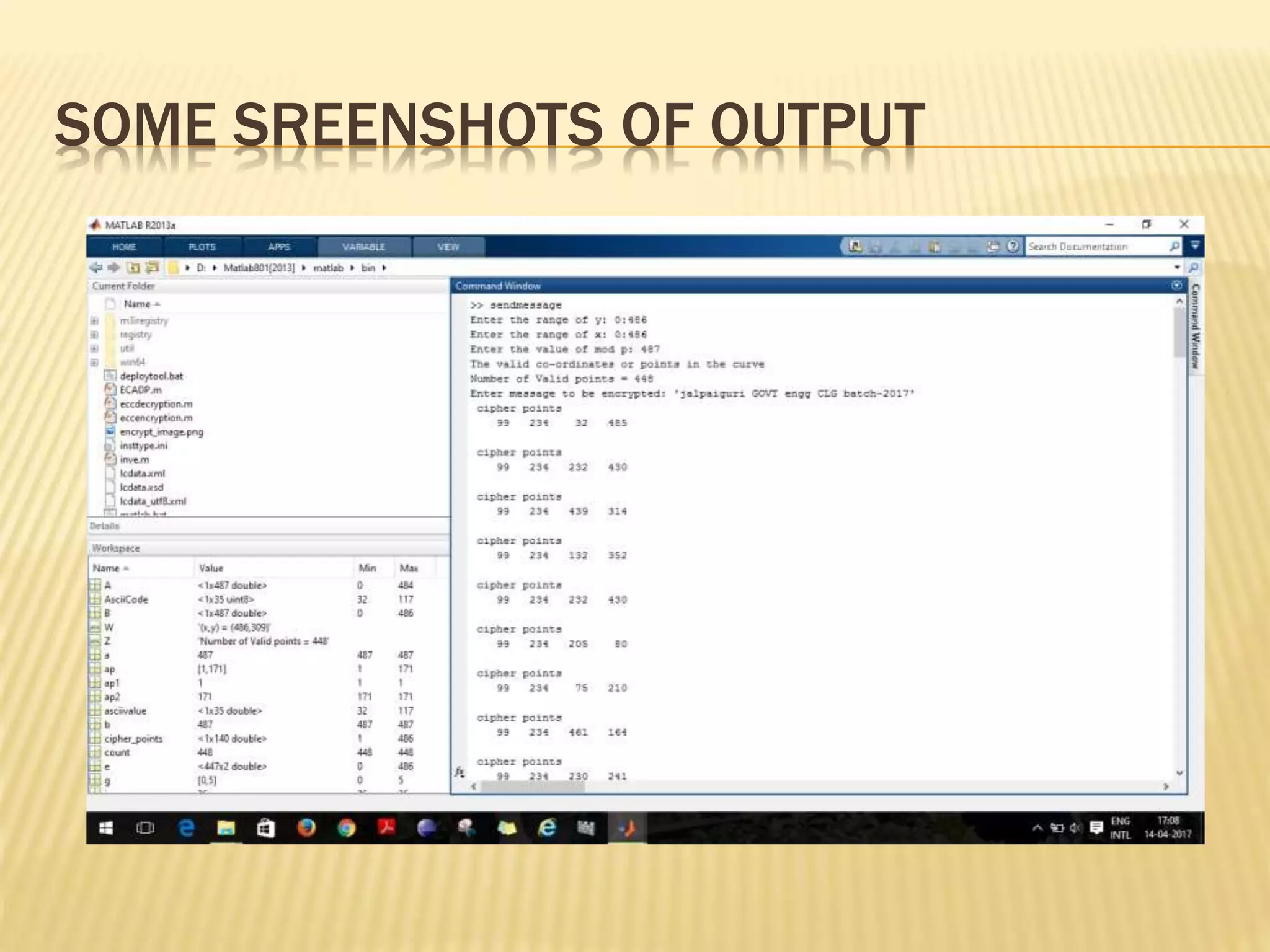
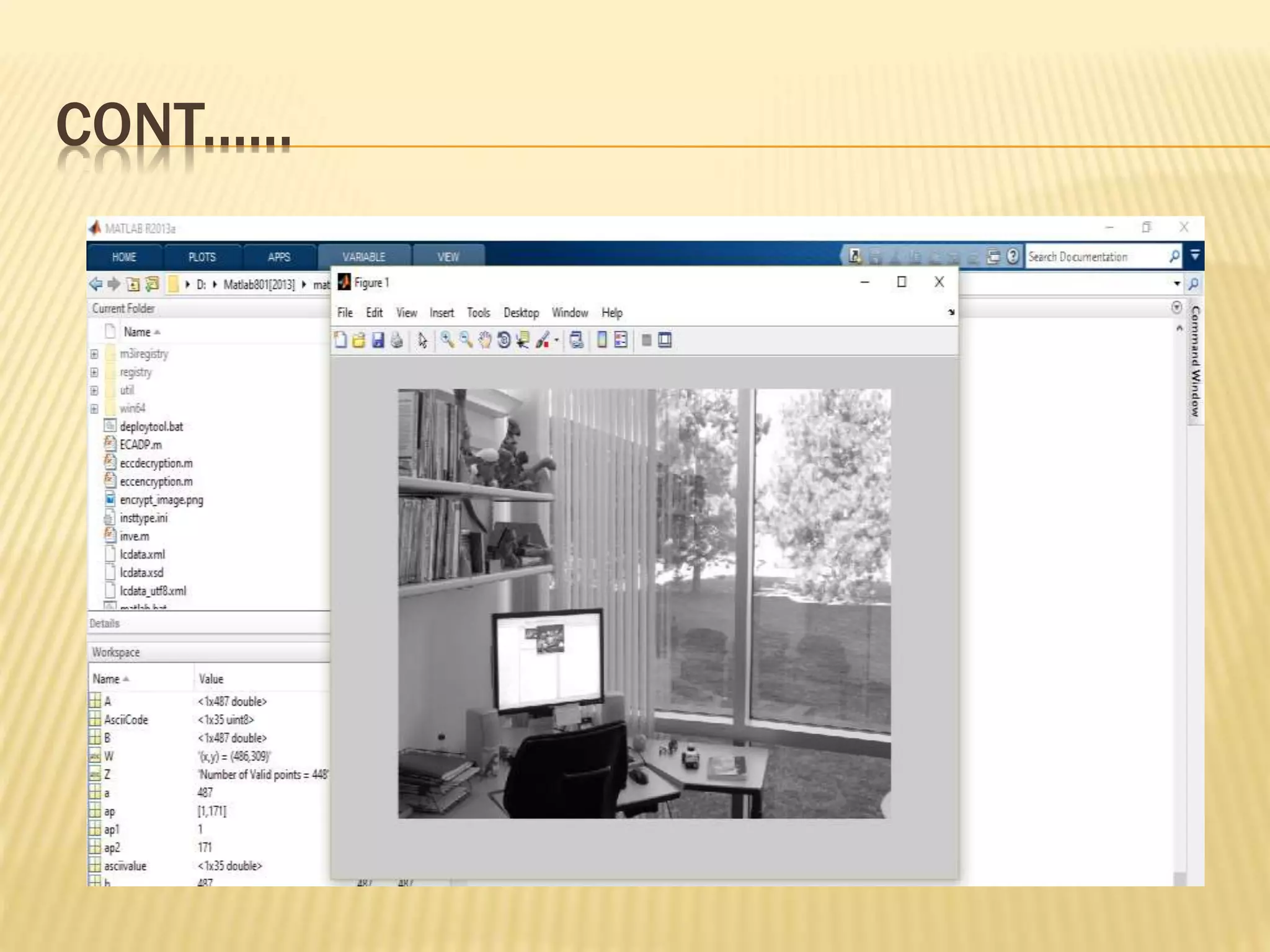
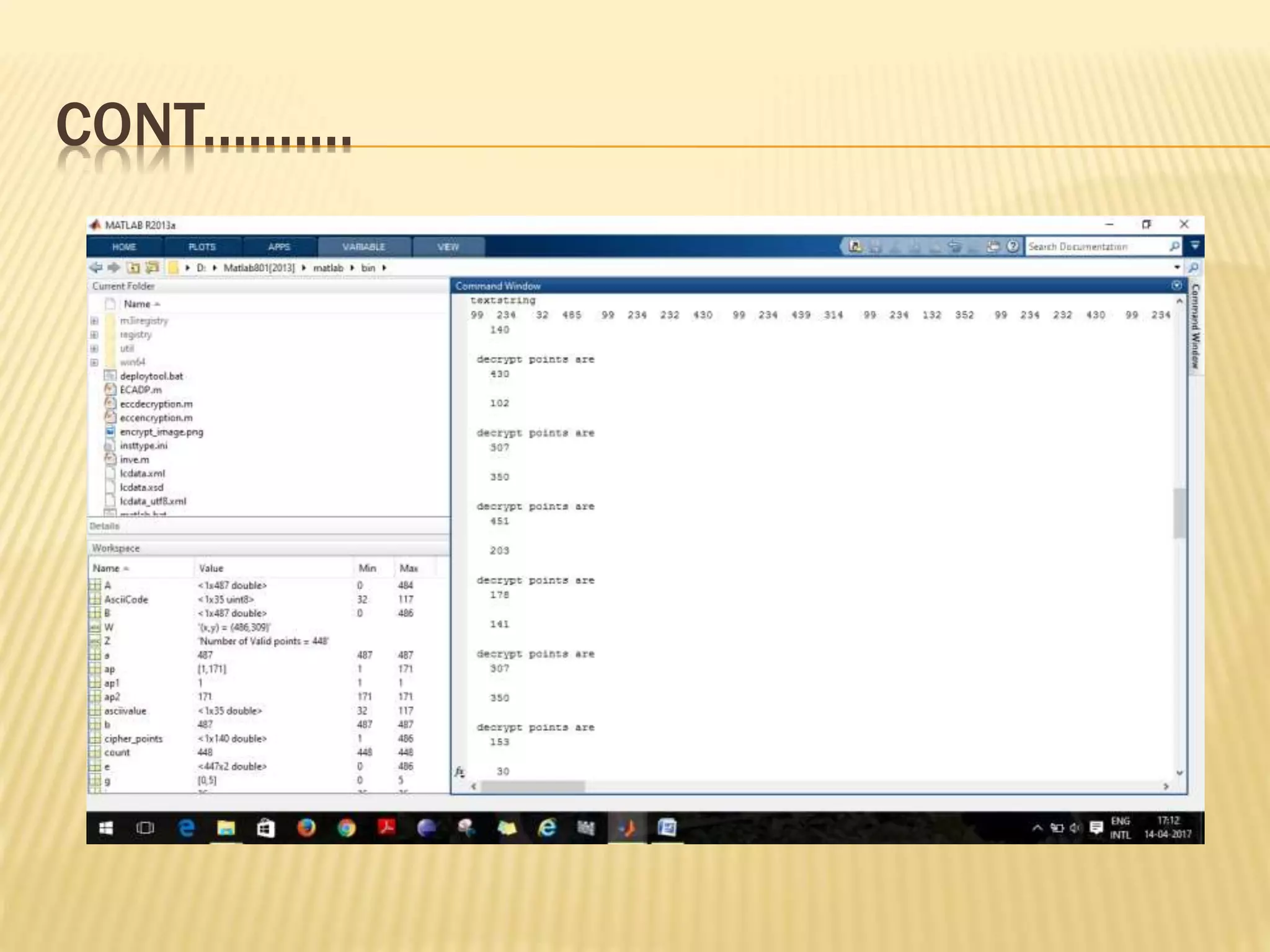
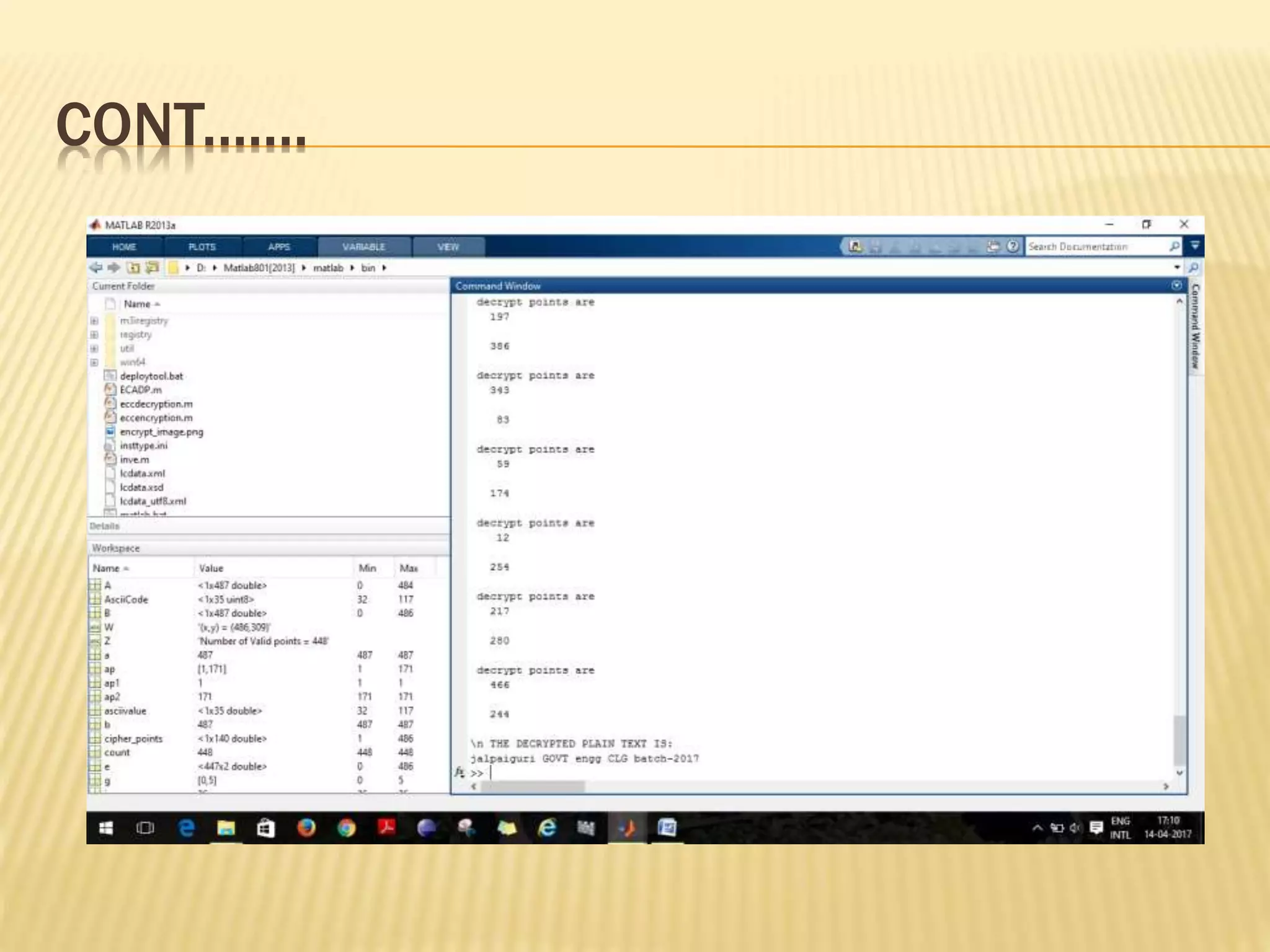
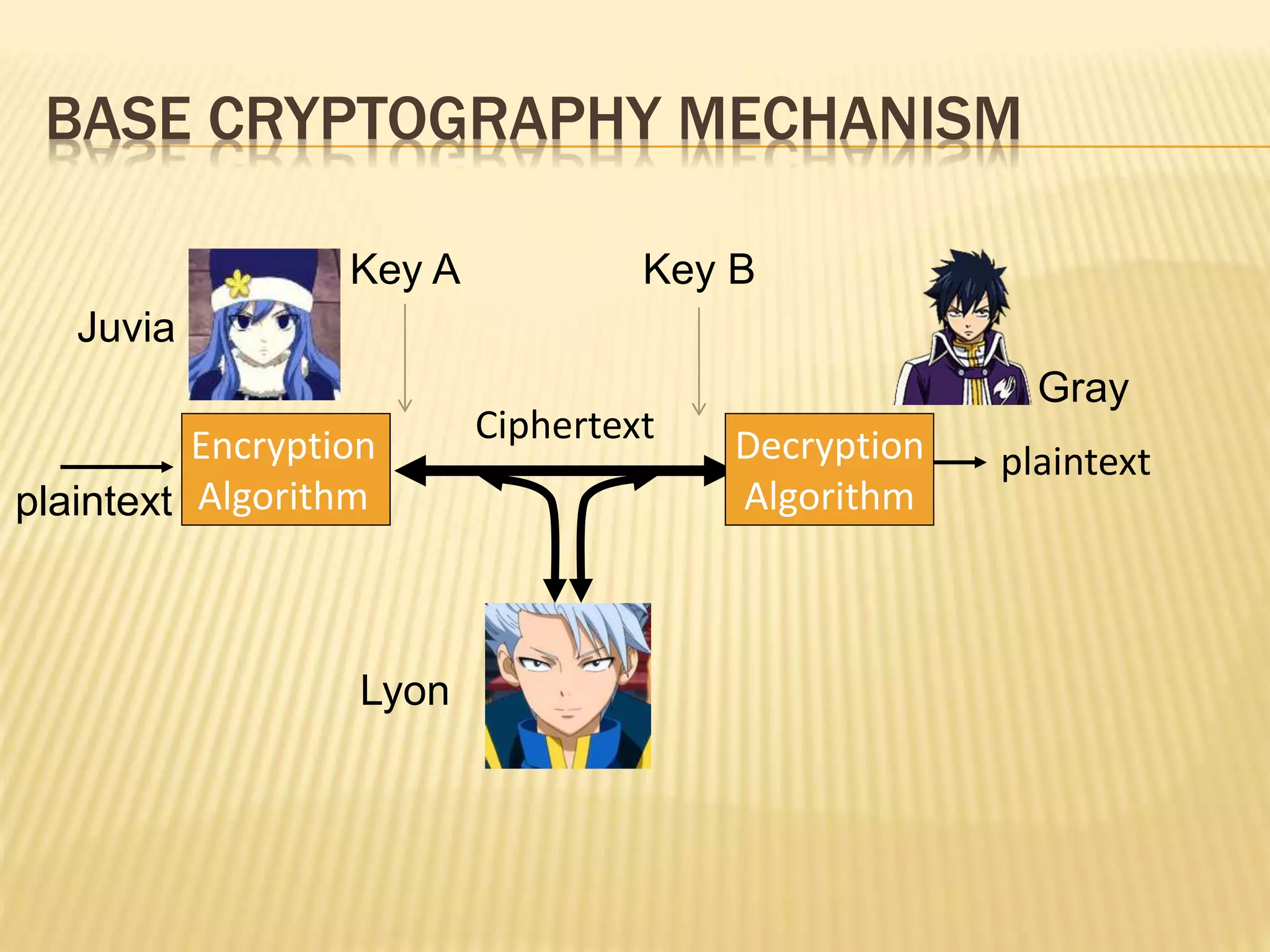
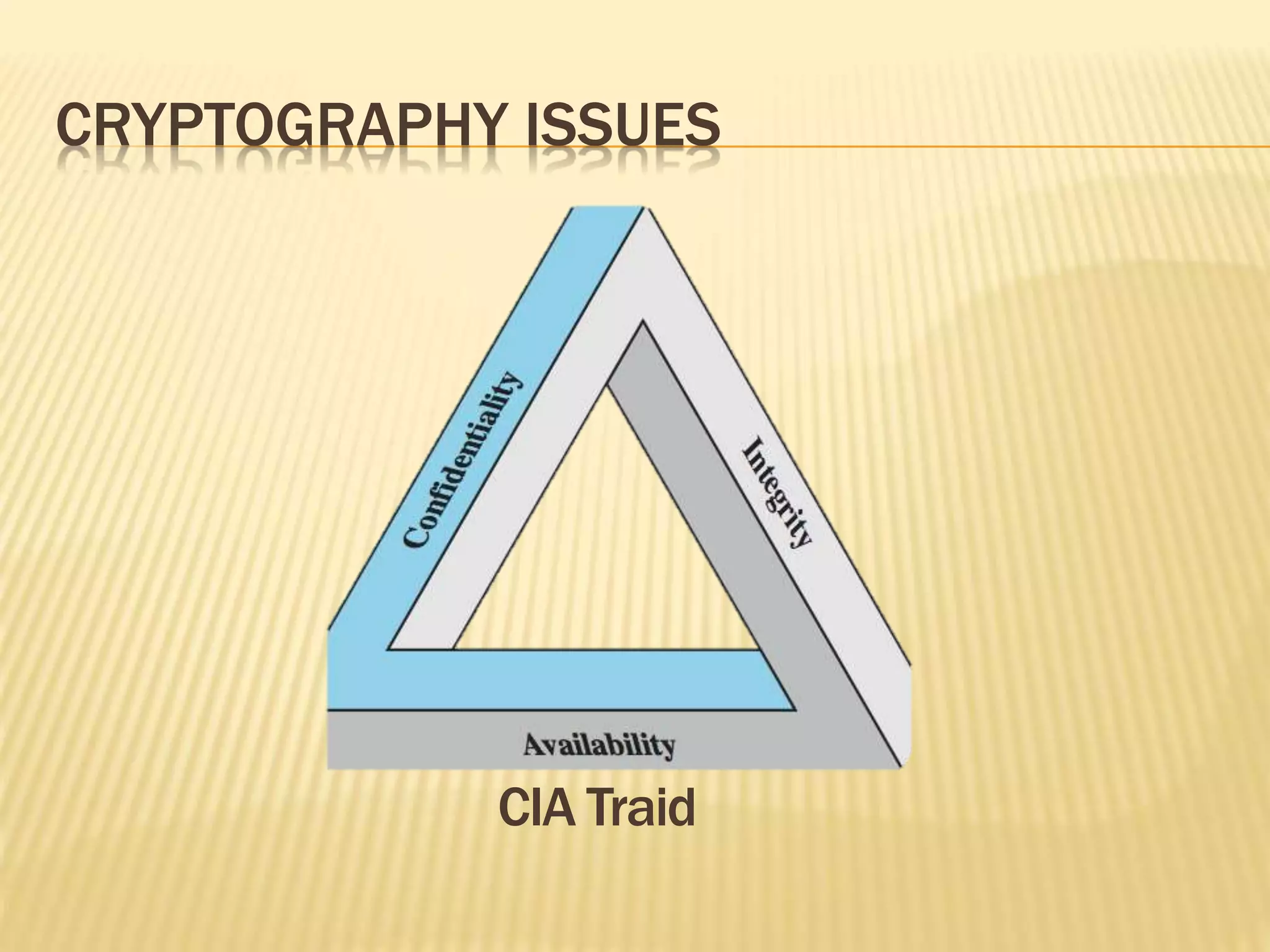
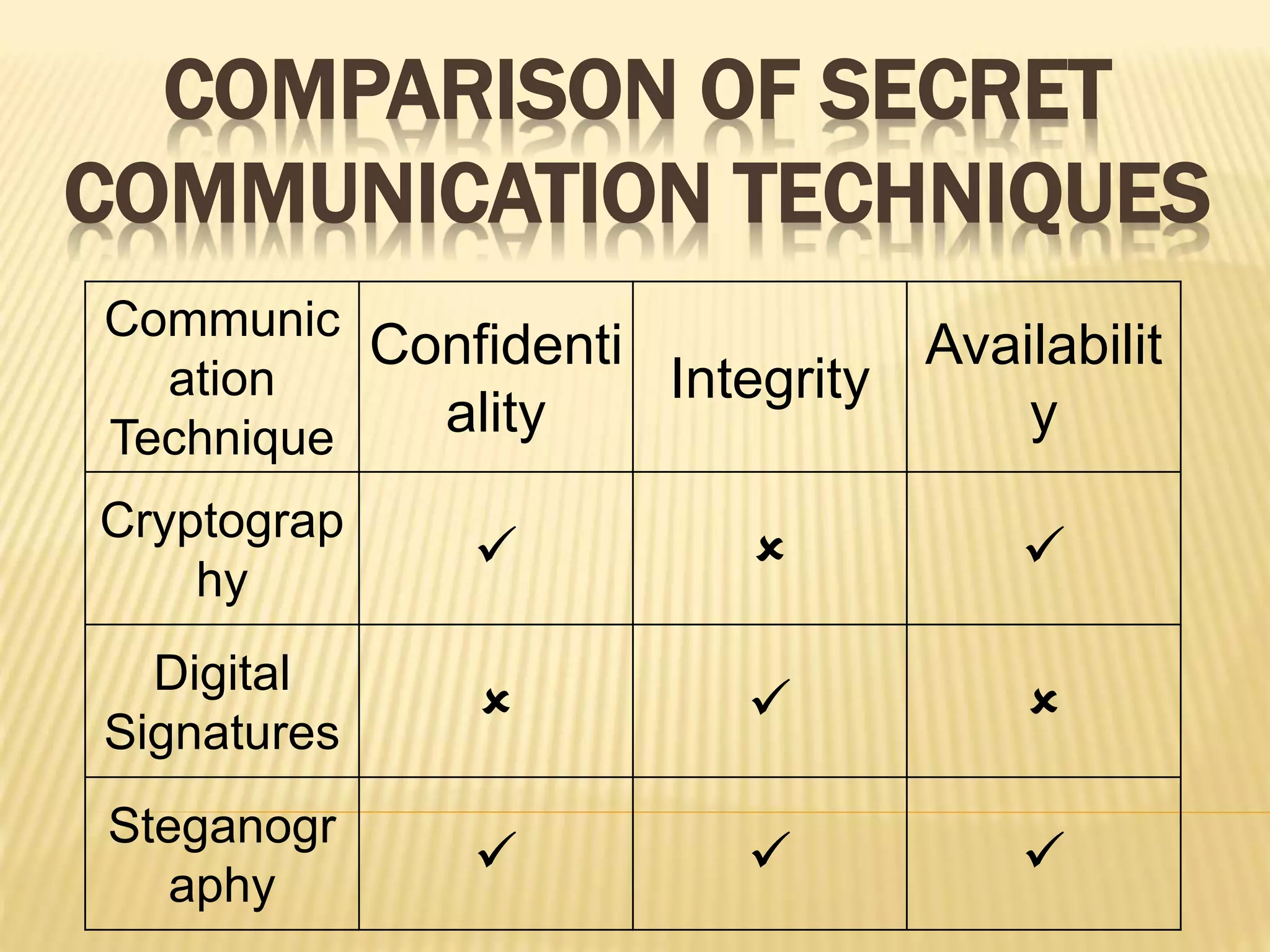
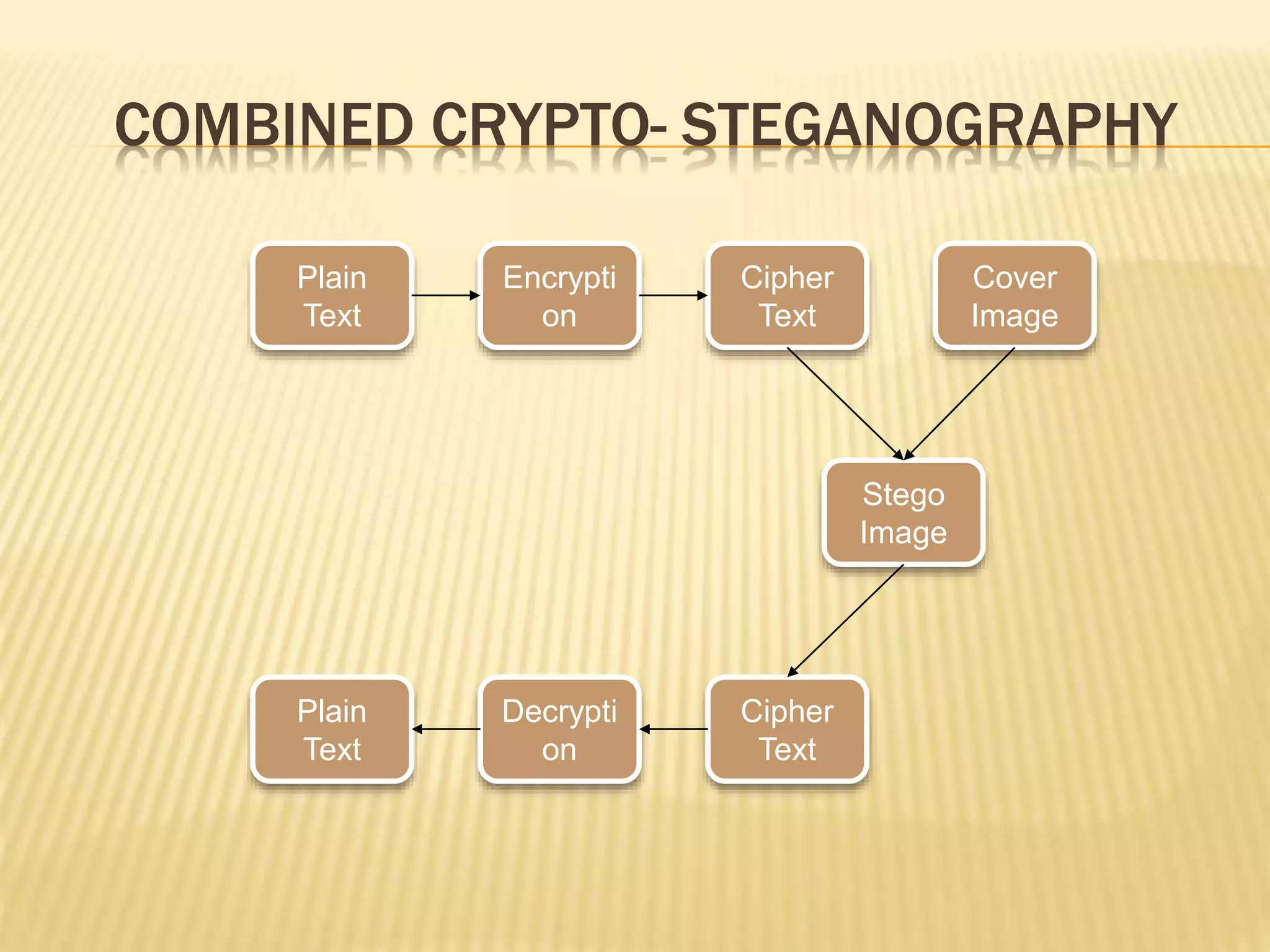
The document discusses an improved security system utilizing steganography and elliptic curve cryptography to ensure secure data transmission over networks, addressing the growing need for data protection from unauthorized access. It outlines key cryptographic concepts, techniques for image steganography, and proposes a combined approach to enhance security through dual methods of encryption and data concealment. The conclusion emphasizes the effectiveness of the model for secure communications in sensitive fields such as defense, banking, and government operations.







![PROPOSED ECC TECHNIQUE
A general Elliptic Curve equation takes the general form:
Yˆ2= xˆ3+ ax + b ………………(1)
(x, y) = co-ordinates on the EC.
a, b = coefficients
However for finite fields a modified equation is used [5]:
yˆ2 mod p = (xˆ3+ax + b) mod p (2)
where p = prime number for which the EC be defined
a, b satisfy the equation [2]
(4a3+ 27b2 ) mod p ≠ 0 mod p ………………… (3)
An elliptic curve E over GF (p) consist of the solutions (x, y) defined
by (1) and (2), along with an additional element
called 0, which is the point of EC at infinity. The set of points (x, y)
are said to be affine coordinate point representation.
The basic operations on elliptic curves are addition and doubling. A
scalar multiplication with a point can be
represented as a combination of addition operations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/improvedsecuritysystemusingsteganographyandellipticcurvecryptography-170420070611/75/Improved-security-system-using-steganography-and-elliptic-curve-cryptography-10-2048.jpg)
![CONT.............
Say, given a point P (x, y) is to be multiplied k times, say k = 37. Thus we have
to calculate 37P.
In terms of addition it can be represented as
37P = P + P + P +… + P (37 times)
For addition of two points P(x1, y1) & Q(x2, y2). First calculate the tangent to
the curve at point P [5].
L = [(y2- y1)/(x2-x1)] mod p, for x1 ≠ x2 (4)
L = [(3x1ˆ2+ a)/ 2yP] mod p, for x1 = x2 (5)
P+Q = R
x3 = (L2 - x1 - x2) mod p
y3 = (L (x1 - x3) –y2] mod p
where Q = (x2, y2) = co-ordinates of Q change with every addition method
applied, i.e. after first addition its co-ordinates
will be (x3, y3), and so on.
L = tangent to the curve at point P.
R = (x3, y3), resultant co-ordinates
Thus applying addition methods, determined by the value of ‗k‘, we obtain
point R (x3, y3). Each point thus obtained
is also an affine point on the Elliptic Curve.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/improvedsecuritysystemusingsteganographyandellipticcurvecryptography-170420070611/75/Improved-security-system-using-steganography-and-elliptic-curve-cryptography-11-2048.jpg)
![EXAMPLE – ELLIPTIC CURVE CRYPTOSYSTEM
• Suppose Alice wants to send to Bob an encrypted message.
– Both agree on a base point, B.
– Alice and Bob create public/private keys.
• Alice
– Private Key = a
– Public Key = PA = a * B
• Bob
– Private Key = b
– Public Key = PB = b * B
– Alice takes plaintext message, M, and encodes it onto a point, PM, from the
elliptic group.
Alice chooses another random integer, k from the interval [1, p-1]
– The ciphertext is a pair of points
• PC = [ (kB), (PM + kPB) ]
– To decrypt, Bob computes the product of the first point from PC and his private
key, b
• b * (kB)
– Bob then takes this product and subtracts it from the second point from PC
• (PM + kPB) – [b(kB)] = PM + k(bB) – b(kB) = PM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/improvedsecuritysystemusingsteganographyandellipticcurvecryptography-170420070611/75/Improved-security-system-using-steganography-and-elliptic-curve-cryptography-12-2048.jpg)



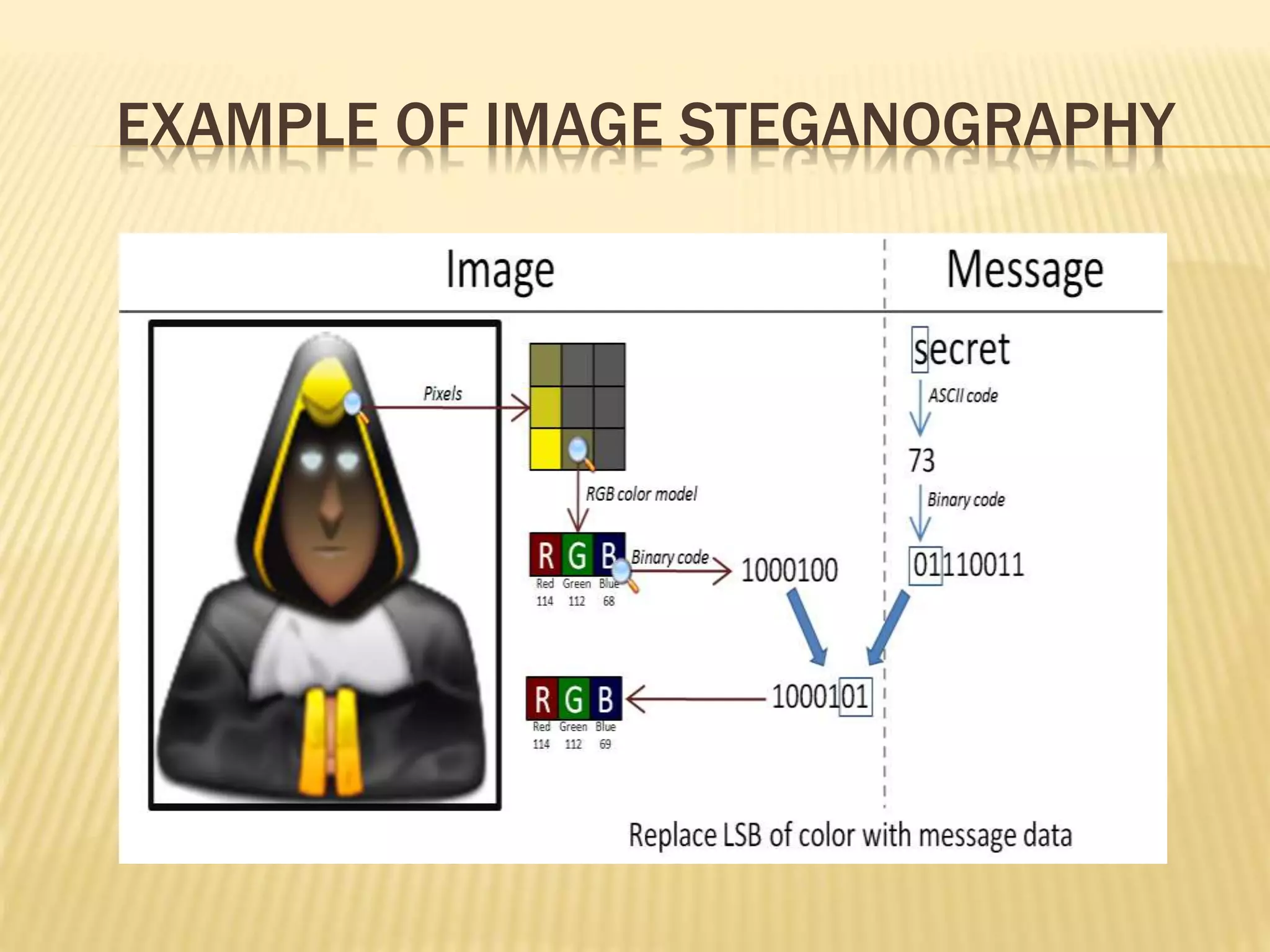
![LSB [LEAST SIGNIFICANT
BIT] METHOD
Least significant bit (LSB) insertion is a common, simple
approach to embedding information in a cover image
The least significant bit (in other words, the 8th bit) of some or
all of the bytes inside an image is changed to a bit of the secret
message
When using a 24-bit image, a bit of each of the red, green and
blue color components can be used, since they are each
represented by a byte. In other words, one can store 3 bits in
each pixel. An 800 × 600 pixel image, can thus store a total
amount of 1,440,000 bits or 180,000 bytes of embedded data
In its simplest form, LSB makes use of BMP images, since
they use lossless compression](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/improvedsecuritysystemusingsteganographyandellipticcurvecryptography-170420070611/75/Improved-security-system-using-steganography-and-elliptic-curve-cryptography-16-2048.jpg)
![ENCRYPTION AND LSB EMBEDDING
INPUT: Elliptic Curve Domain parameters (p, E, P, n),
public key Q, Plaintext m, message image I, Cover
image C. OUTPUT: Stego-image CI, Stego key
1. Represent the message ‘m’ as a point M in E (𝐹𝑝).
2. Select K ∈𝑅[1, n-1].
3. Compute 𝐶1=k×𝑒1(𝑥1,𝑦1)
4. Compute 𝐶2= M +k×𝑒2(𝑥2,𝑦2).
5. RGB cover image=C.
6. Hide (C1, C2) into I using LSB Steganography.
7. Hide I into C using Steganography.
8. Return (CI)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/improvedsecuritysystemusingsteganographyandellipticcurvecryptography-170420070611/75/Improved-security-system-using-steganography-and-elliptic-curve-cryptography-20-2048.jpg)