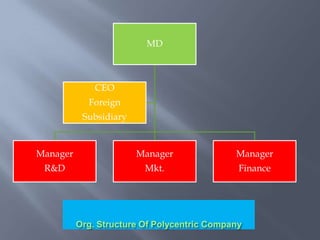
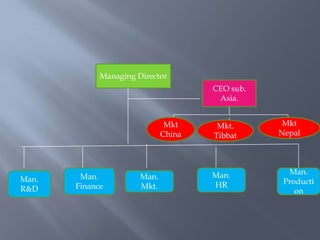
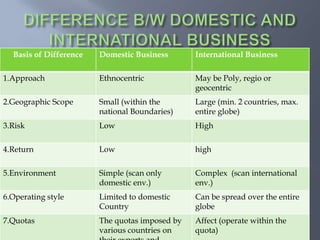
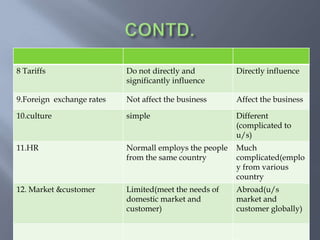
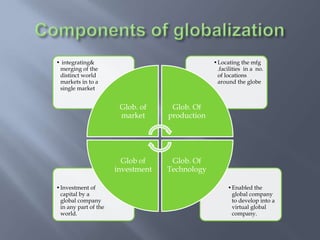
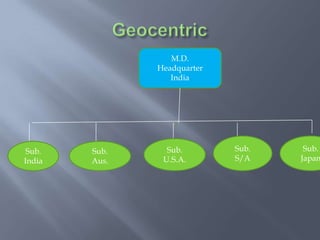
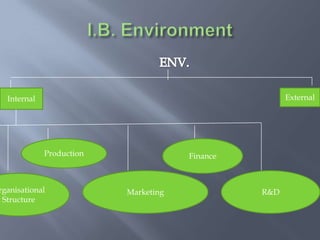
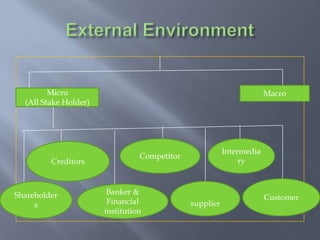
International business involves focusing global resources and opportunities to produce, buy, sell, or exchange goods and services worldwide. There are five stages of internationalization for companies: domestic, international, multinational, global, and transnational. As companies progress through these stages, their approach shifts from ethnocentric to polycentric to geocentric. International business environments are complex with many political, economic, socio-cultural, technological, legal, and natural factors that companies must consider when operating globally. Globalization has increased integration between world economies through liberalized trade, investment, and technological changes.