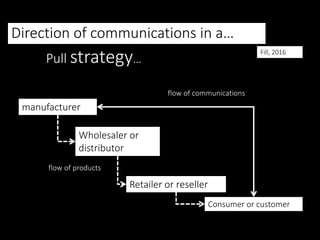
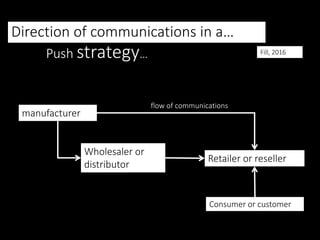
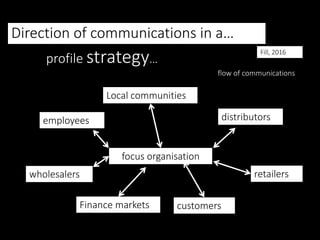
This document discusses integrated marketing communications (IMC) and strategies. There are three main promotional strategies: pull, push, and profile. Pull strategy influences consumers, push influences channel members, and profile influences stakeholders. An ideal IMC plan blends these strategies. IMC requires coordinating communications strategies, resources, and messages to engage audiences meaningfully. Key drivers of IMC include relationship marketing and overcoming barriers like organizational silos. Proper IMC implementation focuses on customers and requires planning communication tactics coherently.