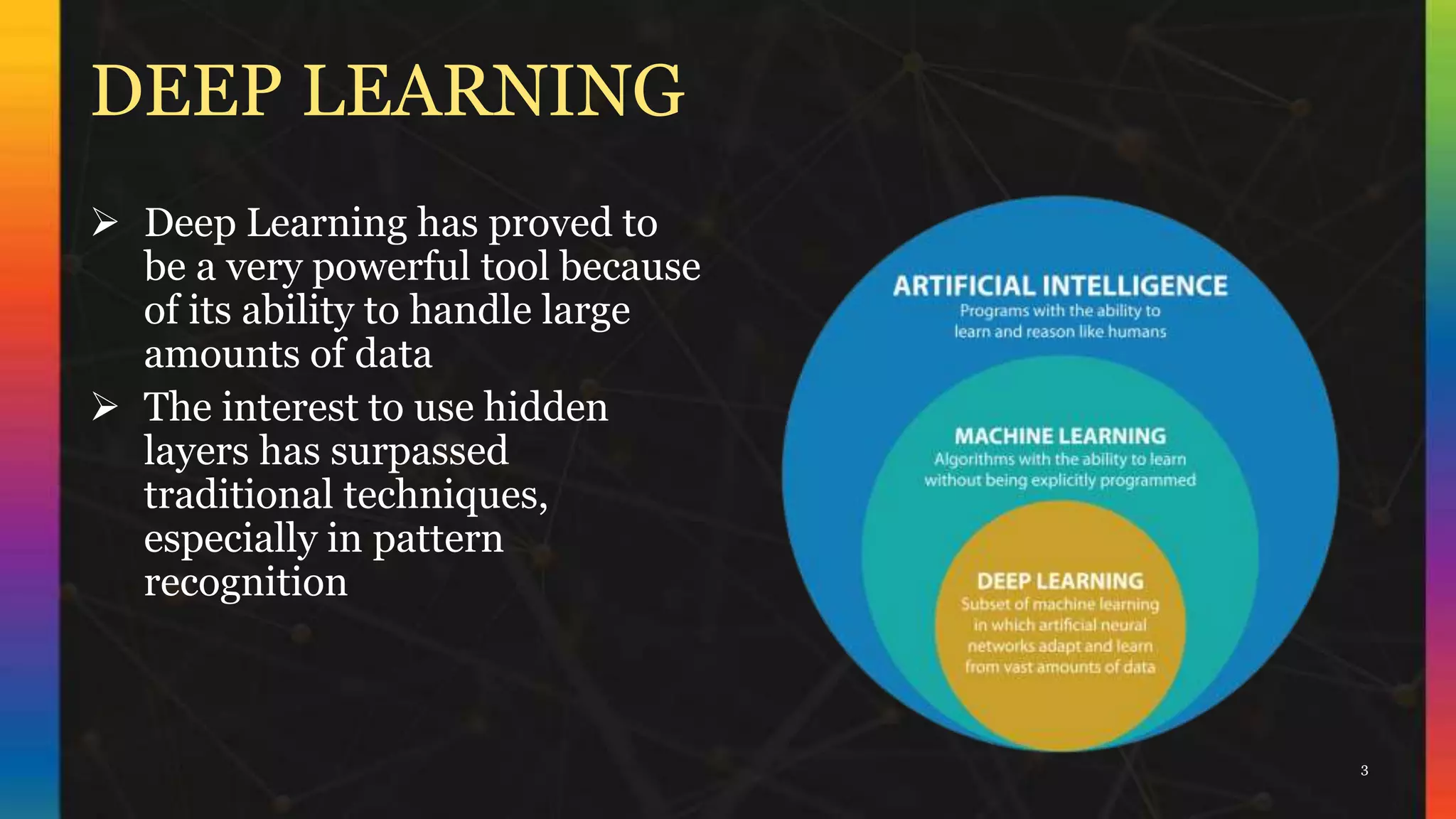
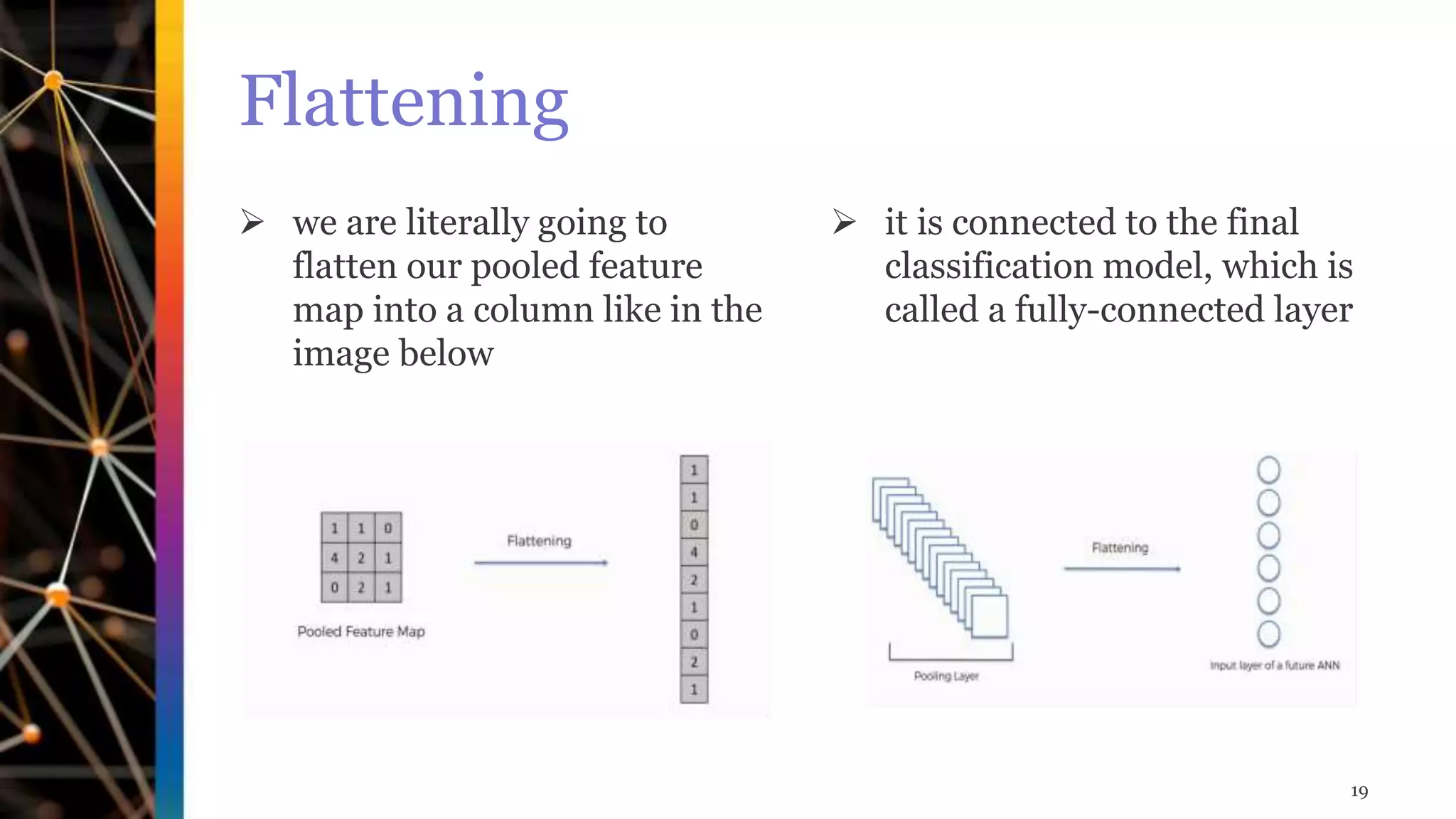
The document discusses Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). It explains that CNNs are a type of neural network that use convolutional operations in at least one layer. CNNs are well-suited for image classification and segmentation problems. The key layers in a CNN are convolutional layers, pooling layers, flattening layers, and fully connected layers. Convolutional layers act as feature extractors, pooling layers reduce spatial size, flattening layers transform pooled features into a vector, and fully connected layers are for classification.