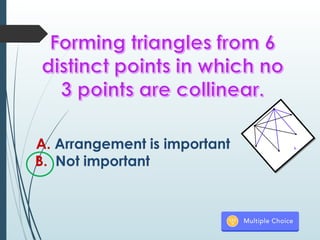
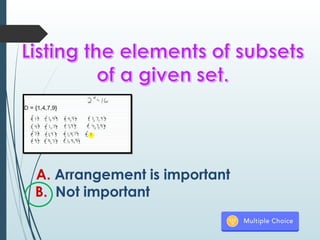
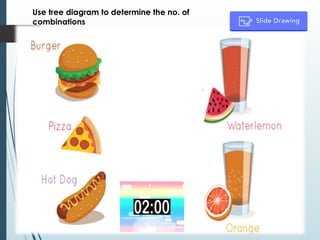
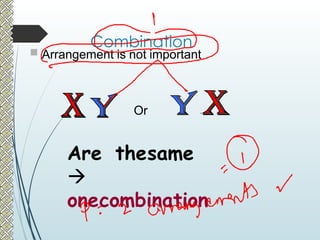
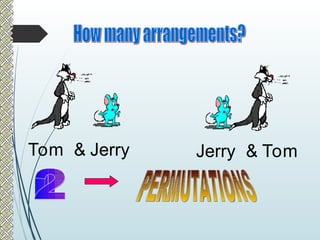
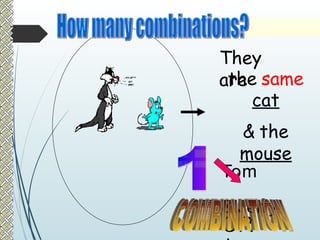
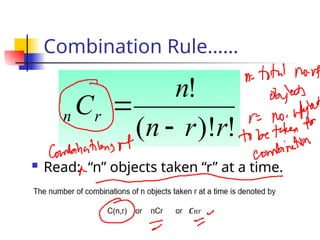
The document explains the concepts of permutations and combinations, highlighting their definitions and differences through examples. It discusses the applications of these concepts in various scenarios, such as selecting groups or menu items without regard to order. Additionally, it provides formulas for calculating combinations and permutations along with practical examples to illustrate their use.