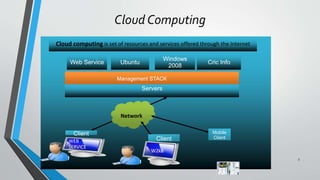
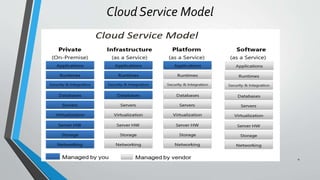
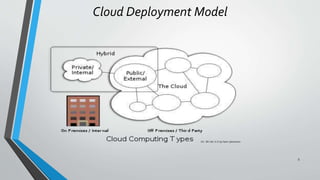
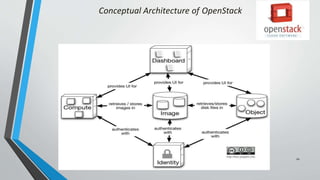
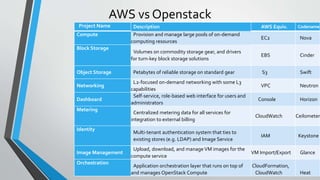
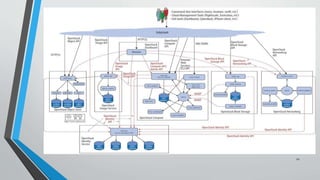
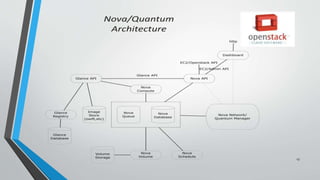
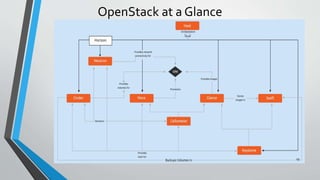
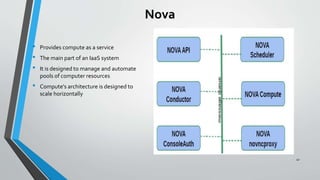
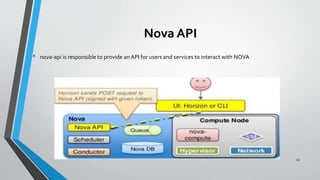
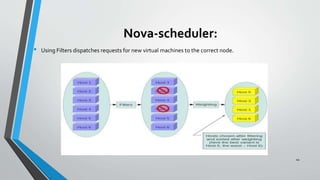
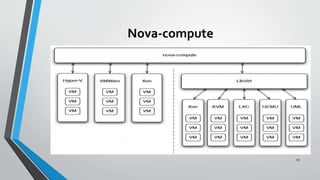
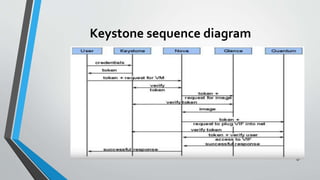
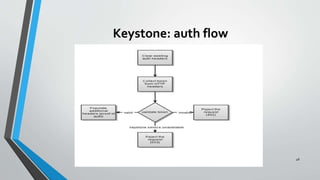
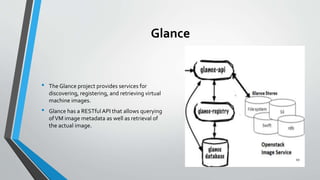
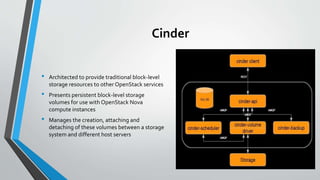
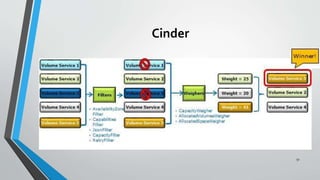
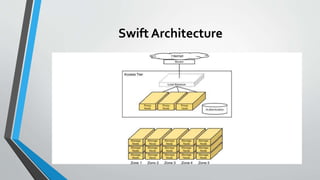
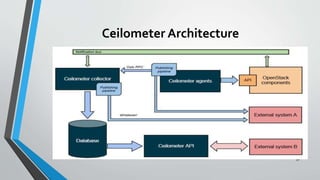
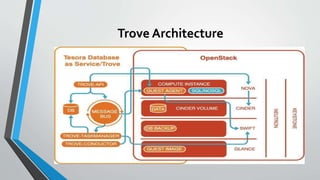
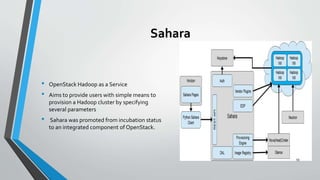
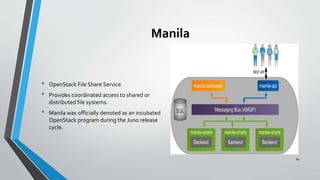
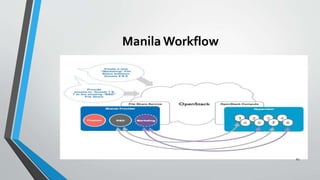
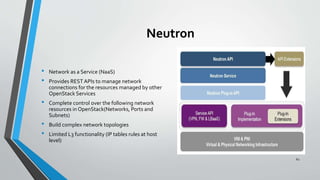
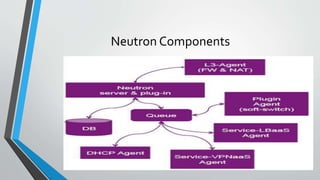
OpenStack is an open source cloud computing platform that provides infrastructure as a service. It consists of interrelated components that control hardware resources like processing, storage, and networking. The key components include Nova for compute, Glance for images, Cinder for block storage, Swift for object storage, Keystone for identity, Horizon for the dashboard, Ceilometer for metering, and Neutron for networking. OpenStack provides APIs and dashboards to allow users to provision resources on demand.