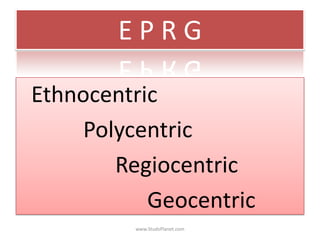
Globalization refers to the integration of economic, technological, cultural, and political activities worldwide. It involves four main components: the globalization of markets, labor and production, finance, and technology. As countries integrate their economies through trade, foreign direct investment, and capital flows, globalization impacts domestic industries, employment rates, and standards of living both positively through economic growth and negatively by increasing competition. Multinational corporations play a key role in driving globalization by operating subsidiaries across borders. Companies approach international business using strategies that range from ethnocentric to geocentric as they adapt to different country markets.