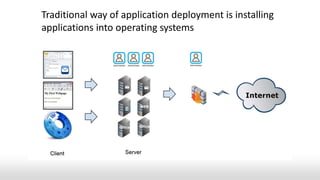
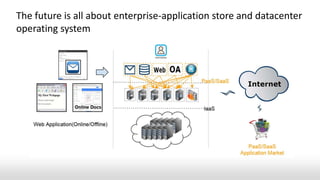
This document discusses Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) from its origins to the present and future. It covers:
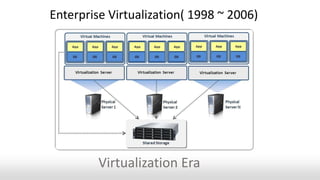
- The evolution of IaaS from traditional IT infrastructure (1998-2006) to virtualization (1998-2006) to the current IaaS model (2006-present).
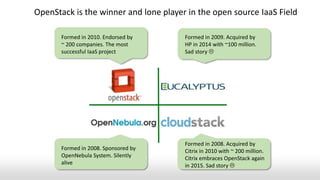
- OpenStack emerging as the dominant open source IaaS project, though its community success did not necessarily translate to business success for companies.
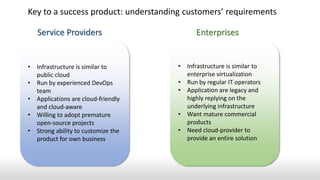
- ZStack, founded in 2015, aiming to solve problems through a well-designed product with simplicity, stability, flexibility and scalability.
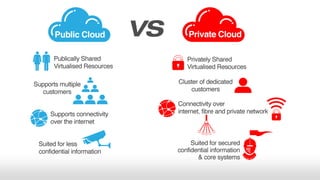
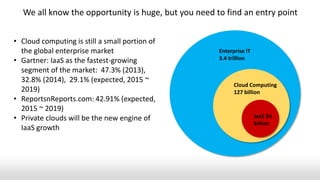
- While public cloud computing is growing, the largest opportunities remain in private clouds and traditional enterprise IT, which prefer mature