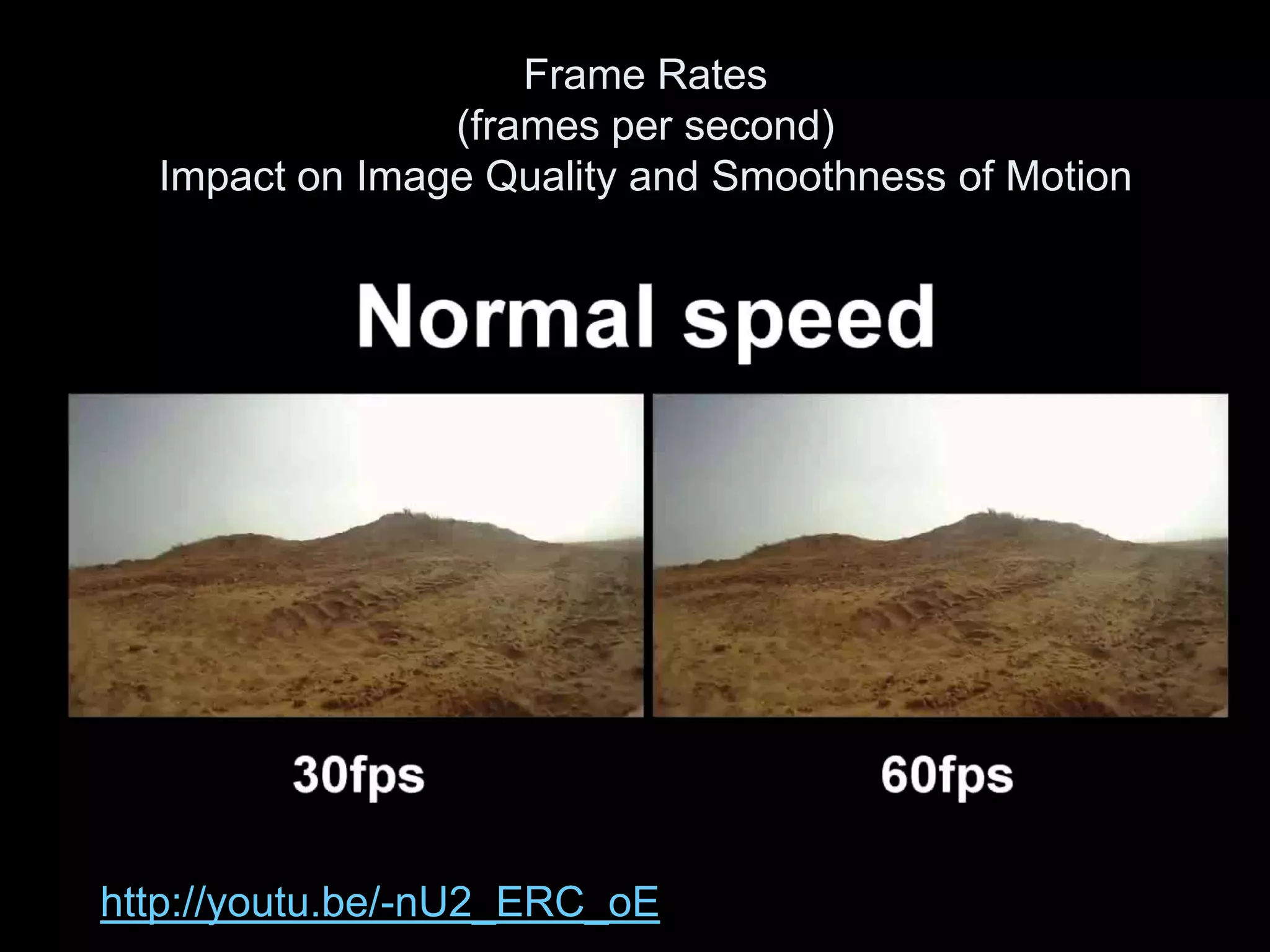
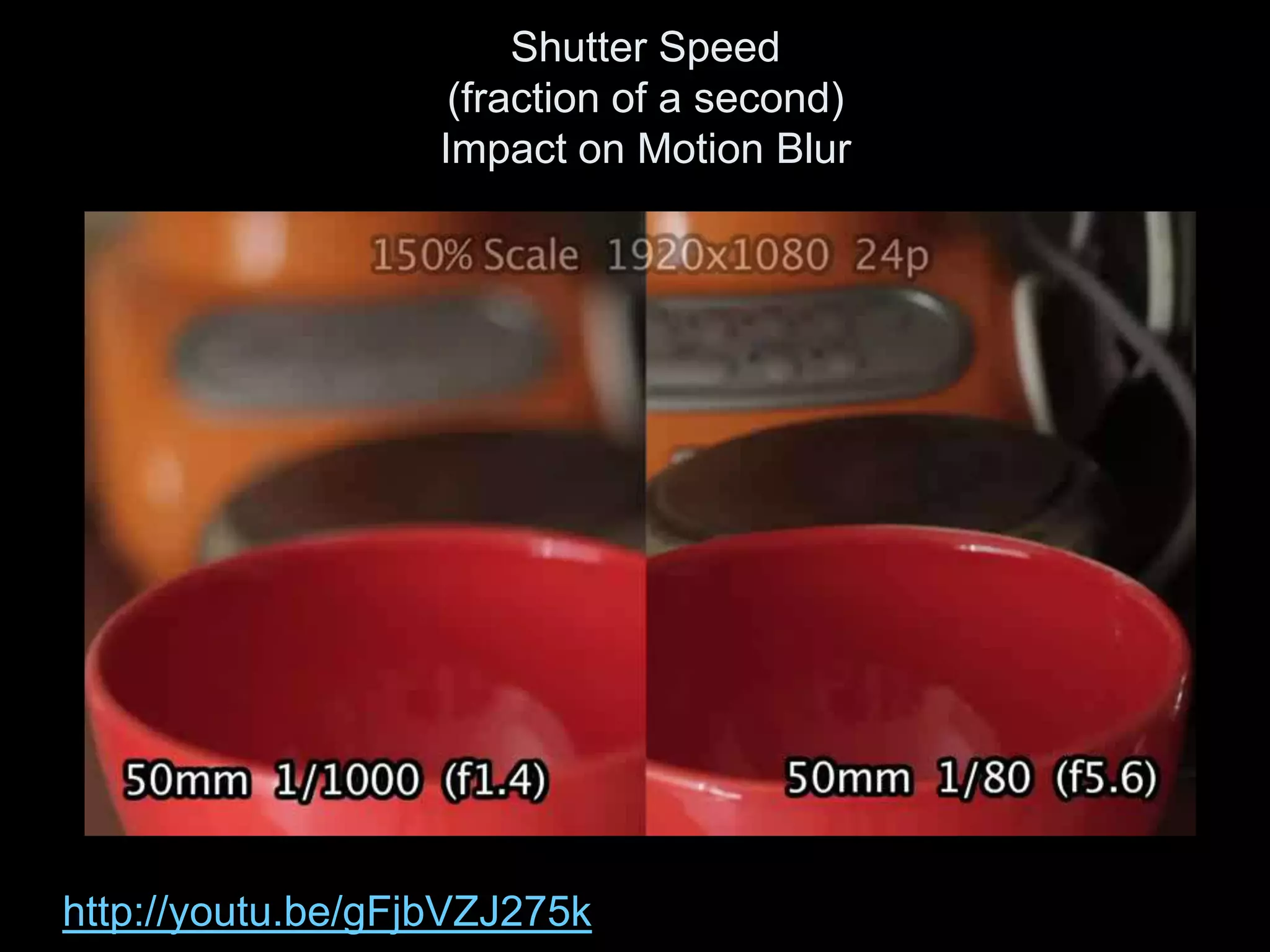
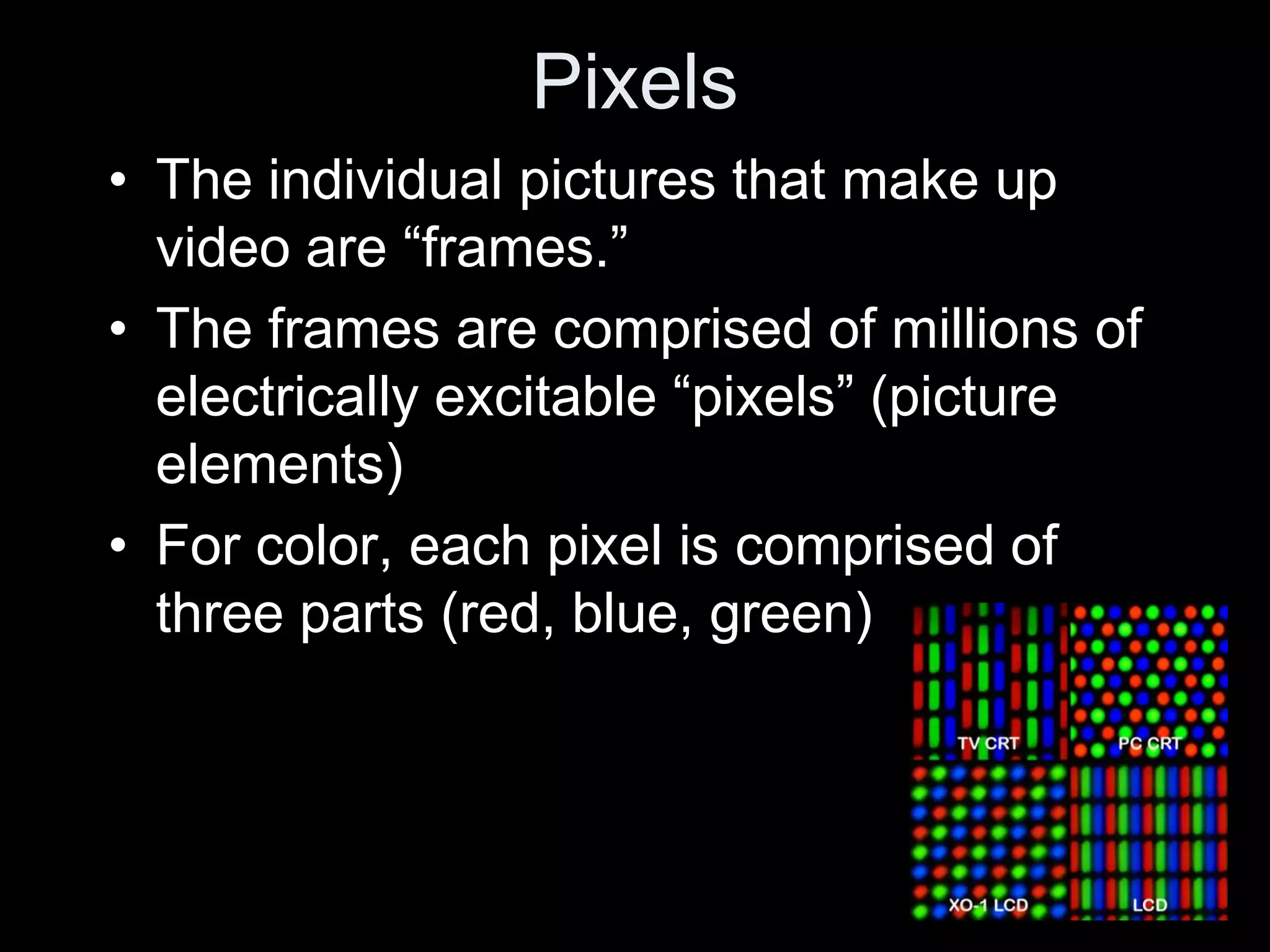
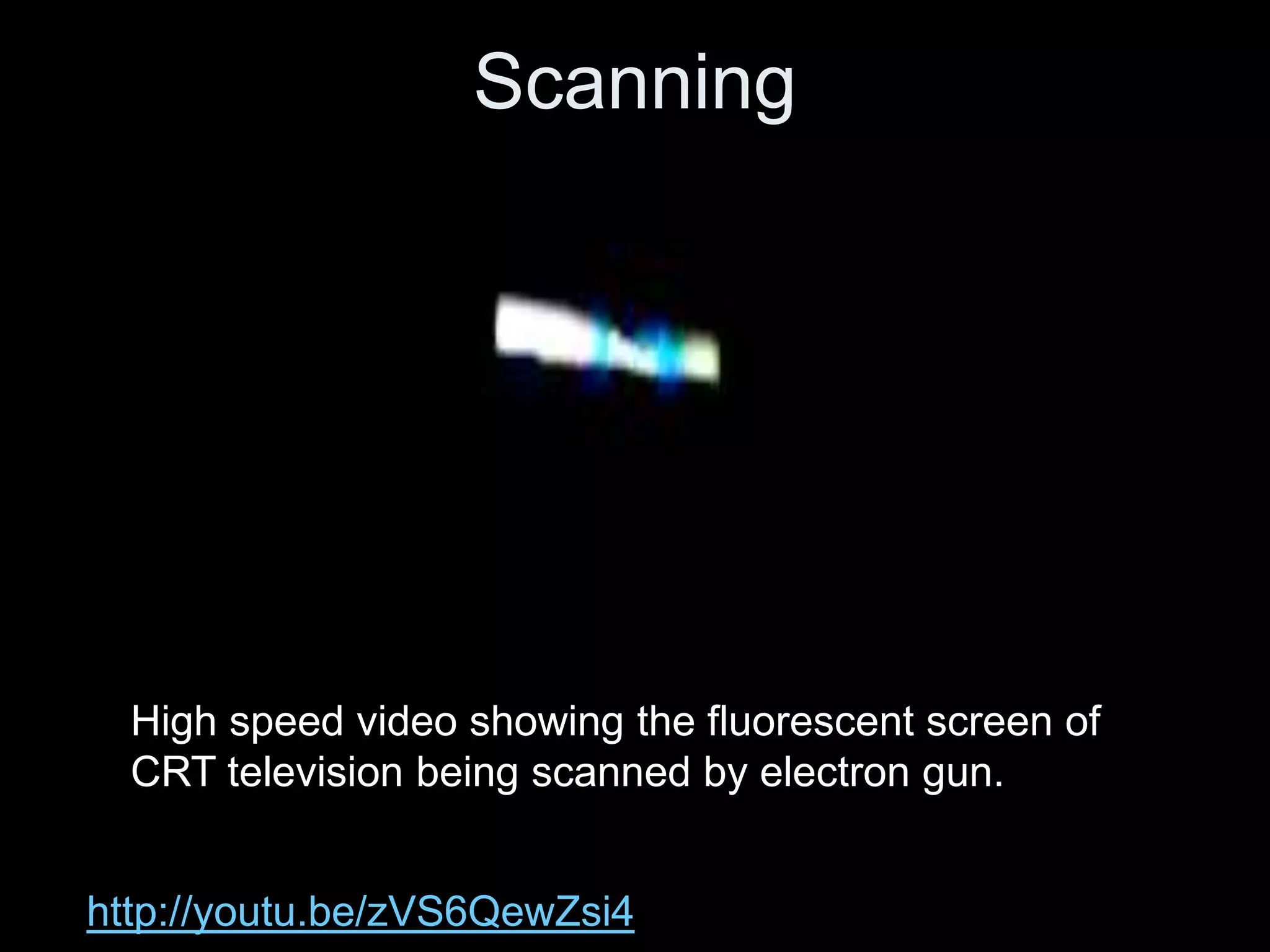
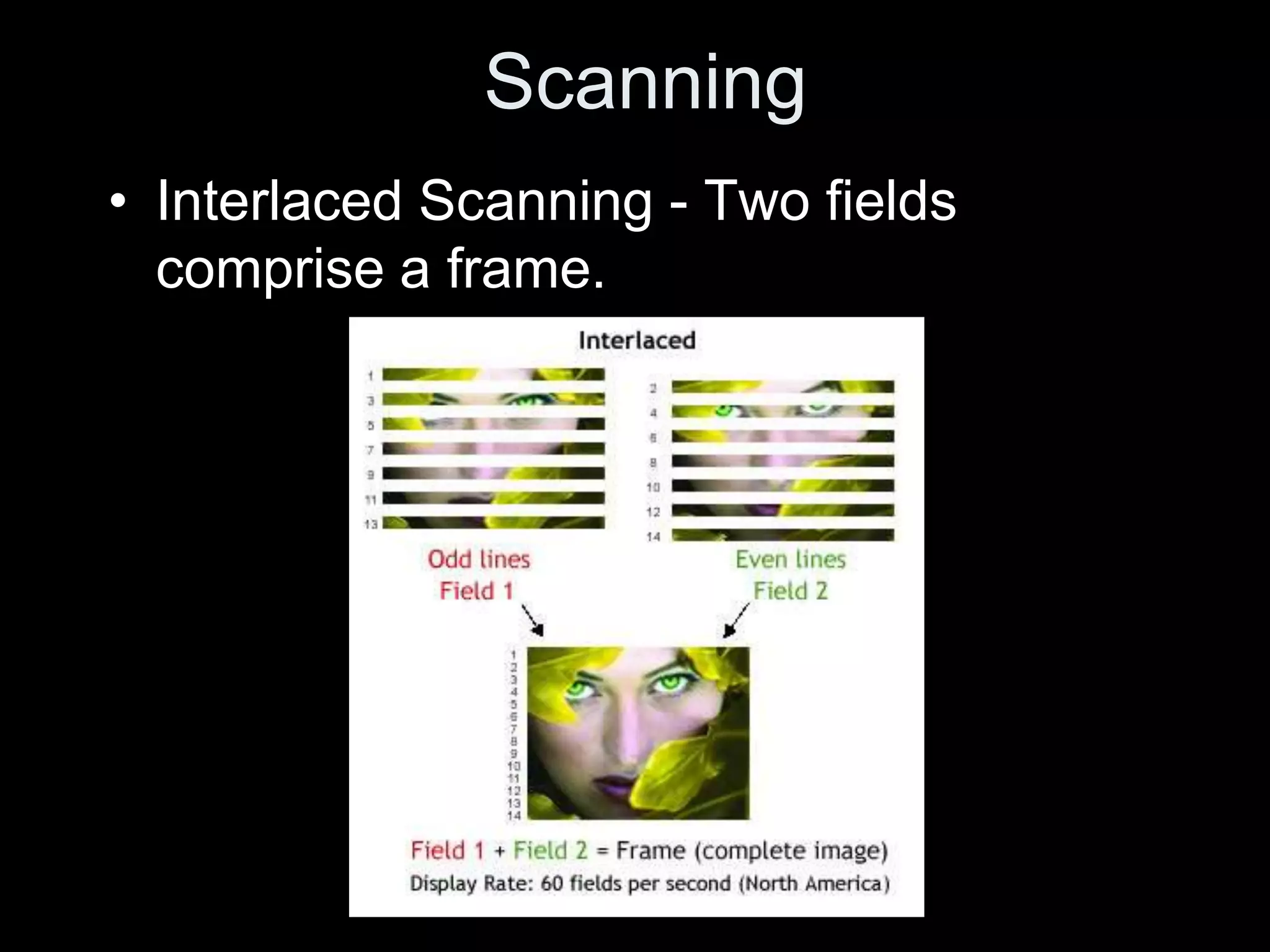
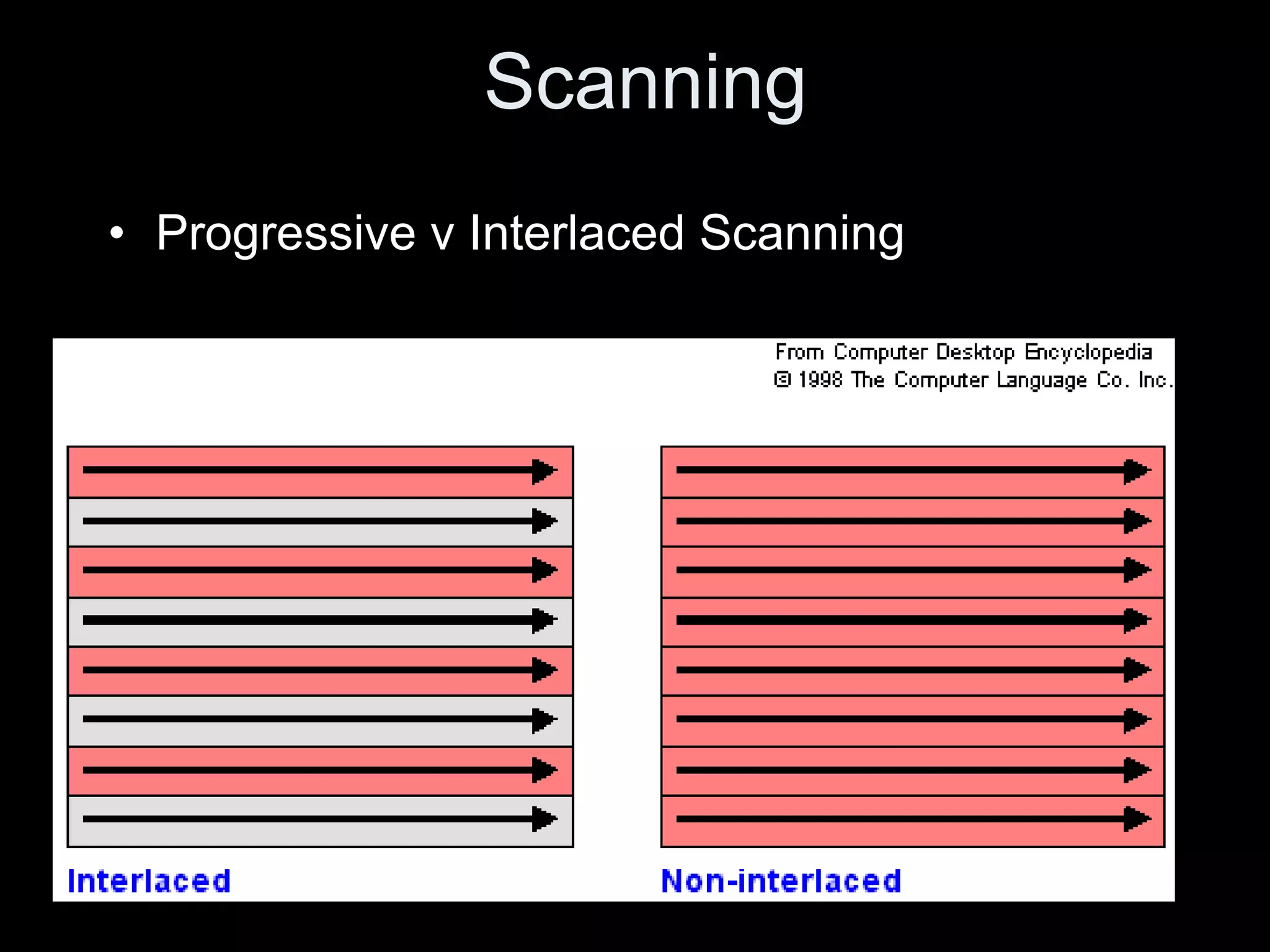
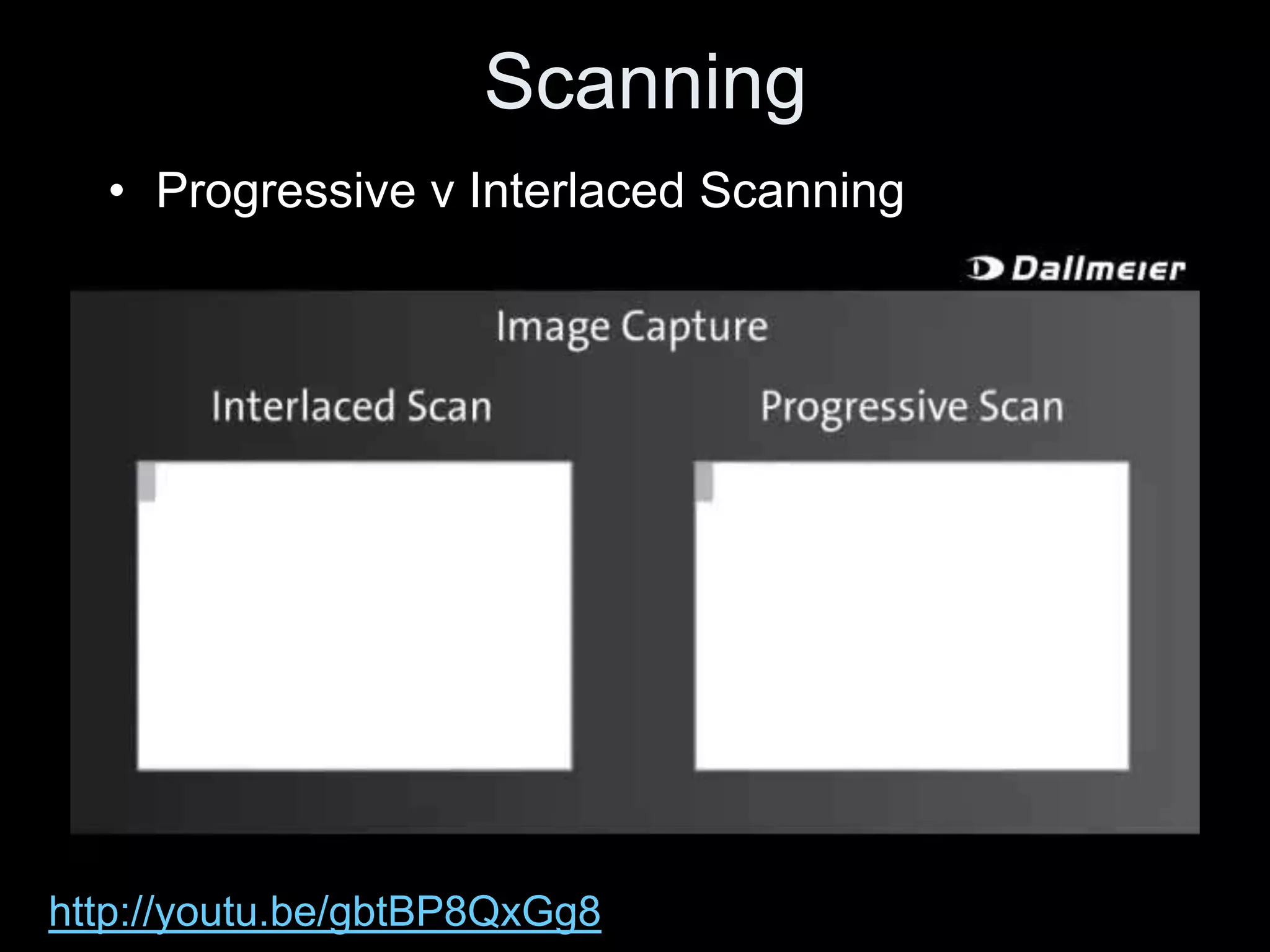
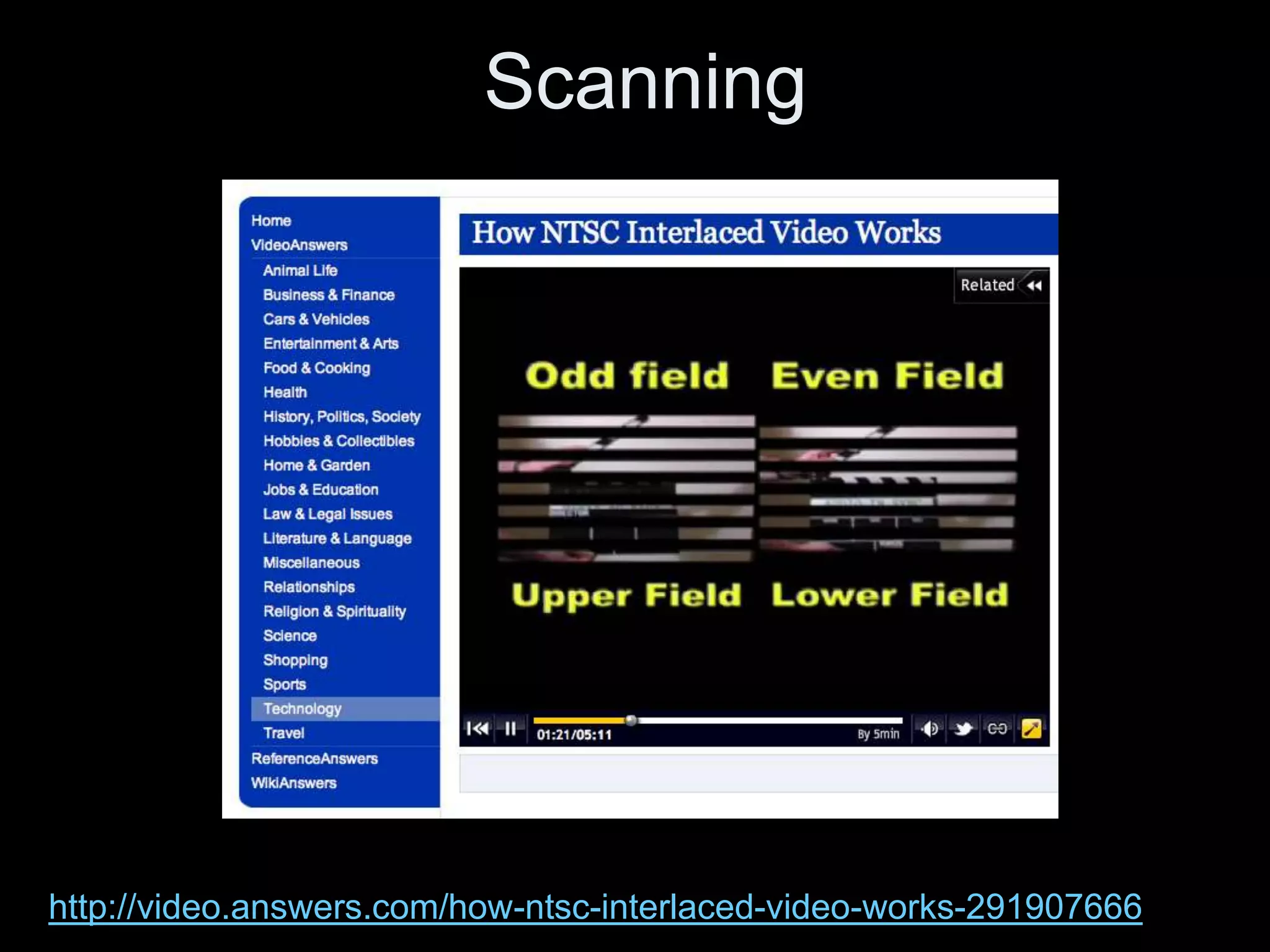
Video is created by capturing sequential still images called frames rapidly enough to create the illusion of motion when played back. Frames are made up of pixels which are tiny light-sensitive dots that capture color. Images are drawn by scanning across pixels from left to right and top to bottom using either progressive or interlaced scanning. Higher frame rates and resolutions provide smoother motion and more detail but require more storage space. Playing back video at the same rate it was captured maintains normal speed, while changing the rate can create slow or fast motion effects.
























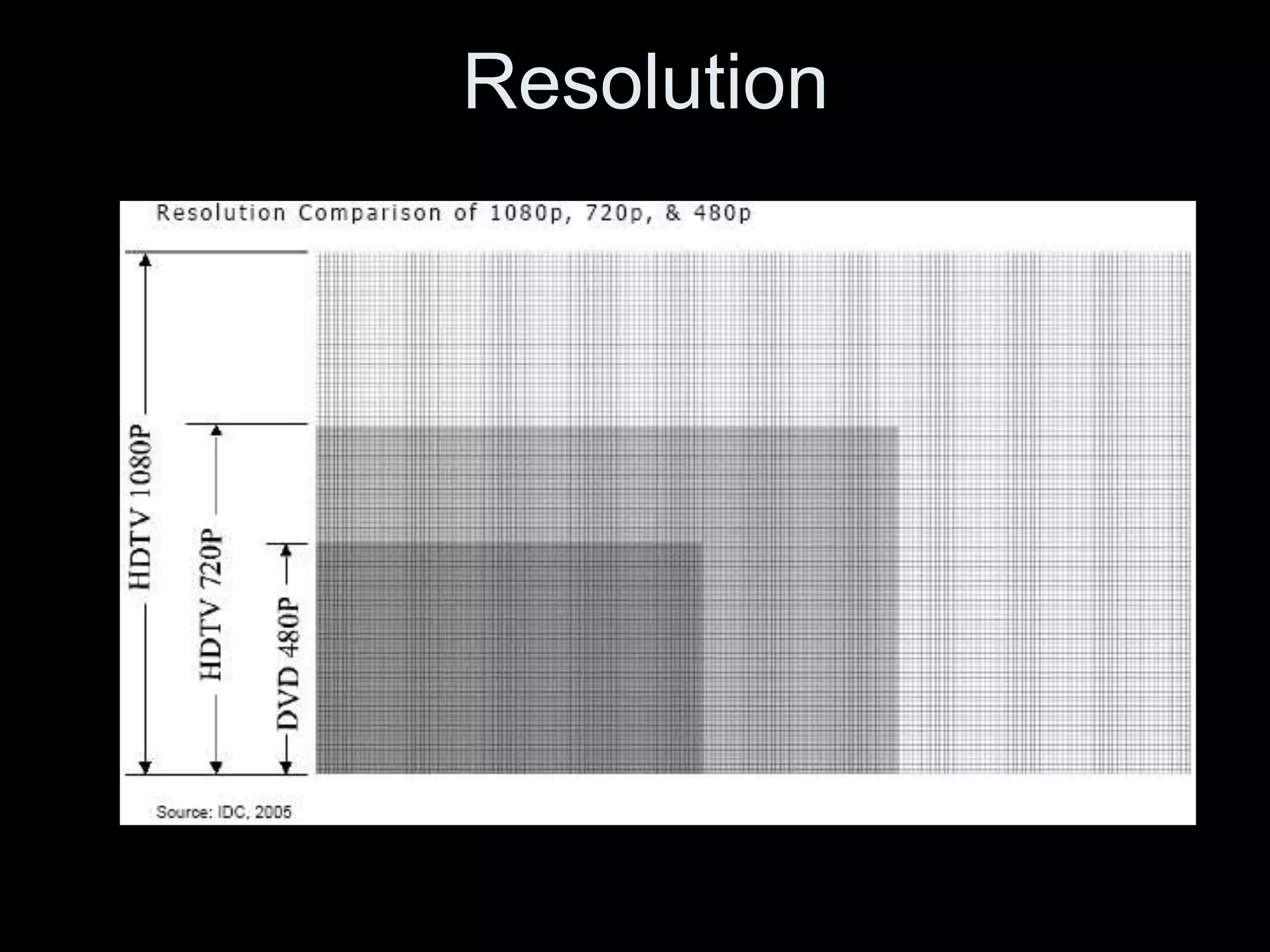
![Resolution
Digital Television (DTV)
• Higher Picture Resolution
• Truer Color
• Wider Contrast Ratio
Four prominent systems:
• 480p (progressive, 480 visible lines, 60 frames per
second)
• 720p (progressive, 720 visible lines, 60 frames per
second, High Definition Television [HDTV]
• 1080i (interlaced, 60 fields/30 frames per
second, High Definition Television [HDTV]
• 1080p (progressive, 60 frames per second, [HDTV]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imagedigitalv03-120119122055-phpapp02/75/EMC-3130-Spring-2012-Lecture-One-Image-Digital-36-2048.jpg)