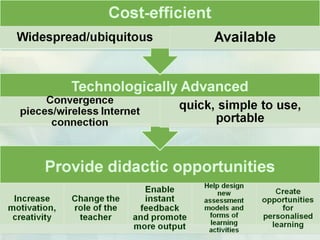
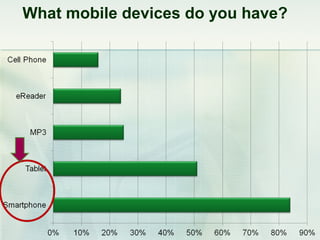
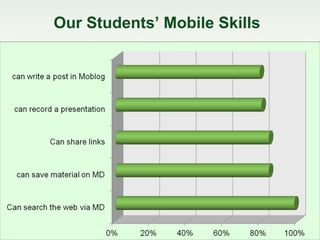
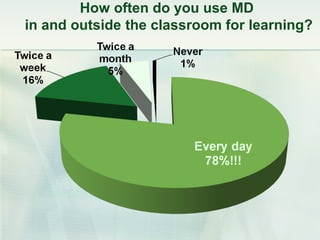
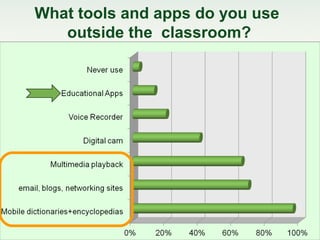
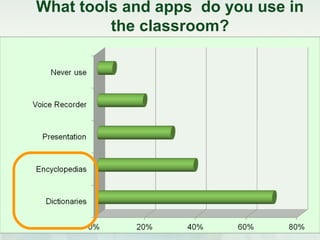
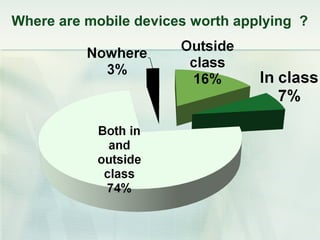
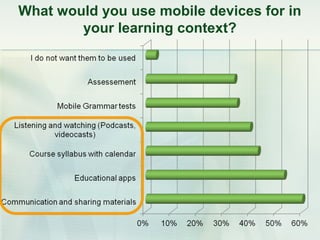
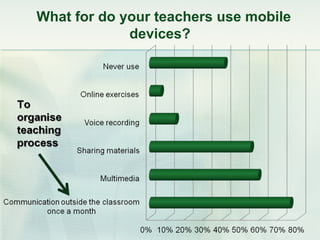
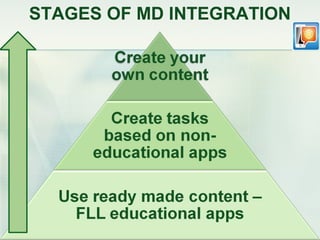
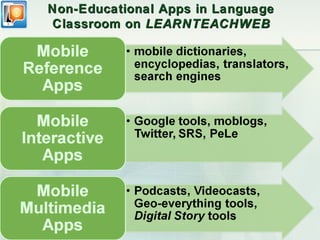
This document discusses challenges and perspectives in teaching "mobile natives" or students who have grown up with mobile devices in Russia. It notes that mobile devices have become widespread in Russia, with over 237 million mobile devices owned. It explores how mobile learning can provide just-in-time, collaborative learning and increase student motivation. Research with students found they are ready to use mobile devices for learning but teachers do not fully guide their use of educational apps. The challenges are developing teacher mobile literacy and strategies for integrating mobile devices into traditional classrooms.