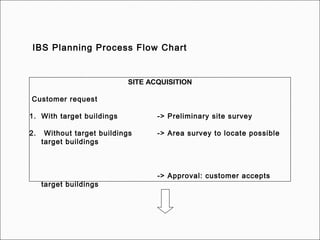
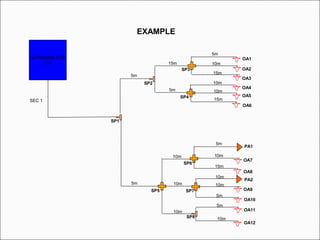
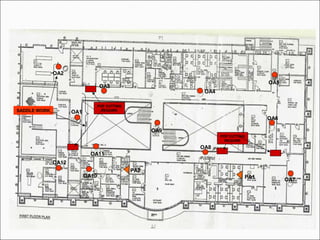
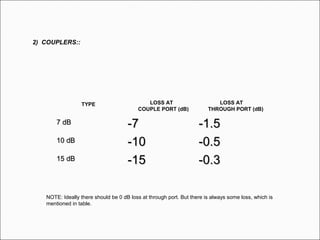
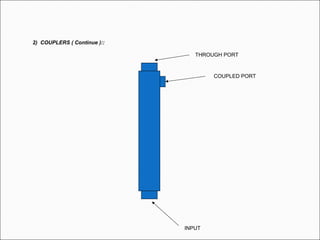
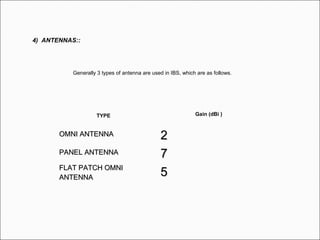
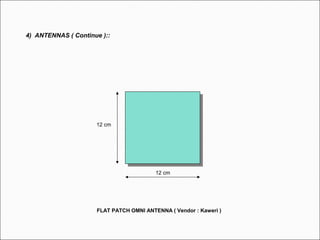
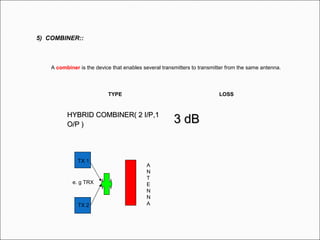
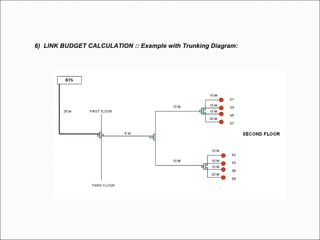
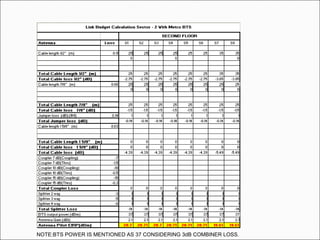
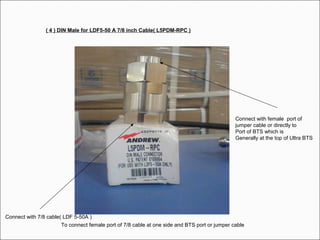
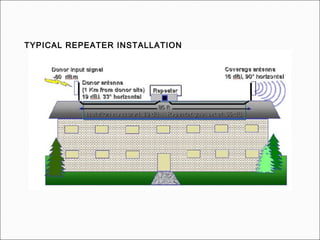
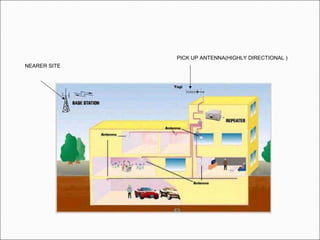
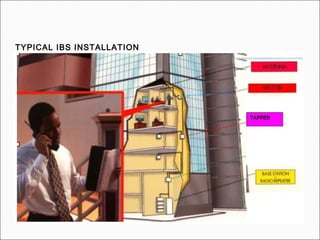
The document provides comprehensive guidelines for In-Building Solutions (IBS) and Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) implementation, including site surveys, design preparation, and installation steps. It covers the necessity of IBS to enhance indoor coverage, the types of buildings suitable for IBS, and the tools required for thorough surveys. Additionally, it outlines quality standards for installation, networking components involved, and technical considerations such as link budget calculations and antenna system specifications.