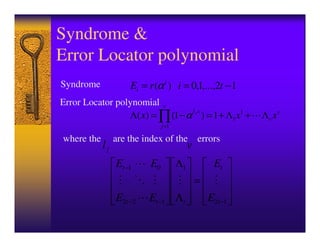
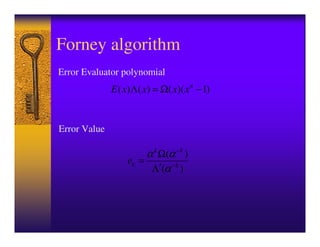
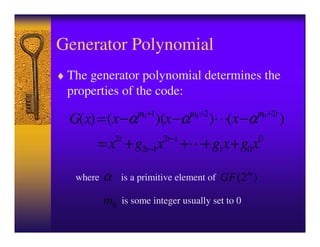
This document introduces Reed-Solomon codes. It describes Reed-Solomon codes as word-oriented, non-binary BCH codes that are simple, robust, and perform well for burst errors. It explains that a Reed-Solomon code block length is N=2m-1, with a capacity to correct t errors using 2t parity check words. The document outlines the generator polynomial, encoding, decoding procedures including syndrome calculation, Berlekamp-Massey algorithm, Chien search, and Forney algorithm. It concludes with potential future tasks related to Reed-Solomon codes.


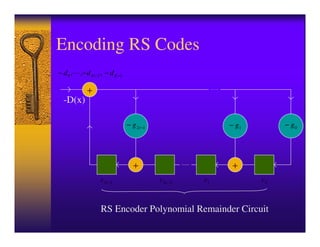
![Encoding RS Codes
C ( x) = D( x) ⋅ x 2t − [ D( x) ⋅ x 2t mod G ( x)]
where C(x) is the transmitted codeword polynomial, of
degree N-1
D(x) is the user data polynomial, of degree K-1
G(x) is the generator polynomial of the code, of
degree 2t
and N – K = 2t
d K −1 d K − 2 d1 d0 c2t −1 c2t − 2 c1 c0
User Data Parity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13642983-120715025646-phpapp01/85/IntrRSCode-4-320.jpg)