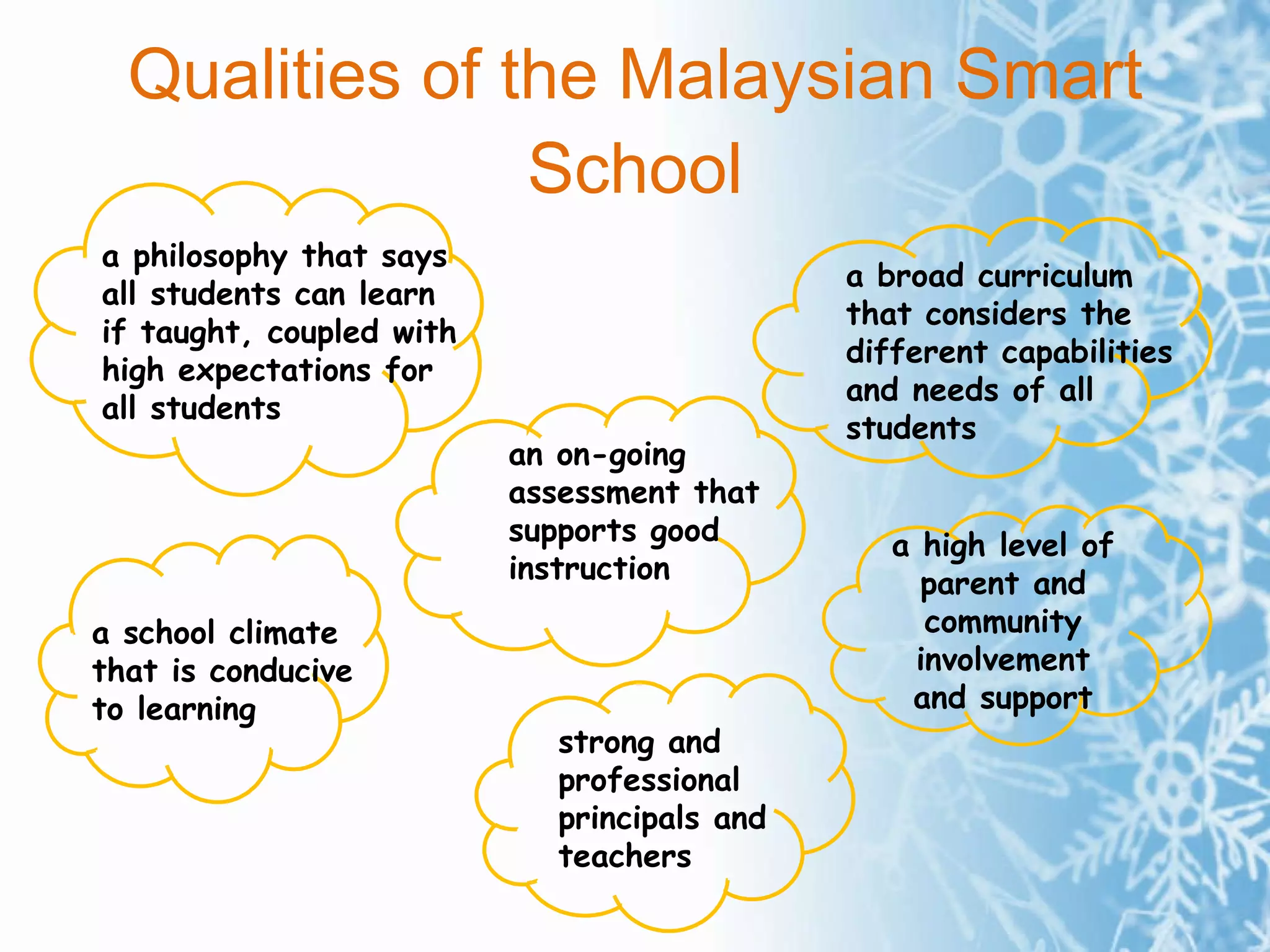
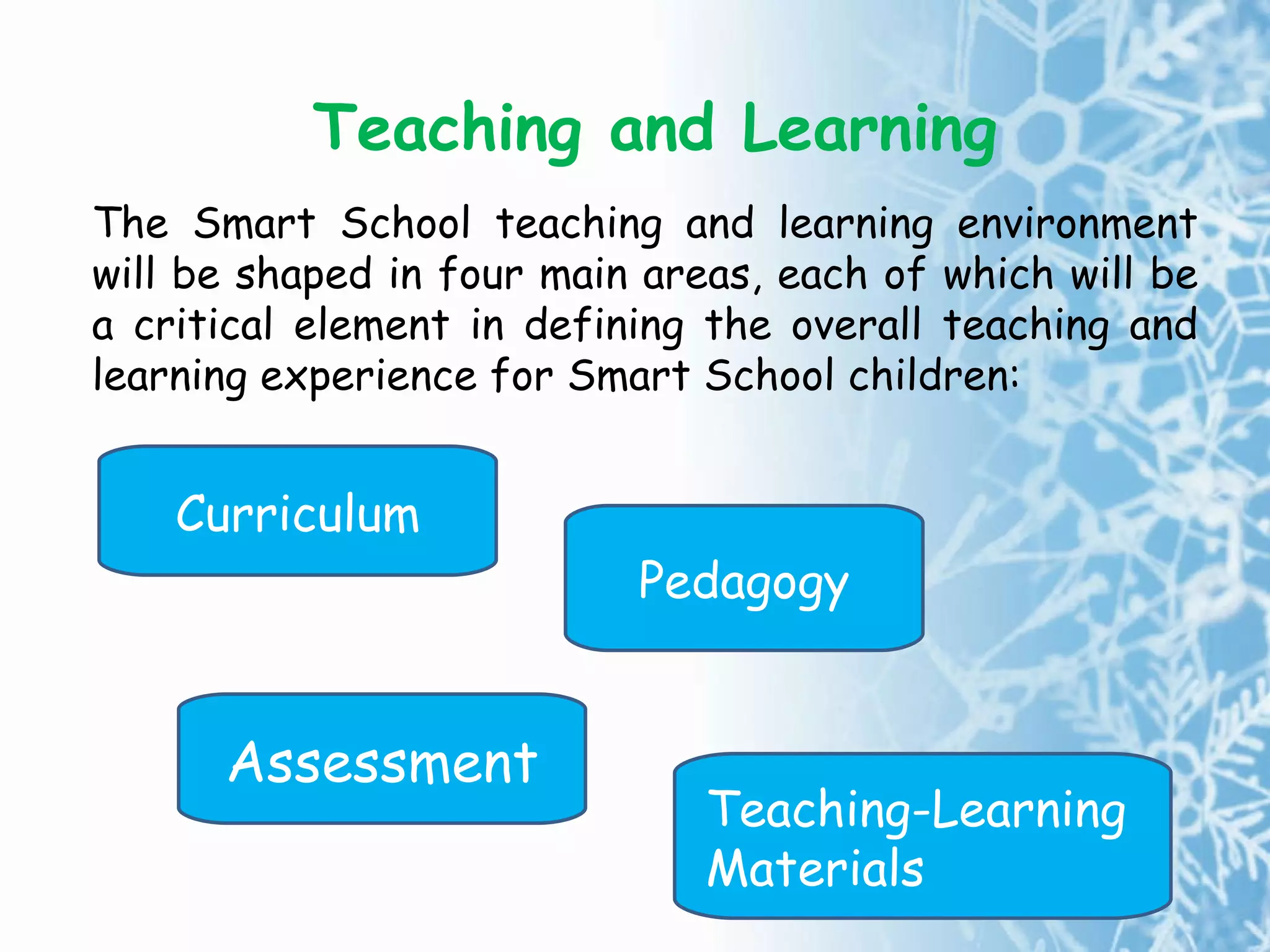
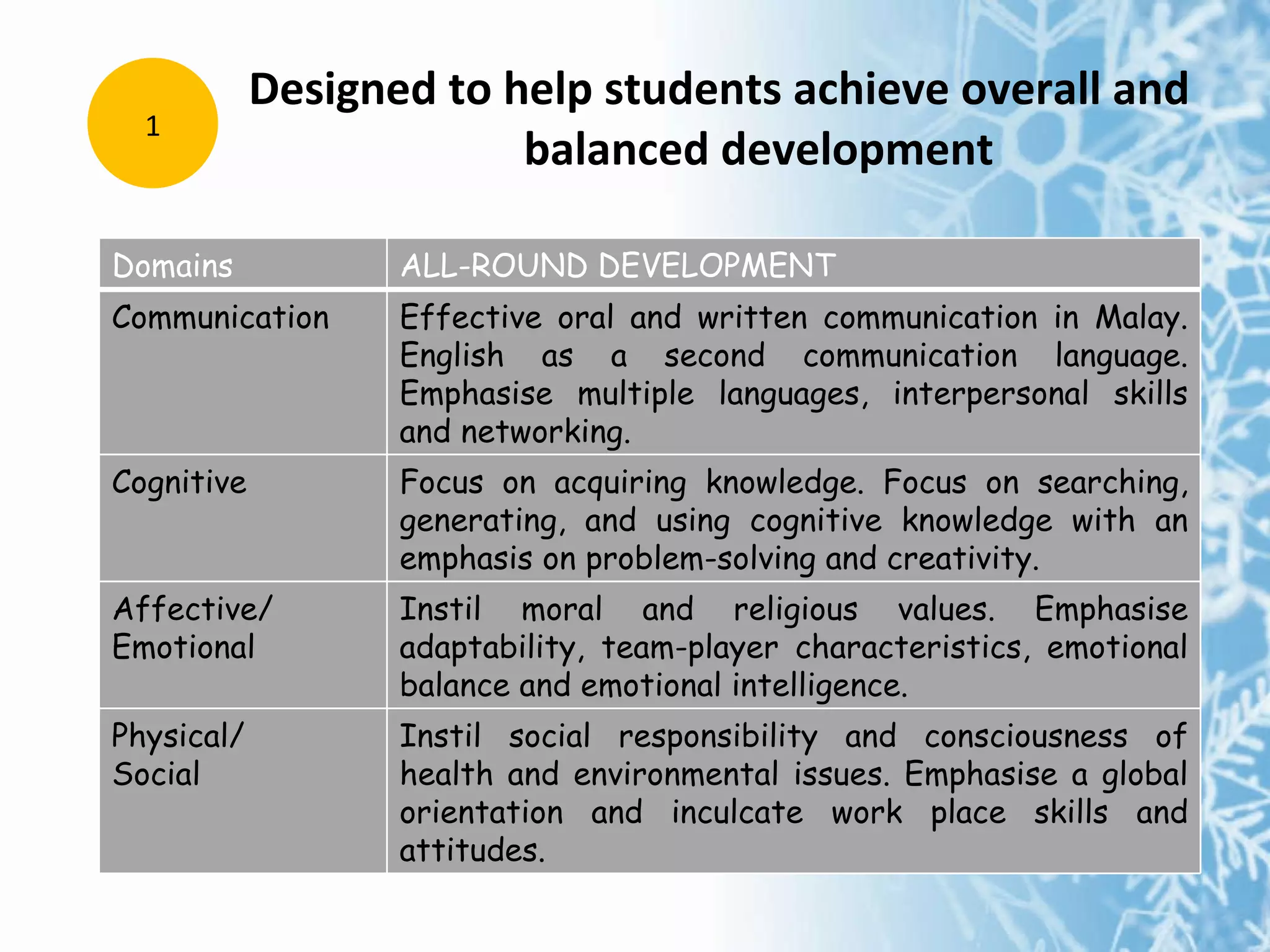
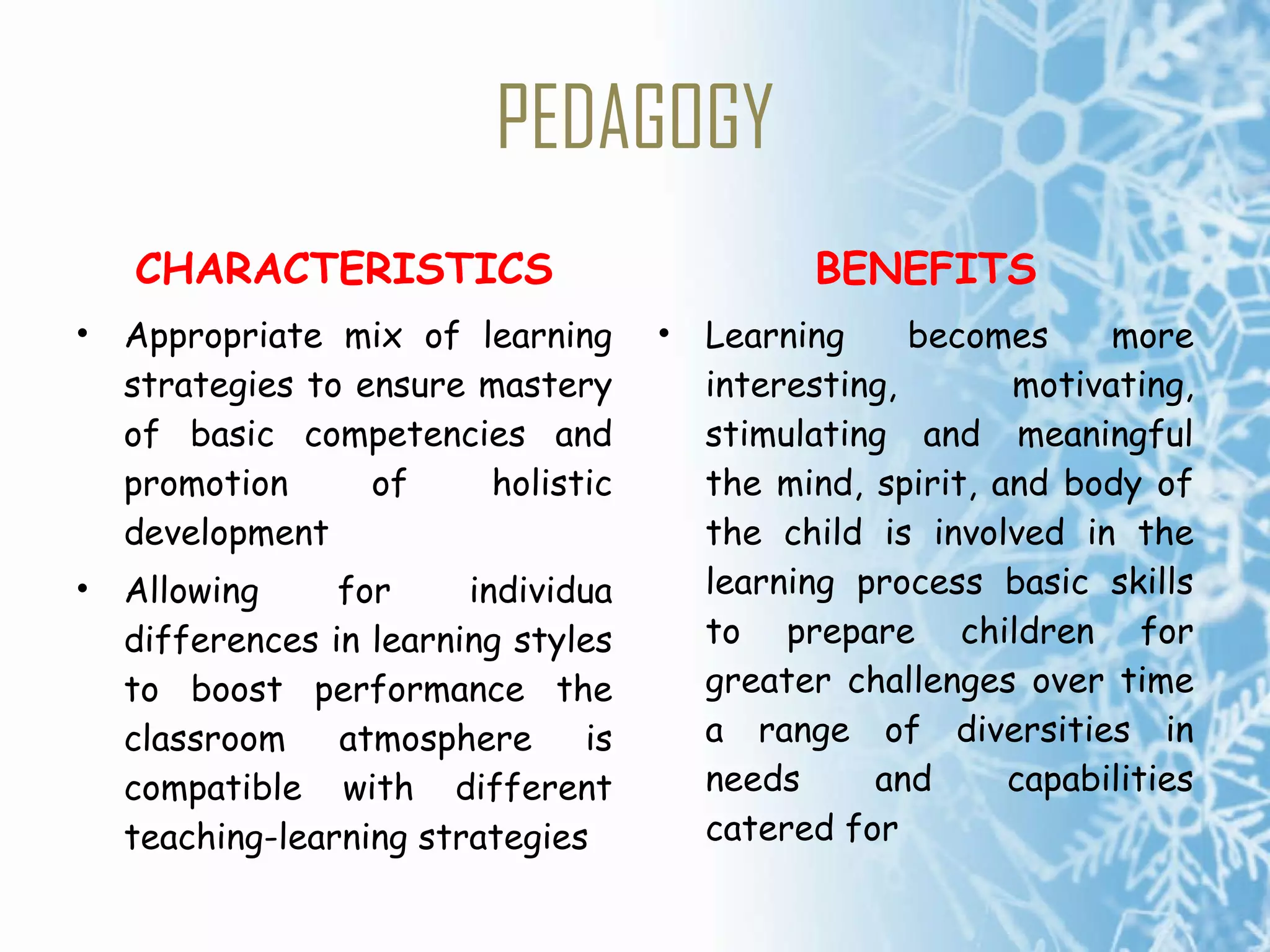
The document summarizes the key concepts of the Malaysian Smart School, including its philosophy, qualities, components, curriculum, pedagogy, assessment, management, people, technology, processes, and policies. The Smart School aims to prepare students for the information age through a broad, integrated curriculum; varied teaching methods; ongoing assessment; strong leadership; community involvement; and appropriate use of technology.