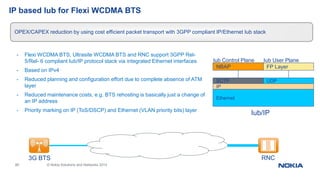
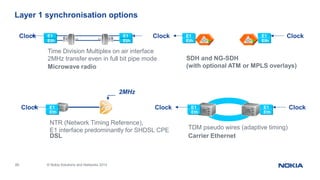
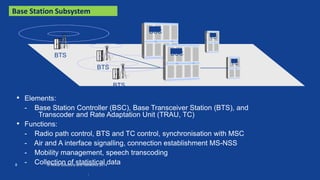
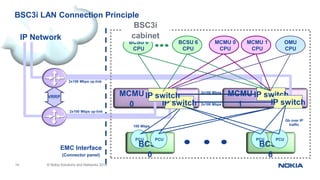
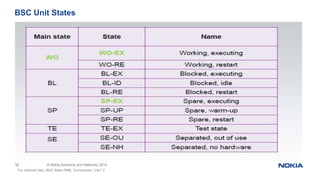
This document provides an overview of the architecture and components of a Nokia BSS (Base Station Subsystem). It describes the functional units of the BSC3i including the BCSU, MCMU, OMU, PCU, hard disks, and MO unit. It also outlines the GSWB, clock, and ET units. The document is intended to provide basic information to BSS engineers on the BSC architecture and troubleshooting process.






























































![67 © Nokia Solutions and Networks 2014
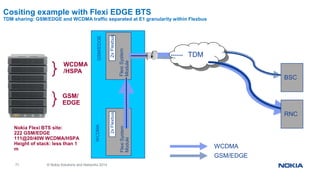
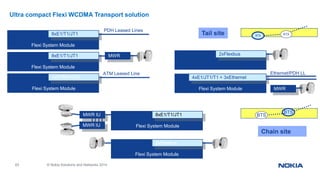
Flexi WCDMA BTS Transmission Cables and GE SFP's
SI SI Name Length [m] For Remarks
470312A FTCA OD CABLE RJ48C - TQ-M/0 120ohm 5 m 5 FTPB,FTIA RJ48C to TQ, 1xE1
470309A FTCB OD CABLE RJ48C 120ohm 15 m 15 FTPB,FTIA One open end, 1xE1
471713A FTCV OD CABLE RJ48C 120ohm 30 m 30 FTPB,FTIA One open end, 1xE1
471714A FTCX OD CABLE RJ48C 120ohm 50 m 50 FTPB,FTIA One open end, 1xE1
470313A FTCD OD CABLE SMB-F/0 75ohm 5 m 5 FTEB, FTJA SMB to BT43, 1xE1 coax
470310A FTCE OD CABLE SMB-F/0 75ohm 15 m 15 FTEB, FTJA One open end, 1xE1 coax
471715A FTCF OD CABLE SMB-F/0 75ohm 30 m 30 FTEB, FTJA One open end, 1xE1 coax
471716A FTCG OD CABLE SMB-F/0 75ohm 50 m 50 FTEB, FTJA One open end, 1xE1 coax
470311A FTCH OD CABLE LC SM 1310 15 m 15 FTOA LC to LC fiber
471391A FTCJ OD cable TNC-F7O-TNC M/O 50 ohm 2.5 m 2.5 FTFA Flexbus
471408A FTCR OD CABLE RJ45 CAT5E 15 m 15 FTIA, FTJA One open end, 1xEthernet
471548A FTCP OD CABLE MDR-68 100ohm 30M for FTHA 30 FTHA MDR-68 at both sides
471717A FTCS OD CABLE RJ45 CAT5E 30 m 30 FTIA, FTJA One open end, 1xEthernet
471718A FTCT OD CABLE RJ45 CAT5E 50 m 50 FTIA, FTJA One open end, 1xEthernet
471392A FTCM OD Adapter Cable RJ48-C 120 ohm 2.5 FMUA&FMUB with FTPB or FTIA RJ48C male, RJ48C female
471393A FTCN OD Adapter Cable SMB 75 ohm 2.5 FMUA&FMUB with FTEB or FTJA
471394A FTCO OD Adapter Cable TNC 2.5 FMUA&FMUB with FTFA
471881A FOSD Flexi Optical Telecom SFP GbE 850nm MM - FTIA, FTJA, FTIB LC, multi mode
471880A FOSC Flexi Optical Telecom SFP GbE 1310nm - FTIA, FTJA, FTIB LC, single mode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nokiaengineerbasictrainingsessionv1-191129203611/85/Nokia-engineer-basic_training_session_v1-67-320.jpg)
![68 © Nokia Solutions and Networks 2014
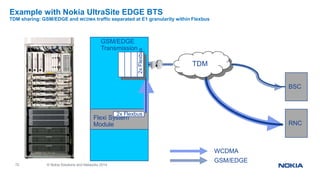
Flexi WCDMA BTS System Module - Cables and SFP’s
Optical cables are equipped at both the ends with Dual LC connectors for SFP modules, so they can be used also for other
purposes like transport module connections
*: Halogen free cables
SI SI Name Length [m] For Remarks
471395A FSFB Flexi System Fibre B 50m 50 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471396A FSFC Flexi System Fibre C 100m 100 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471743A FSFD Flexi System Fibre D 4m 4 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471707A FSFF Flexi System Fibre F 10m 10 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471708A FSFG Flexi System Fibre G 20m 20 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471709A FSFH Flexi System Fibre H 30m 30 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471710A FSFI Flexi System Fibre I 40m 40 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471711A FSFK Flexi System Fibre K 75m 75 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471712A FSFP Flexi System Fibre P 200m 200 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable
471851A FSFO Flexi System Fibre HF 2m 2 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable, LZH version*
471852A FSFQ Flexi System Fibre HF 50m 50 System - RF Feederless MM optical cable, LZH version*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nokiaengineerbasictrainingsessionv1-191129203611/85/Nokia-engineer-basic_training_session_v1-68-320.jpg)