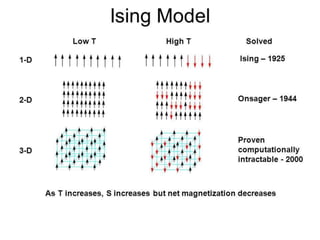
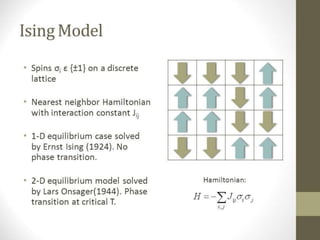
1. The Ising model is a statistical mechanics model of ferromagnetism. It represents magnetic dipole moments as "spins" on a lattice that can point in one of two directions and interact with neighboring spins.
2. The Ising model can explain phase transitions like ferromagnetism, anti-ferromagnetism, gas-liquid transitions, and liquid-solid transitions.
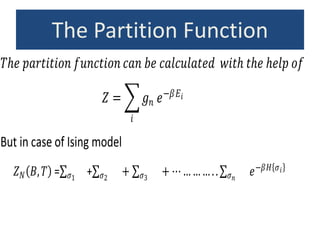
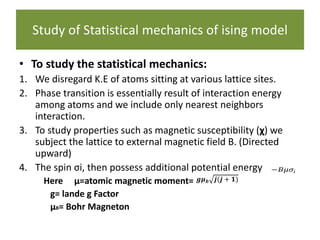
3. The statistical mechanics of the Ising model are studied using the Hamiltonian, which includes terms for spin-spin interaction energy and the energy of an external magnetic field interacting with the magnetic moments. Partition functions are then used to calculate thermodynamic properties.






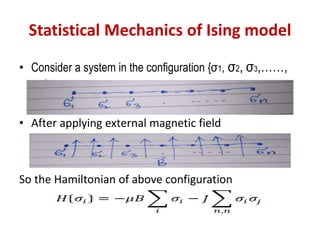

![ if spins are in same direction,
𝜎𝑖 𝜎𝑗 =(1)(1)=1
If spins are in opposite direction, then
𝜎𝑖 𝜎𝑗 =(1)(-1)=-1
The above equation is known as Ising model equation.
•Due to change in magnetic field:
•J is exchange energy/Ising Interaction/ Ising Energy
Exchange interaction occurs between identical particles.
This effect is due to wave function of indistinguishable particles
being subject to exchange symmetry.
It is Quantum mechanical effect.
For the given configuration of N particles
−𝜇𝐵𝜎1+ −𝜇𝐵𝜎2 + −𝜇𝐵𝜎3 … … … . . +(−𝜇𝐵𝜎 𝑛 )
= −𝜇𝐵[𝜎1+ 𝜎2 + 𝜎3 … … … . . +(𝜎 𝑛 )]=−𝜇𝐵 𝜎𝑖
𝑛
𝑖=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isingmodel-200628112548/85/Ising-model-11-320.jpg)