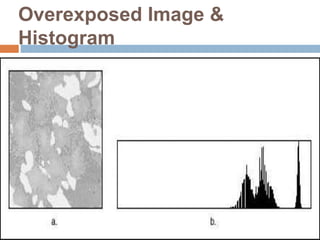
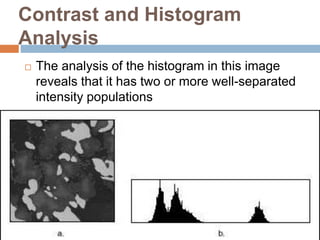
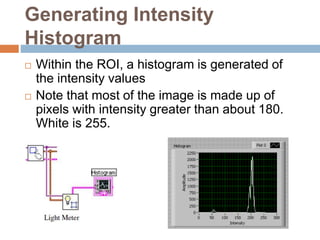
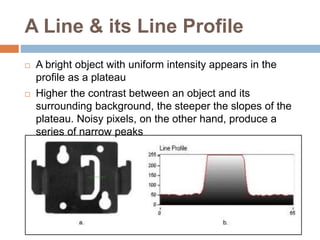
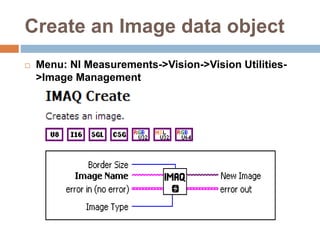
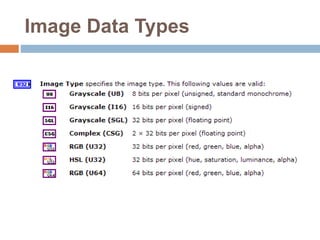
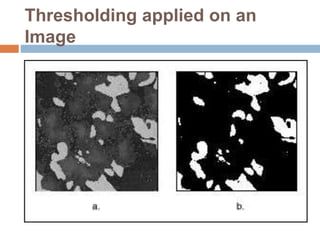
This document provides an overview of image processing and machine vision tools in LabVIEW. It discusses key LabVIEW applications in areas like design, control, and measurement. It then describes tools for reading and analyzing image files in LabVIEW Vision, including functions for acquiring images from cameras and developing simple vision-based measurement systems. The rest of the document outlines various image analysis techniques in LabVIEW like histogram analysis, line profiling, blob analysis, and thresholding; and explains how they can be used for tasks like inspection, object detection, and dimensional measurements.