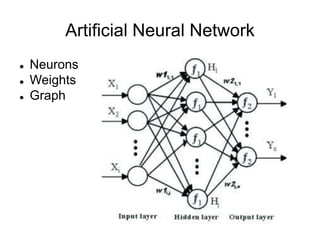
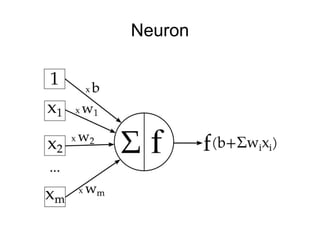
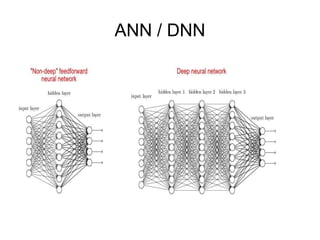
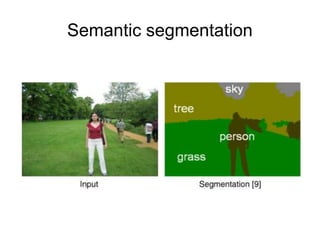
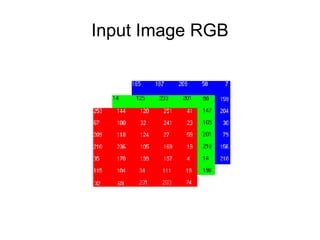
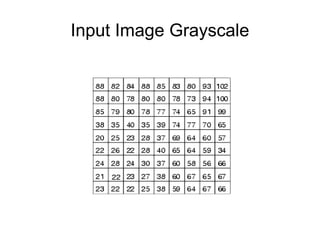
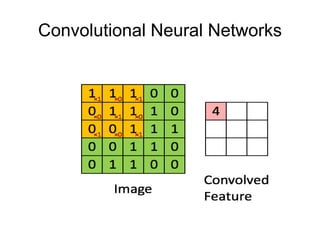
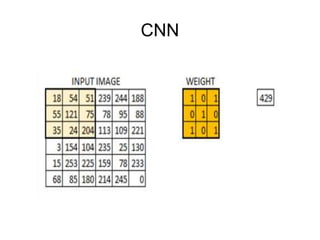
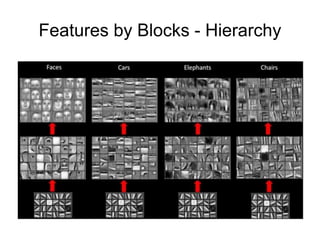
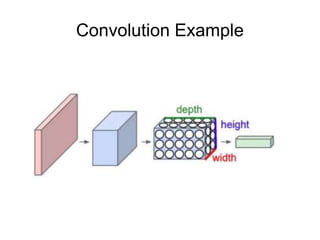
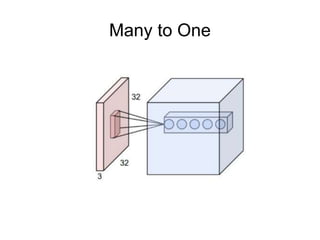
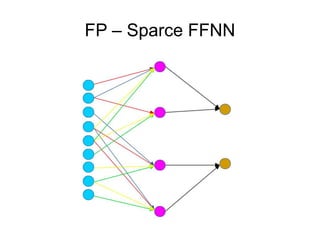
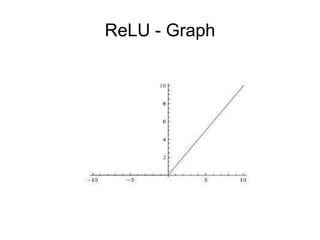
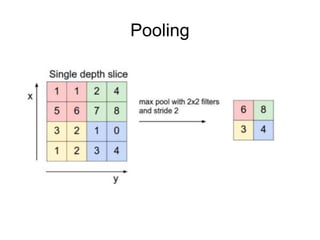
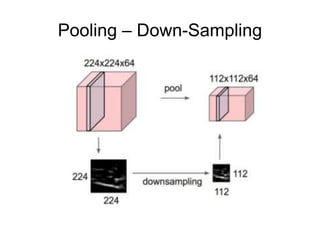
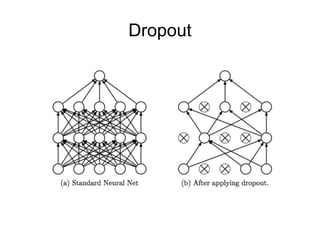
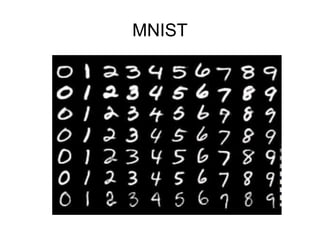
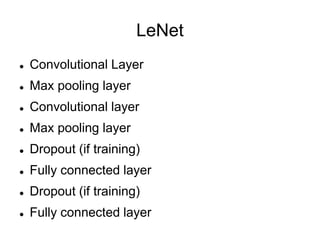
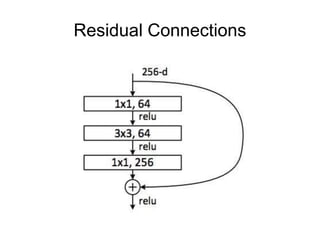
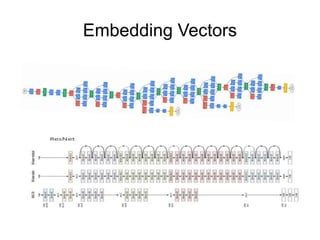
This document provides an overview of deep learning techniques for image analysis using convolutional neural networks (CNNs). It discusses how CNNs use convolutional filters to extract hierarchical features from images and how techniques like pooling, dropout and residual connections improve CNN performance. Practical examples are given on using CNNs for tasks like object recognition, object detection and semantic segmentation on datasets like MNIST and pretrained models like ResNet-18.