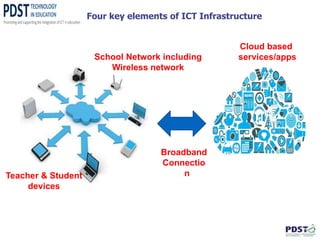
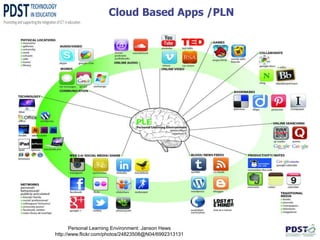
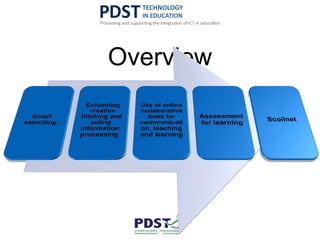
This document discusses the use of ICT in teaching and learning. It provides an overview of how ICT can enhance education, including using online tools and resources to improve comprehension, research skills, and creative thinking. Specific tools are described, such as StudyStack for vocabulary building and Animoto for digital storytelling. The document also discusses online collaboration using tools like Google Docs, video conferencing, and cloud-based services. It highlights the new Scoilnet website as a resource for Irish teachers and promotes responsible and ethical use of ICT.