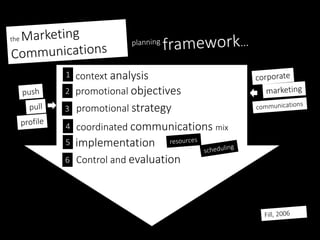
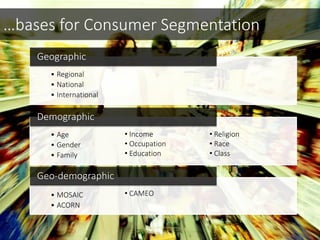
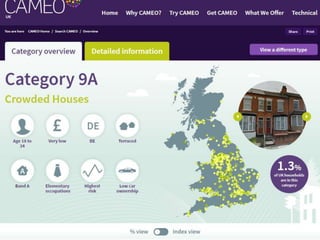
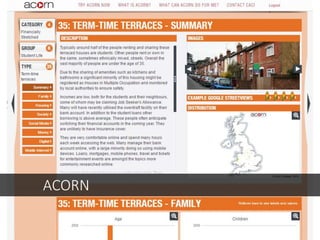
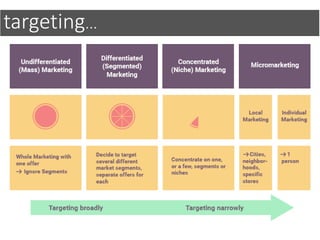
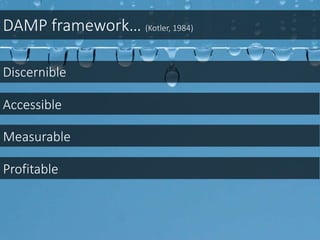
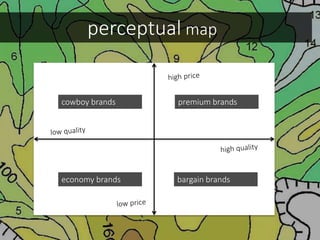
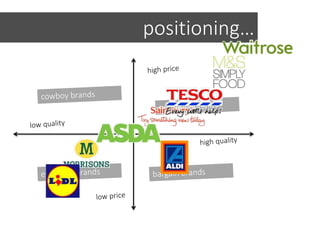
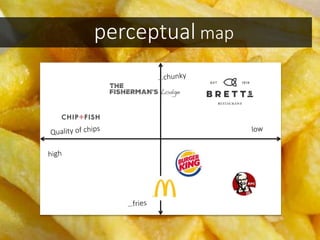
This document discusses integrated marketing communications and key concepts such as segmentation, targeting, positioning, and establishing communications objectives. It emphasizes that communications objectives should support broader business and marketing goals and be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound (SMART). Segmentation provides a framework but should avoid stereotyping; targeting depends on market factors and a segment's viability. Positioning focuses products based on features and benefits in relation to competitors.