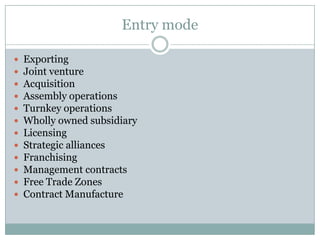
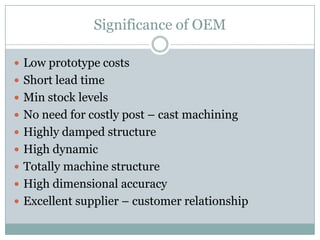
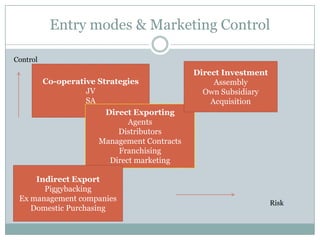
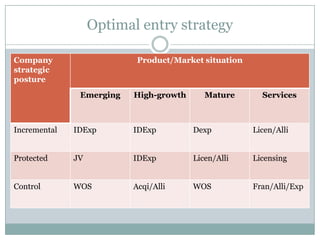
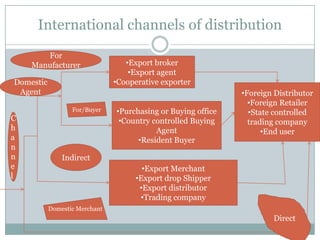
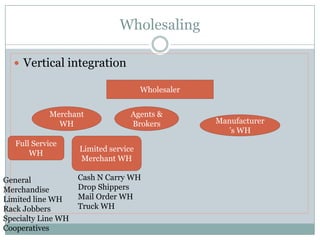
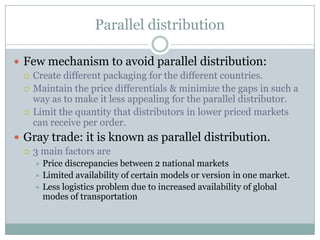
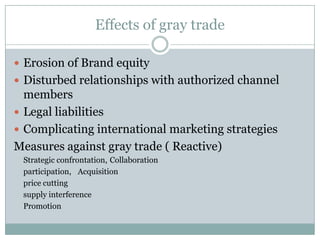
The document discusses various topics related to entry modes and global distribution for international business. It describes different entry modes like exporting, joint ventures, acquisitions, etc. It also discusses strategic alliances, original equipment manufacturing, and their significance. Additionally, it covers topics like entry modes and marketing control, optimal entry strategies, global distribution functions, international channels of distribution, transportation, parallel distribution and its effects, and developing an effective global distribution system.